Force and Energy Worksheets
Are you in need of worksheets that effectively engage young learners in the concepts of force and energy? Look no further! Our comprehensive collection of force and energy worksheets is designed to provide a range of activities that captivate students while enhancing their understanding of these important scientific concepts. With clear instructions and visually appealing designs, our worksheets make learning about force and energy both engaging and enjoyable for students of all levels.
Table of Images 👆
- TIDAL WAVE ALTERNATIVE ENERGY
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets Middle School
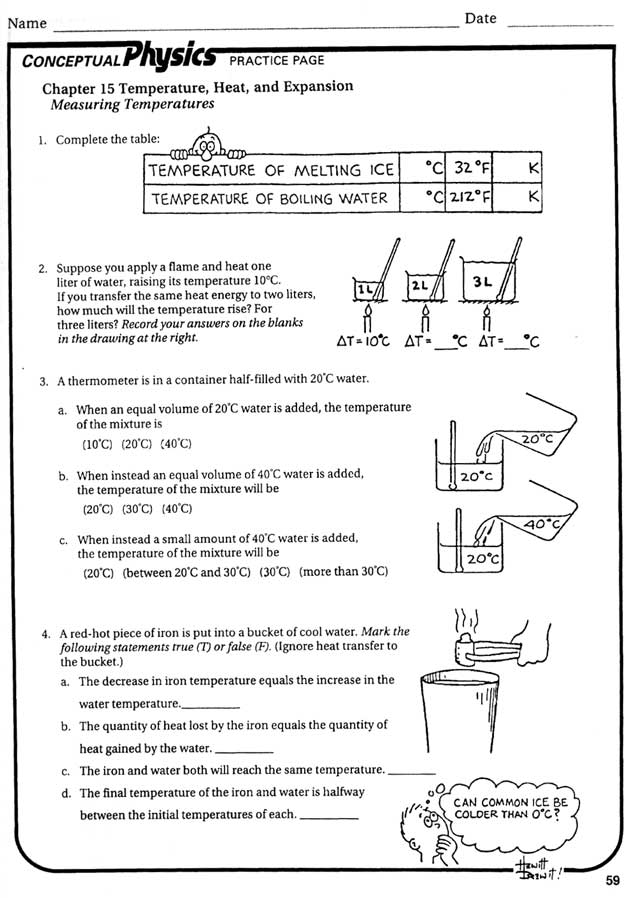
- Thermal Energy Worksheet Heat and Temperature
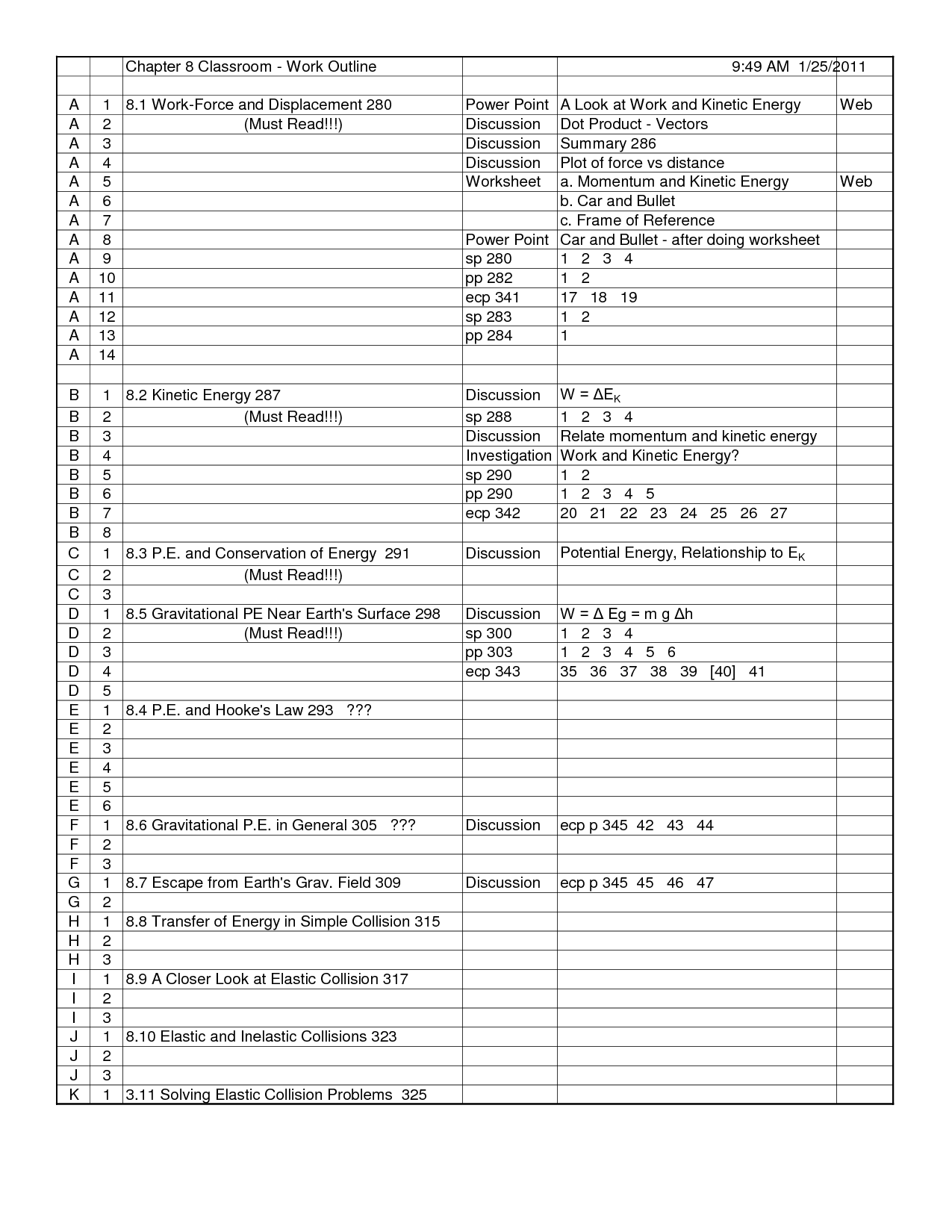
- Work and Power Worksheet Answers
- Force and Motion Worksheets
- Work Energy and Power Worksheet Answers
- Science Force and Motion Worksheets
- 8th Grade Forces and Motion Worksheets
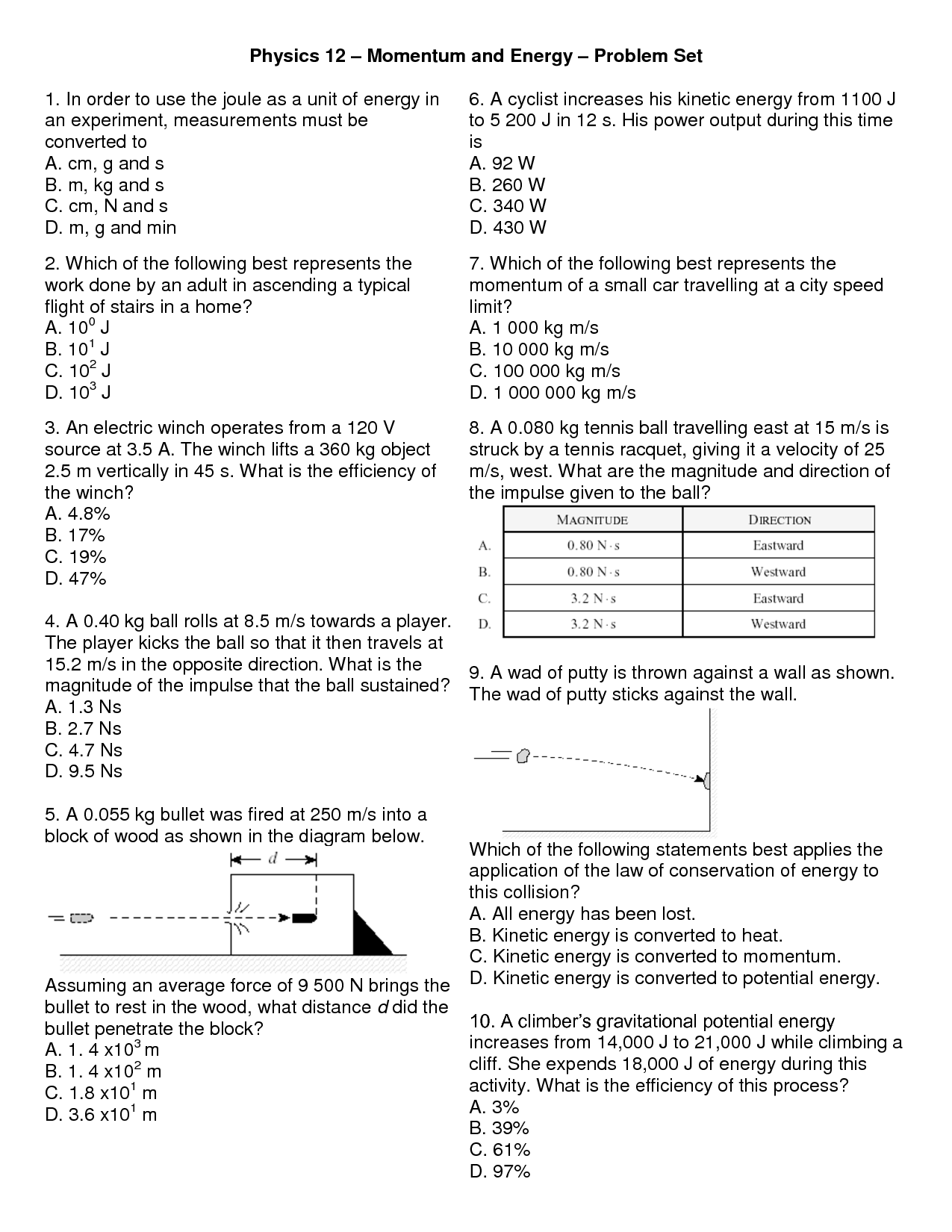
- Physics Work Energy and Power Worksheet
- Work Energy and Power Worksheet
- Force and Motion Worksheets 5th Grade
- Elastic Potential Energy Worksheet
- Force and Motion Crossword Puzzle
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is force?
Force is a physical interaction that causes an object to accelerate or deform. It is typically measured in units of newtons and can be classified into various types such as gravitational, electromagnetic, and contact forces. In essence, force is what pushes or pulls objects in the direction of motion or in resistance to motion.
How is force measured?
Force is measured in units called Newtons (N). One Newton is equivalent to the force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Force can be measured using various instruments such as spring scales, force gauges, and dynamometers, which calculate the amount of force being applied in a given situation.
What is the difference between contact and non-contact forces?
Contact forces are those that require physical contact between two objects, such as friction or tension, while non-contact forces can act through a distance without direct touch, such as gravity or magnetic force. Contact forces depend on the interaction at the point of contact, whereas non-contact forces can act over a distance by exerting a force field.
Give an example of a contact force.
One example of a contact force is the force exerted by a person kicking a soccer ball. This force is generated by the direct physical contact between the person's foot and the soccer ball, causing the ball to move in the direction of the kick.
What is energy?
Energy is a fundamental property of matter and the ability to do work or cause change. It exists in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, electrical, and more, and can be transferred between objects or converted from one form to another. Energy plays a crucial role in all aspects of the universe, whether by powering machines, fueling living organisms, or driving natural processes.
What are the different forms of energy?
There are several forms of energy, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), thermal energy (heat energy), chemical energy (energy stored in bonds of atoms and molecules), electrical energy (energy carried by electrons in a conductor), nuclear energy (energy stored in the nucleus of an atom), and electromagnetic energy (energy carried by waves, including light and radio waves).
Explain the law of conservation of energy.
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can only be transferred or transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time. Energy can change from potential to kinetic, thermal, radiant, or other forms, but the total energy within the system will always remain the same. This fundamental principle governs all physical processes and plays a key role in understanding the behavior of energy in various systems and phenomena.
How is energy transferred?
Energy is transferred through various mechanisms such as conduction, convection, and radiation. In conduction, heat or energy is transferred through direct contact between particles or objects. Convection involves the transfer of energy through the movement of fluids like air or water. Radiation is the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves such as light or infrared radiation. Each of these mechanisms plays a crucial role in how energy moves from one place to another.
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is the stored energy an object possesses due to its position or condition, such as gravitational potential energy or chemical potential energy, whereas kinetic energy is the energy of motion an object possesses due to its velocity. In simple terms, potential energy is the energy that could be released or converted into kinetic energy when the object moves or changes its position.
Explain how work is related to force and energy.
Work is the amount of energy transferred when a force is applied over a distance. In order to do work, a force must be exerted on an object, and this force must cause the object to move in the direction of the force. The amount of work done is directly proportional to both the force applied and the distance over which the force is applied. Therefore, work, force, and energy are interconnected concepts in physics, with work being the transfer of energy through the application of force.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments