Force and Motion Worksheet for First Grade
If you're a first-grade teacher looking for a way to reinforce force and motion concepts, you've come to the right place. Worksheets can be a valuable tool in engaging young students while offering them a tangible way to practice and apply their knowledge. By providing an entity-focused and subject-specific worksheet, you can tailor the learning experience to suit the needs of your classroom.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Motion Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Projectile Motion Worksheet
- Gravity Worksheets 2nd Grade
- 2nd Grade Science Worksheets Force
- Force and Motion Worksheets 5th Grade
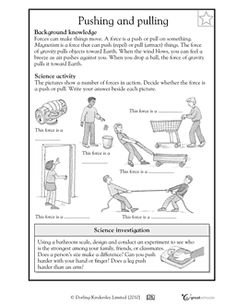
- Push and Pull Science Activities
- Science Force and Motion Worksheets
- Plant Tree Map Kindergarten
- Pushes and Pulls Worksheets
- Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
- Calvin and Hobbes Loopholes
- Ecosystem Worksheet Food Chain
- Planet Mercury Worksheets
- Matter Solid-Liquid Gas Worksheet
More 1st Grade Worksheets
First Grade Reading Comprehension WorksheetsTelling Time Worksheets for First Grade
Math Worksheets Subtraction 1st Grade
For First Grade Addition Worksheets
First Grade Handwriting Practice Worksheets
First Grade Fraction Worksheets
Free Printable Phonics Worksheets First Grade
Heart Worksheets for First Grade
First Grade Science Worksheets Matter
Following Directions First Grade Worksheets
What is force?
Force is a physical quantity that describes the interaction between objects or particles, resulting in a change in their motion or shape. It can be a push or a pull exerted on an object in a specific direction and is typically measured in units like newtons. Forces can be classified as contact forces (like friction or tension) or non-contact forces (like gravity or magnetism), and they play a fundamental role in the behavior and dynamics of all physical systems in the universe.
How does force affect motion?
Force affects motion by causing an object to accelerate in the direction of the force applied. According to Newton's second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, the greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration will be, resulting in a change in its speed or direction of motion.
What are some examples of forces in everyday life?
Some examples of forces in everyday life include gravity pulling objects towards the ground, friction between surfaces when you walk, push or pull an object, tension in a string when you swing a pendulum, and air resistance when you ride a bike. Additionally, muscular forces are exerted when you lift something heavy or kick a ball, while electrostatic forces come into play when you rub a balloon against your hair and it sticks to a wall.
What is motion?
Motion is the act of changing position or location relative to a reference point or frame of reference. It involves an object or being moving from one place to another in response to an applied force or energy. Motion can be described in terms of speed, direction, and acceleration, and it is a fundamental concept in physics that helps describe the behavior of objects in the physical world.
What are the different types of motion?
There are various types of motion, including linear motion (movement in a straight line), rotary motion (movement in a circular path), oscillatory motion (repetitive back-and-forth movement), reciprocating motion (back-and-forth movement in a straight line), and vibrational motion (rapid back-and-forth movement around a central point). These different types of motion play crucial roles in various natural phenomena and everyday activities.
How can we measure motion?
Motion can be measured using various methods, including speed measurement devices like radar guns and speed cameras, distance measuring tools like odometers and GPS systems, and accelerometers that measure changes in velocity. Other methods include video analysis, motion sensors, and laser Doppler velocimetry. Each of these tools has its own advantages and limitations depending on the specific application and required level of accuracy.
What is speed?
Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving in a particular direction. It is typically expressed as the distance traveled by an object in a unit of time, such as meters per second or kilometers per hour. Speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction associated with it.
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of an object's velocity over time, meaning how quickly an object speeds up or slows down. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (how much the speed changes) and direction (whether the object is speeding up or slowing down). Acceleration can be caused by forces such as gravity, friction, or applied forces, and is measured in units of meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How does friction affect motion?
Friction acts as a resistive force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact. It can either slow down or stop the motion of objects. Friction also plays a crucial role in enabling traction for vehicles to grip the road surface, allowing them to move efficiently. Additionally, friction can generate heat as a result of the resistance between surfaces rubbing against each other, which can impact the overall energy efficiency of a system.
How can we change the motion of an object?
The motion of an object can be changed by applying a force on it in the direction you want it to move. This force can be varied in magnitude and direction to control the speed, direction, or acceleration of the object. Other factors that can affect an object's motion include mass, friction, and other external forces acting on the object. By understanding and manipulating these factors, we can effectively change the motion of an object.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments