Geologic History Worksheet
Are you a student or educator seeking a comprehensive and engaging tool to delve into the fascinating world of geologic history? Look no further! Introducing the Geologic History Worksheet—a valuable resource designed to enhance your understanding of this enthralling subject. Developed with meticulous attention to detail, this worksheet is tailored to provide an enriching learning experience for middle school and high school students.
Table of Images 👆
More History Worksheets
Free Printable History WorksheetsU.S. History Worksheets
Black History Worksheets for Kindergarten
What is Geologic history?
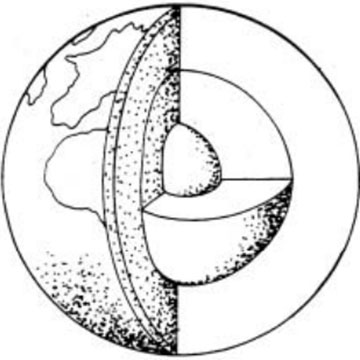
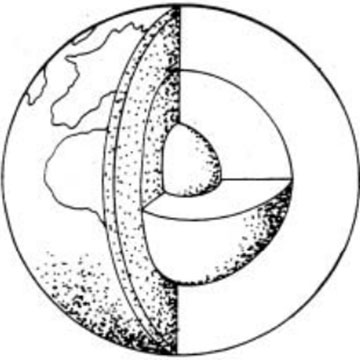
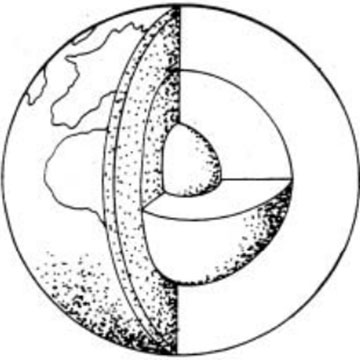
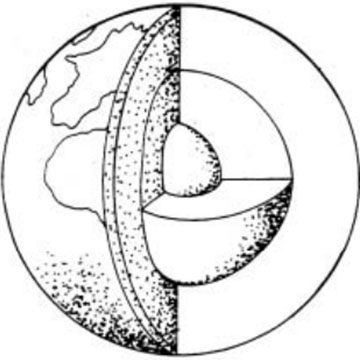
Geologic history refers to the study and interpretation of earth's past, including the formation of rocks, minerals, fossils, and landforms over billions of years. It involves the analysis of sedimentary layers, tectonic events, climate changes, and the evolution of life on Earth. By examining these geological processes and events, scientists can reconstruct the timeline of Earth's history and gain insights into its complex and dynamic geological evolution.
What are fossils?
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms from the past that provide valuable evidence of life on Earth millions of years ago. Fossils are typically found in sedimentary rocks and can include bones, shells, footprints, and imprints. They offer insights into evolution, past environments, and the history of life on our planet.
What is the theory of continental drift?
The theory of continental drift proposes that Earth's continents were once joined together as a single landmass called Pangea, which later broke apart and drifted to their current positions over millions of years. This movement is driven by the slow motion of Earth's tectonic plates, which float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere layer of the Earth's mantle. The theory was first proposed by Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century and has since been supported by evidence from geology, paleontology, and paleoclimatology.
What is the difference between relative and absolute dating?
Relative dating is a method of determining the age of a fossil or archaeological specimen based on its position within rock layers, while absolute dating involves determining an exact age of an object through techniques like radiometric dating. Relative dating provides an approximation of age based on the context of where an object is found, while absolute dating gives a specific numerical age.
How do geologists use the principle of superposition?
Geologists use the principle of superposition to determine the relative ages of rock layers. This principle states that in any undisturbed sequence of rock layers, each layer is younger than the one beneath it and older than the one above it. By observing the arrangement of rock layers in a particular area, geologists can infer the chronological order of events that have shaped the Earth's surface over time. The principle of superposition helps geologists unravel the geological history of a region and understand the sequence of events that have occurred.
What are igneous rocks and how do they form?
Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on Earth's surface, formed from the solidification of molten magma. When magma cools and solidifies either beneath the Earth's surface (intrusive igneous rocks) or on the surface (extrusive igneous rocks), it forms igneous rocks. As the magma cools, minerals crystallize and interlock to create the characteristic textures and compositions of igneous rocks. Examples of igneous rocks include granite, basalt, and obsidian.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
The three types of plate boundaries are divergent boundaries, where plates move away from each other; convergent boundaries, where plates move towards each other; and transform boundaries, where plates slide past each other horizontally.
How are mountains formed?
Mountains are formed through a process called orogenesis, which involves tectonic plates colliding or separating. When two continental plates collide, the forces involved can cause the Earth's crust to fold and buckle, creating mountain ranges. Alternatively, when tectonic plates move apart, magma rises from the mantle, cools, and solidifies to form new crust, leading to the formation of volcanic mountains. Over time, the forces of erosion and weathering shape and sculpt the mountains into their final diverse and majestic forms.
What is erosion and what are some of its main agents?
Erosion is the process of wearing away the earth's surface by natural forces such as water, wind, and ice. Some of the main agents of erosion include rainfall, rivers, glaciers, waves, and wind. These agents gradually break down rocks and soil, carrying away material and shaping the landscape over time.
How does the rock cycle contribute to Earth's geologic history?
The rock cycle plays a crucial role in Earth's geologic history by continuously transforming rocks between different forms such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. This process of rock formation, destruction, and transformation over geologic timescales has shaped the Earth's surface, created mountains, contributed to the formation of continents, influenced erosion patterns, and played a key role in the development of Earth's diverse landscapes and geological features. By cycling through different rock types, the rock cycle is a fundamental process that has played a significant role in shaping Earth's geological history.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments