Genetic Variation Meiosis Worksheet
Are you a biology student seeking a comprehensive and informative resource on genetic variation and meiosis? Look no further! Our Genetic Variation Meiosis Worksheet is designed to provide a clear and concise overview of this essential topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Variation Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Stages Worksheet
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet
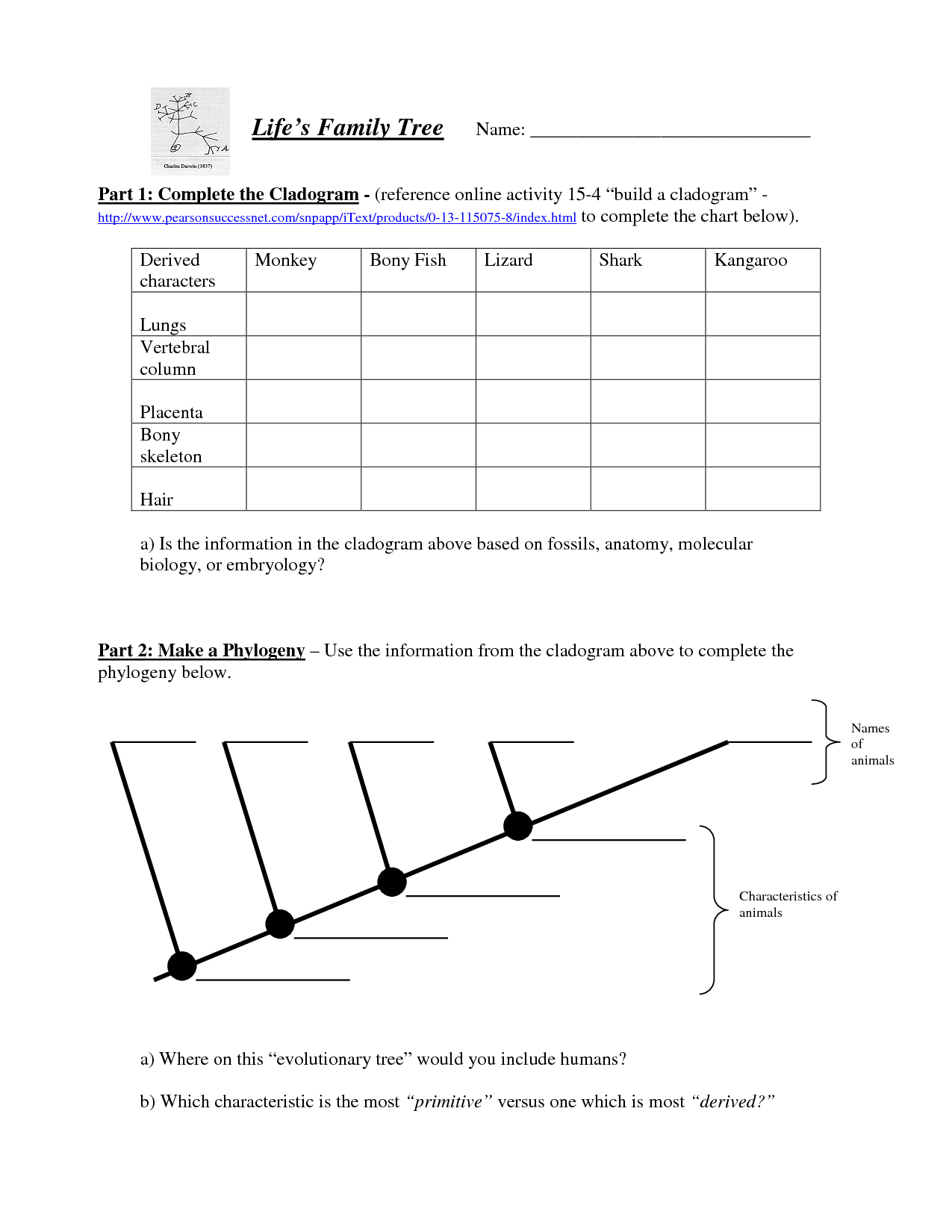
- Cladograms and Phylogenetic Trees Worksheet
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Engineering Worksheet Answers
- Gregor Mendel Genetics Pea Plants
- XY Chromosomes Worksheet
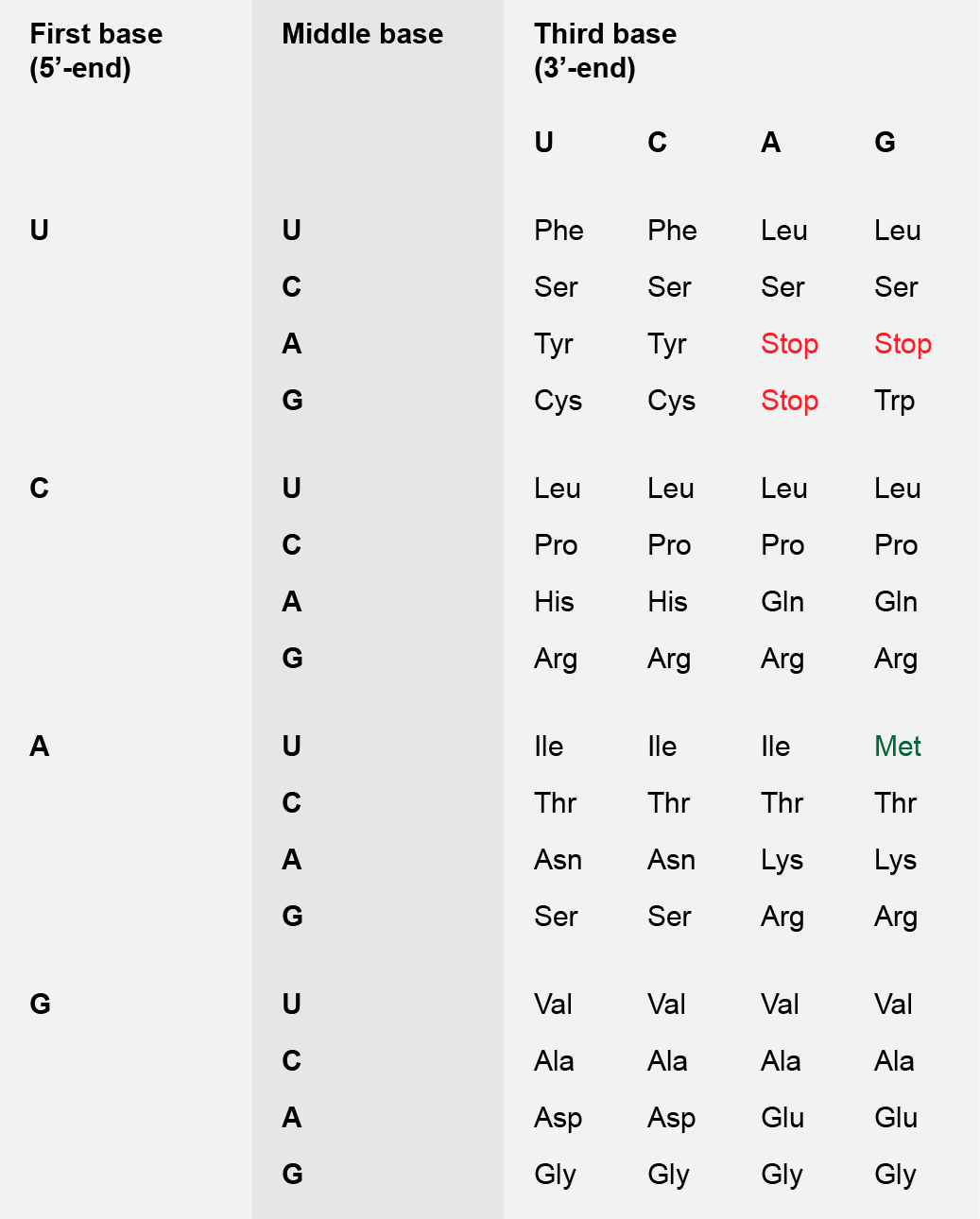
- Methionine Amino Acid Code
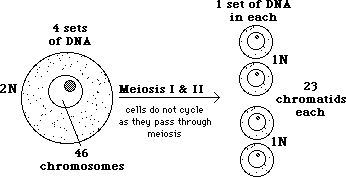
- How Many Chromatids in Meiosis and Mitosis Are There
- DNA Structure Coloring Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is genetic variation?
Genetic variation refers to the diversity of genetic information within a population or species, resulting from differences in DNA sequences. This variation is essential for evolution and adaptation, as it can lead to differences in physical traits, susceptibility to diseases, and other characteristics among individuals. Processes such as mutation, recombination, and gene flow contribute to genetic variation and play a crucial role in the survival and success of living organisms.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation?
Meiosis contributes to genetic variation through processes such as crossing over during prophase I, random assortment of homologous chromosomes during metaphase I, and random fertilization. These mechanisms lead to the creation of genetically diverse gametes, each containing a unique combination of alleles that can result in different combinations of traits in offspring, increasing genetic variation within a population.
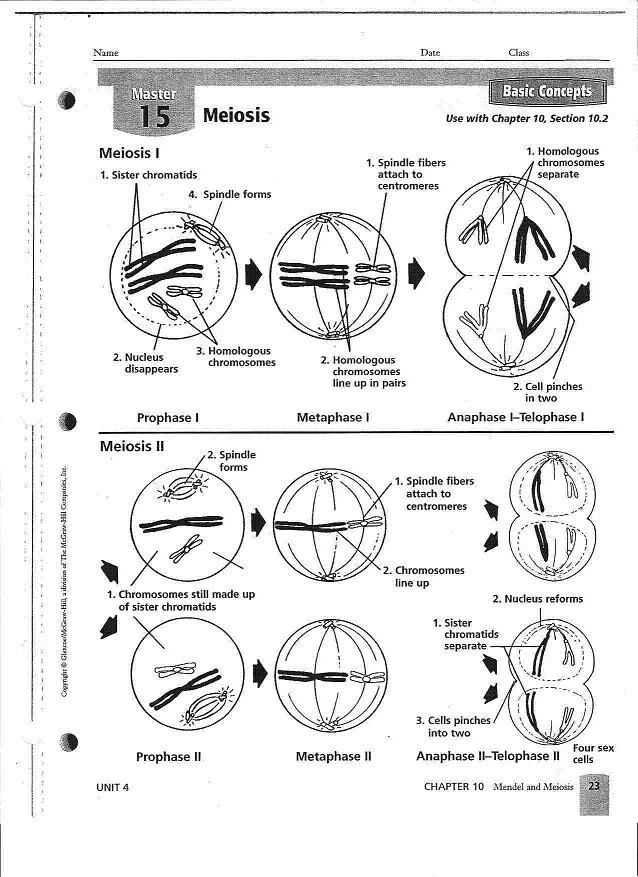
What are the stages of meiosis?
Meiosis is divided into two main stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, resulting in two haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes. Meiosis II involves the separation of sister chromatids, producing four haploid cells with unduplicated chromosomes. Each stage consists of specific phases, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, which result in genetic variation through independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization.
Describe the process of crossing over in meiosis.
Crossing over in meiosis is a genetic process that occurs during prophase I where homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material. Enzymes break the DNA strands and sections of chromatids swap places, resulting in new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes. This genetic recombination creates genetic diversity by shuffling alleles between the maternal and paternal chromosomes, and the resulting chromosomes are then separated into different gametes during meiosis, leading to offspring with unique genetic makeup.
What is the significance of independent assortment in meiosis?
Independent assortment in meiosis is significant because it leads to genetic diversity. During meiosis, the random alignment and separation of homologous chromosomes can result in various combinations of genes being passed on to offspring. This shuffling of genetic material ensures that each gamete produced is genetically unique, allowing for the production of diverse offspring with different combinations of traits. Independent assortment increases the chances of producing individuals with advantageous traits and plays a crucial role in evolution by providing a mechanism for genetic variability within a species.
How does random fertilization contribute to genetic variation?
Random fertilization is when any sperm can fertilize any egg, resulting in different combinations of genetic material being passed on to the offspring. This process leads to the creation of unique genetic combinations in each individual, increasing genetic variation within a population. By allowing for the mixing of genetic material from the parents in a random manner, random fertilization promotes diversity and adaptability in populations, which is essential for evolution and survival in changing environments.
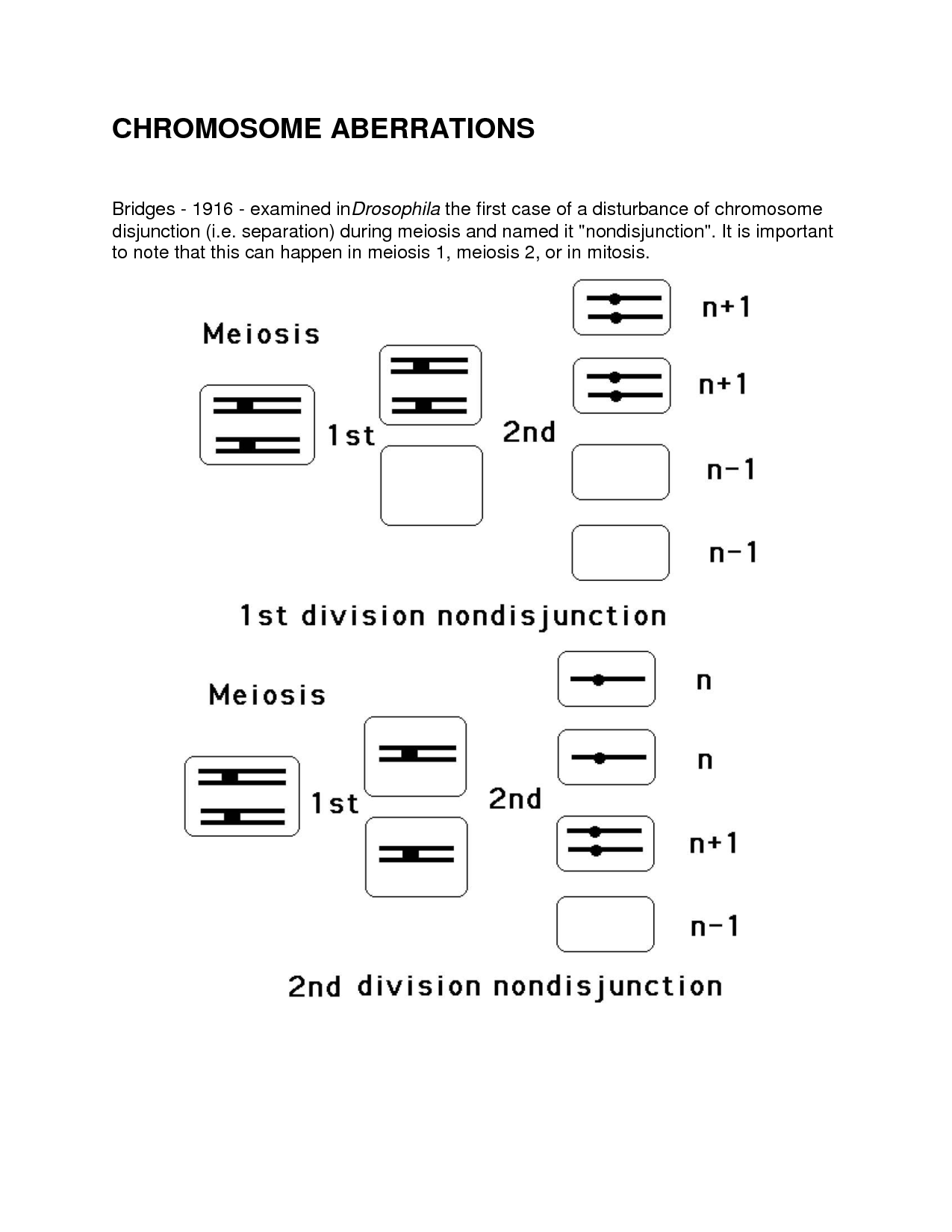
What role does non-disjunction play in genetic variation?
Non-disjunction is a genetic phenomenon that can lead to an abnormal number of chromosomes being present in a cell, which can result in genetic variation. When non-disjunction occurs during meiosis, it can lead to the creation of gametes with an extra chromosome (trisomy) or a missing chromosome (monosomy). If a fertilization event involves one of these abnormal gametes, it can result in offspring with genetic variations such as Down syndrome (trisomy 21) or Turner syndrome (monosomy X). Thus, non-disjunction plays a crucial role in generating genetic variation by causing chromosomal abnormalities that can be passed on to future generations.
Explain the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids.
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that have similar genetic information but come from different parents, one from the mother and one from the father. They have the same genes in the same order, but potentially different versions of those genes. On the other hand, sister chromatids are identical copies of a single chromosome that are created during DNA replication. They are attached at the centromere and are produced to ensure each new cell receives a complete set of genetic information during cell division.
How does sexual reproduction promote genetic diversity?
Sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity by shuffling and combining genetic information from two parents to create unique offspring. During meiosis, the process of creating gametes, genetic material undergoes recombination, resulting in different combinations of traits that are passed on to the next generation. This genetic variation enhances the adaptability of populations to changing environments and increases the chances of survival and evolution.
What are some factors that can influence genetic variation in a population?
Factors that can influence genetic variation in a population include natural selection, mutation, gene flow (immigration/emigration), genetic drift (random changes in allele frequencies), and non-random mating (selective mating preferences). Additionally, environmental factors, such as geographic isolation or climate changes, can also impact genetic variation in a population.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments