Forces Worksheets Middle School
Are you on the hunt for engaging and educational worksheets that will help your middle school students grasp the concept of forces? Look no further! Our collection of forces worksheets is specifically designed to teach and reinforce the principles of physics in a way that is clear and accessible for students at this level. By focusing on the core concepts and using relatable examples, these worksheets make learning about forces both interesting and impactful.
Table of Images 👆
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Worksheet Answers
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Worksheet
- Force and Motion Worksheets 5th Grade
- First Grade Printable Science Worksheets
- Weathering and Erosion Worksheet
- Science Fossils Worksheets for 3rd Grade
- 5 Grade English Worksheets
- Science Force and Motion Worksheets
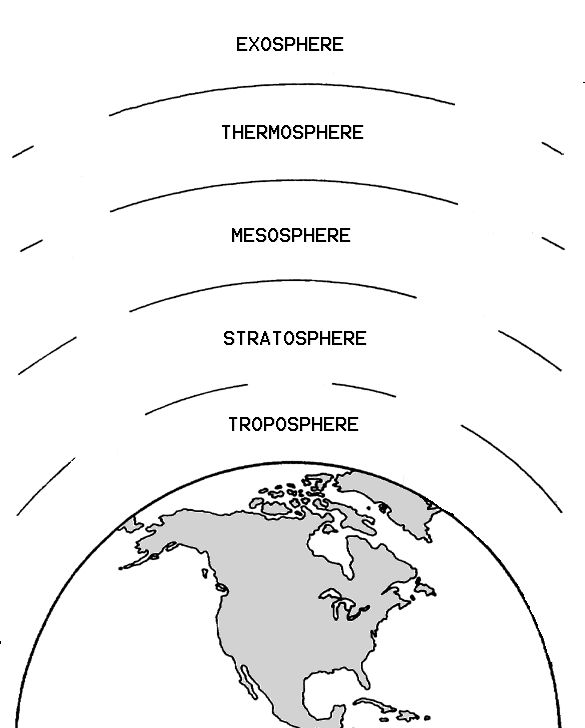
- Earth Atmosphere Layers Worksheet
- Middle Ages Medical Timeline
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a force?
A force is a push or pull that can cause an object to move, change direction, or deform. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction, and is usually expressed in units of newtons (N). Forces can be applied in various forms, such as gravitational, electromagnetic, frictional, or tension forces, and play a fundamental role in understanding the interactions between objects in physics.
What are the two main types of forces?
The two main types of forces are contact forces and non-contact forces. Contact forces occur when two objects are physically touching and interact through direct contact, such as friction and tension. Non-contact forces, on the other hand, act at a distance without direct contact between objects, like gravitational and magnetic forces.
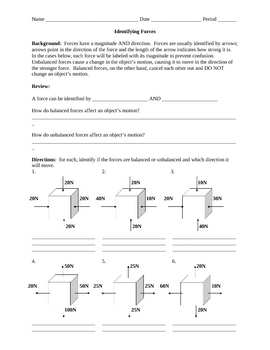
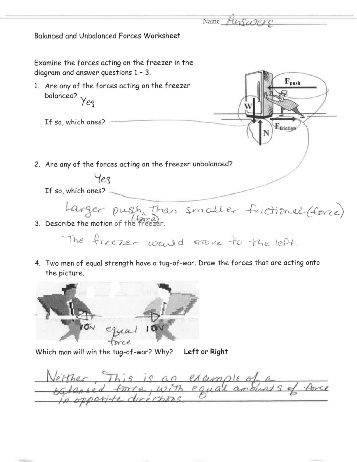
What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?
Balanced forces refer to two or more forces that are equal in size and opposite in direction, resulting in no change in an object's motion. On the other hand, unbalanced forces are unequal in size or not in the opposite direction, causing a change in an object's motion by either speeding it up, slowing it down, or changing its direction.
What is friction and how does it affect motion?
Friction is the force that resists the relative motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact. It occurs when two surfaces rub against each other. Friction affects motion by slowing down the object in motion, converting some of its kinetic energy into heat. It opposes the direction of motion, making it harder for objects to move smoothly or accelerate quickly.
What is gravity and how does it affect objects on Earth?
Gravity is a fundamental force that attracts objects with mass towards each other. On Earth, gravity is what keeps us grounded and gives weight to objects. It affects all objects on Earth by pulling them towards the center of the planet, causing things to fall towards the ground when not supported. The strength of gravity on Earth is relatively constant, leading to a predictable acceleration and causing objects to accelerate towards the ground at a rate of 9.8 meters per second squared.
What is air resistance and how does it act on falling objects?
Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of an object as it moves through the air. When an object is falling, air resistance slows it down by pushing against it in the opposite direction of its motion. The force of air resistance increases with the speed of the object and the surface area exposed to the air. As a falling object accelerates due to gravity, the force of air resistance eventually balances out with the force of gravity, causing the object to reach a terminal velocity where it falls at a constant speed.
What is the relationship between mass and inertia?
Mass and inertia are directly related in that mass is a measure of an object's inertia, which is its resistance to changes in motion. The greater an object's mass, the greater its inertia, making it harder to accelerate or decelerate the object. Inertia is a property of matter that is determined by the mass of an object, and the more mass an object has, the more inertia it will possess.
What are some examples of contact forces?
Some examples of contact forces include friction, tension, normal force, air resistance, and applied force. These forces occur when two objects are in physical contact and exert a force on each other through direct contact.
What are some examples of non-contact forces?
Some examples of non-contact forces include gravitational force, electromagnetic force, and nuclear force. Gravitational force occurs between any two objects with mass, pulling them towards each other. Electromagnetic force is responsible for interactions between charged particles, such as like charges repelling each other and opposite charges attracting each other. Nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together within an atomic nucleus. These forces can act over distances without physical contact between the interacting objects.
How can forces be measured and represented on a diagram?
Forces can be measured using a force sensor or by calculations based on known factors such as mass and acceleration. To represent forces on a diagram, you can use arrows to indicate the direction and magnitude of the force. The length and direction of the arrow show the size and direction of the force, respectively. Additionally, you can label the arrow with the specific force being applied to provide clarity.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments