Freshman Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
Are you a freshman student studying DNA and genes? In need of answers to the Chapter 11 worksheet? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the solutions for the Freshman Chapter 11 DNA and Genes worksheet.
Table of Images 👆
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 Section 1 Introduction to Genetics Answer Key
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
- Incomplete and Codominance Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Structure Worksheet
- Chapter 11 Introduction to Genetics Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- Biology Genetics Worksheet
- Genetic Variation Worksheet Answers
- Directed Reading Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process in which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA by unraveling the double helix structure of the DNA molecule and using each strand as a template to build a new complementary strand. This essential process ensures that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic information from the parent cell during cell division.
How is DNA different from RNA?
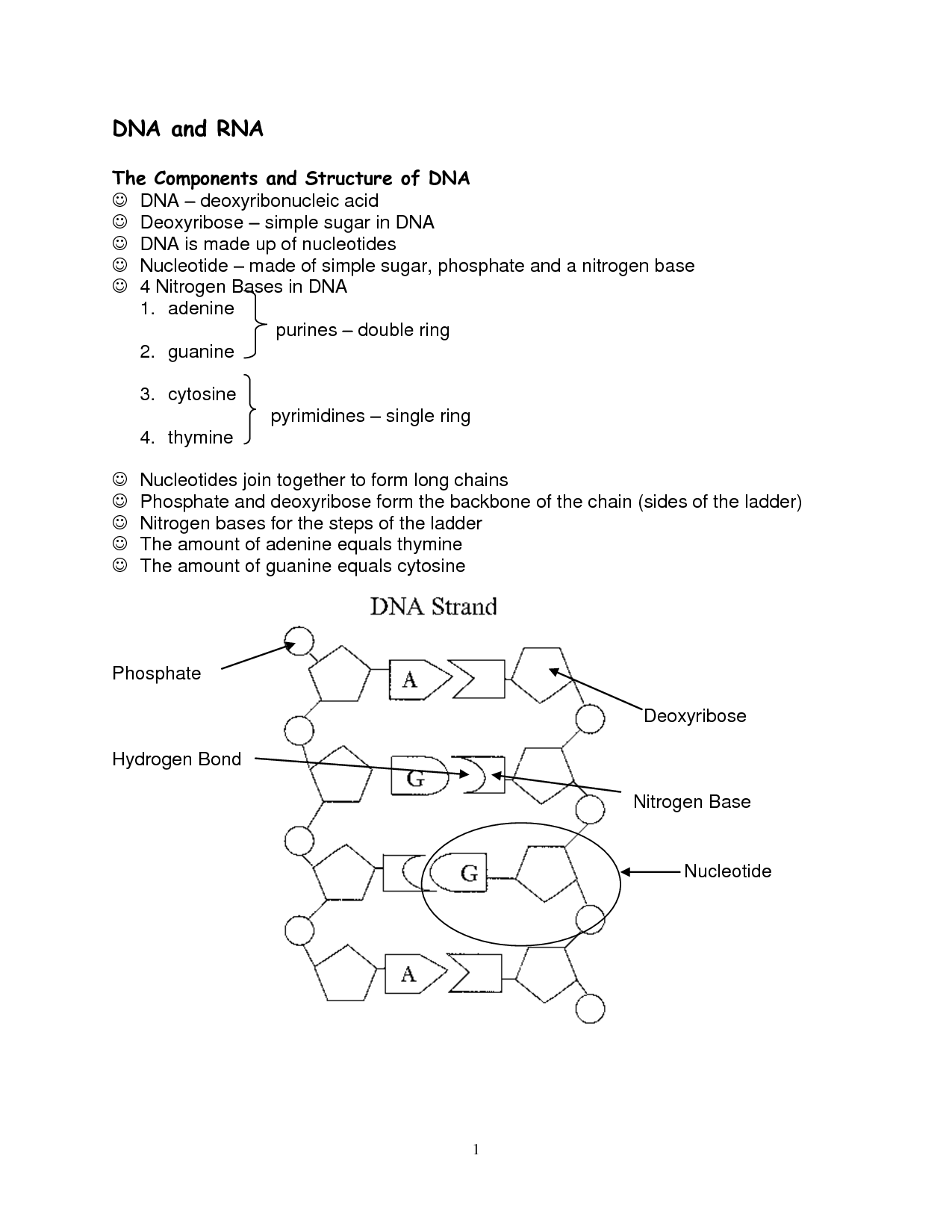
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is double-stranded, while RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is typically single-stranded. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. Additionally, DNA's bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), while RNA's bases are adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). DNA carries genetic information in cells, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and other cellular processes.
What are the different components of DNA?
DNA is made up of four different components: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), known as nucleotides. These nucleotides are arranged in a double helix structure, with adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine. Additionally, DNA also consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone that provides stability to the molecule.
How does DNA function in protein synthesis?
During protein synthesis, DNA serves as the template for the transcription process, where messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized using complementary base pairing. The mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. At the ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring specific amino acids according to the mRNA codons. The tRNA molecules recognize the codons on the mRNA through their anticodons and attach the corresponding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain, resulting in protein synthesis. Overall, DNA plays a crucial role in directing the sequence of amino acids in proteins through the process of transcription and translation in the cell.
What is a gene?
A gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for a specific trait or function in an organism. Genes are the basic unit of heredity and are passed down from parents to offspring. Genes control various characteristics such as eye color, hair texture, and susceptibility to certain diseases by guiding the production of specific proteins within cells.
How are genes expressed in an organism?
Genes are expressed in an organism through a process called gene expression, which involves transcription of the gene to produce mRNA and translation of mRNA into a protein. This process is tightly regulated by several mechanisms, including transcription factors, chromatin modification, and microRNAs, to ensure that genes are expressed at the right time and in the right amount for the organism's needs.
What is the role of DNA helicase in DNA replication?
DNA helicase plays a crucial role in DNA replication by unwinding the double-stranded DNA helix during the process. This unwinding action creates two single strands of DNA that can serve as templates for the synthesis of new DNA strands. This enzyme is responsible for separating the two strands and promoting the accuracy and efficiency of DNA replication by making the genetic information accessible for DNA polymerase to build new DNA strands.
What is transcription and where does it occur?
Transcription is the process where the genetic information encoded in DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule. This process takes place in the cell nucleus of eukaryotic organisms or in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic organisms. During transcription, an enzyme called RNA polymerase reads the DNA sequence and synthesizes a matching RNA strand, which can then be used as a template for protein synthesis.
What is translation and where does it occur?
Translation is the process of converting text or speech from one language to another while maintaining its original meaning and context. It can occur in various settings such as literature, business, government, education, and technology. Translators work in different fields like legal, medical, technical, and literary translations to bridge communication gaps between people who speak different languages. Additionally, automated translation tools and services are also available to facilitate the translation process in today's digital world.
How do mutations in DNA affect protein synthesis?
Mutations in DNA can affect protein synthesis by altering the sequence of nucleotides in the gene, which can lead to changes in the amino acid sequence of the protein. This can result in non-functional or altered proteins being synthesized, impacting the structure and function of the protein. Additionally, mutations can also affect the regulation of gene expression, leading to either increased or decreased production of the protein. Overall, mutations in DNA can have diverse effects on protein synthesis, potentially affecting the overall functioning of the cell or organism.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments