Fourth Grade Science Sound Worksheets
Are you searching for engaging and educational resources to reinforce your fourth-grade students' understanding of sound in science? Look no further! Our collection of fourth-grade science sound worksheets is designed to captivate young learners while they explore the fascinating world of sound waves, vibration, and pitch. These worksheets provide the perfect opportunity to engage your students with hands-on activities and thought-provoking questions, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Life Science Worksheets 4th Grade
- Free Halloween Color by Math Worksheets
- Weathering and Erosion Worksheet
- 6th Grade Vocabulary Template
- Long O Worksheets
- Consonant Digraph CH Worksheets
- Long U Vowel Sound Worksheet
- Long Vowel E Worksheet
- Long O Vowel Sounds Worksheets
- Read All About Me Worksheet
- Science States of Matter Worksheets
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- Day and Night Worksheet Kindergarten
More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Reading Response Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Essay Writing Worksheets
Worksheets 4th Grade Narrative Writing
Long Lined Paper Worksheets 4th Grade Essay-Writing
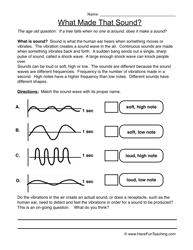
What is sound?
Sound is a form of energy that is produced by vibrations traveling through a medium, such as air, water, or solid materials. These vibrations create waves that can be detected by the human ear and processed by the brain to interpret as sound. Sound is characterized by its pitch (frequency of the vibration), intensity (amplitude of the vibration), and timbre (quality of the sound).
How is sound produced?
Sound is produced when an object vibrates, creating pressure waves that travel through a medium such as air or water. These pressure waves cause the particles in the medium to vibrate, transmitting the sound energy. When the waves reach our ears, they are converted into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sound.
What are the three main properties of sound?
The three main properties of sound are pitch, volume, and timbre. Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a sound, volume is the loudness or softness of a sound, and timbre is the quality that distinguishes one sound from another, such as a guitar from a piano.
How does sound travel through different materials?
Sound travels through different materials by causing particles in the material to vibrate. In solid materials, such as metal or wood, sound waves move through the material by causing the particles to bump into each other and transfer the sound energy. In liquids, such as water, sound waves propagate through the movement of particles bumping into each other and transferring the energy. In gases, such as air, sound waves move through the compression and rarefaction of the air molecules, creating a chain reaction of vibrations that travel through the medium.
What is the difference between pitch and volume?
Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a sound, determined by the frequency of the sound waves produced. Volume, on the other hand, refers to the loudness or softness of a sound, determined by the intensity of the sound waves produced. In summary, pitch is about the frequency of sound waves, while volume is about the intensity of sound waves.
How do our ears allow us to hear sound?
Our ears allow us to hear sound through a process of sound waves entering the ear canal and reaching the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. The vibrations are then transmitted through the middle ear bones to the cochlea in the inner ear, which contains hair cells that convert the vibrations into electrical signals. These signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound.
What is an echo and how is it formed?
An echo is a reflection of sound that arrives at the listener's ear some time after the direct sound. It is formed when sound waves hit a hard surface, such as a wall, and bounce back towards the listener. The brain processes these reflected sounds as a separate, delayed sound, creating the sensation of an echo. The distance between the source of the sound and the reflecting surface, as well as the distance between the reflecting surface and the listener, determines the time delay and intensity of the echo.
How can sound be used to communicate over long distances?
Sound can be used to communicate over long distances by leveraging technology such as telephones, radios, and loudspeakers. By converting sound waves into electrical signals and transmitting them through wires or wireless networks, we can send and receive audio messages over vast distances almost instantaneously. This technology has revolutionized communication, allowing people to connect and convey information across the globe in real-time.
What are some examples of sound pollution?
Examples of sound pollution include noise from traffic, construction sites, airplanes, industrial activities, loud music, and barking dogs. These loud and disruptive sounds can have negative impacts on human health, such as hearing loss, stress, sleep disturbances, and impaired cognitive function, as well as causing harm to wildlife and disrupting natural ecosystems.
How can we protect our hearing from loud sounds?
To protect your hearing from loud sounds, it is important to wear ear protection such as earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments like concerts, construction sites, or when using loud equipment. Limiting exposure to loud noises and taking breaks in quieter settings can also help prevent damage to your hearing. Additionally, turning down the volume on personal electronic devices and using noise-canceling headphones can reduce the risk of hearing loss from prolonged exposure to loud sounds.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments