Food Web Worksheets Free Printables
Food webs are intricate and fascinating networks that depict the relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem. Understanding how these interactions work can help students grasp the complexities of nature and the delicate balance that exists within the natural world. If you are in search of free and printable worksheets to effectively teach about food webs, we have got you covered. Our collection of food web worksheets offers a range of engaging and informative resources for students to explore and learn about this captivating subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
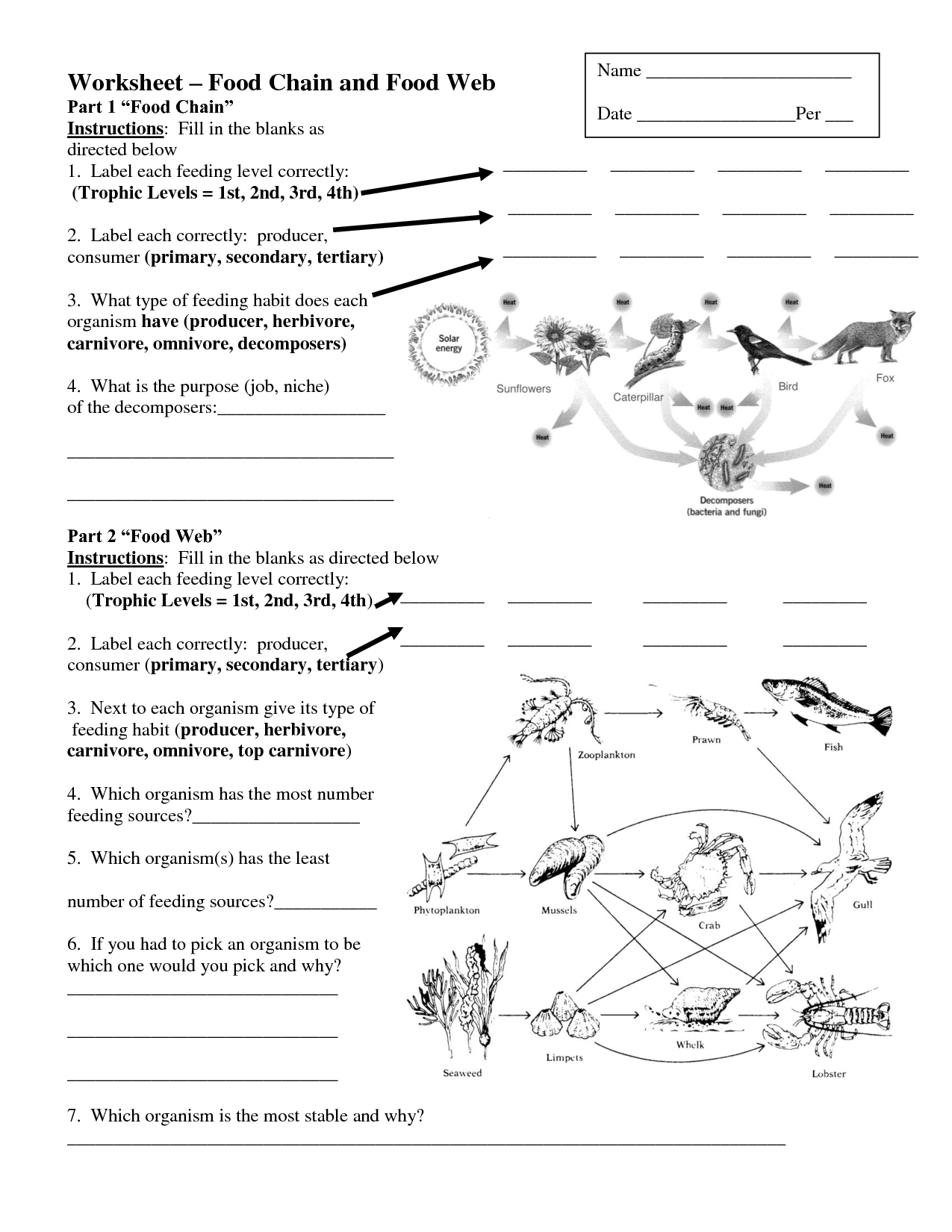
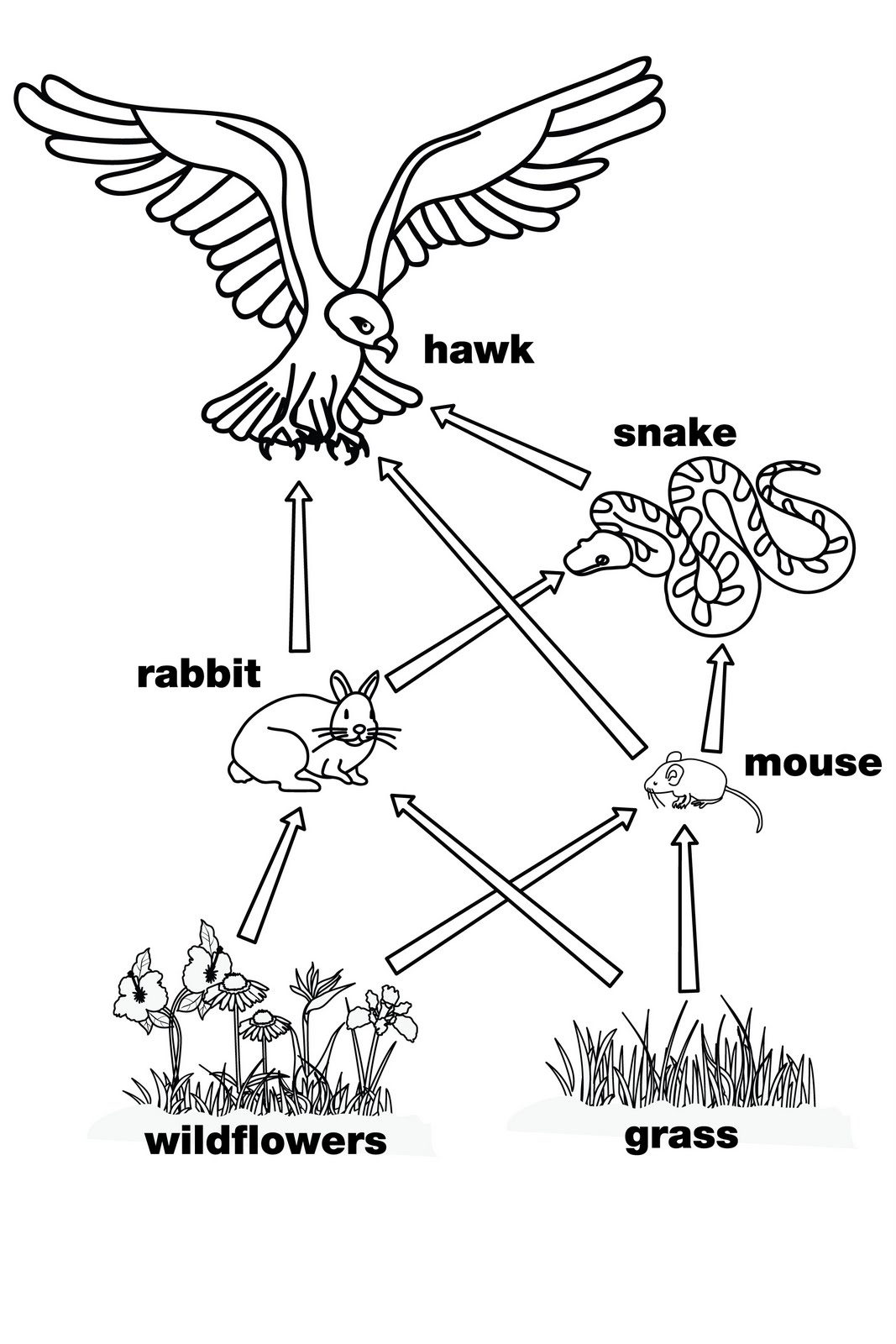
What is a food web?
A food web is a model that shows the interconnected network of food chains within an ecosystem, representing the feeding relationships between different organisms. It demonstrates how energy and nutrients are passed from one organism to another in a complex web of interactions, illustrating the diversity and interconnectedness of life within a given environment.
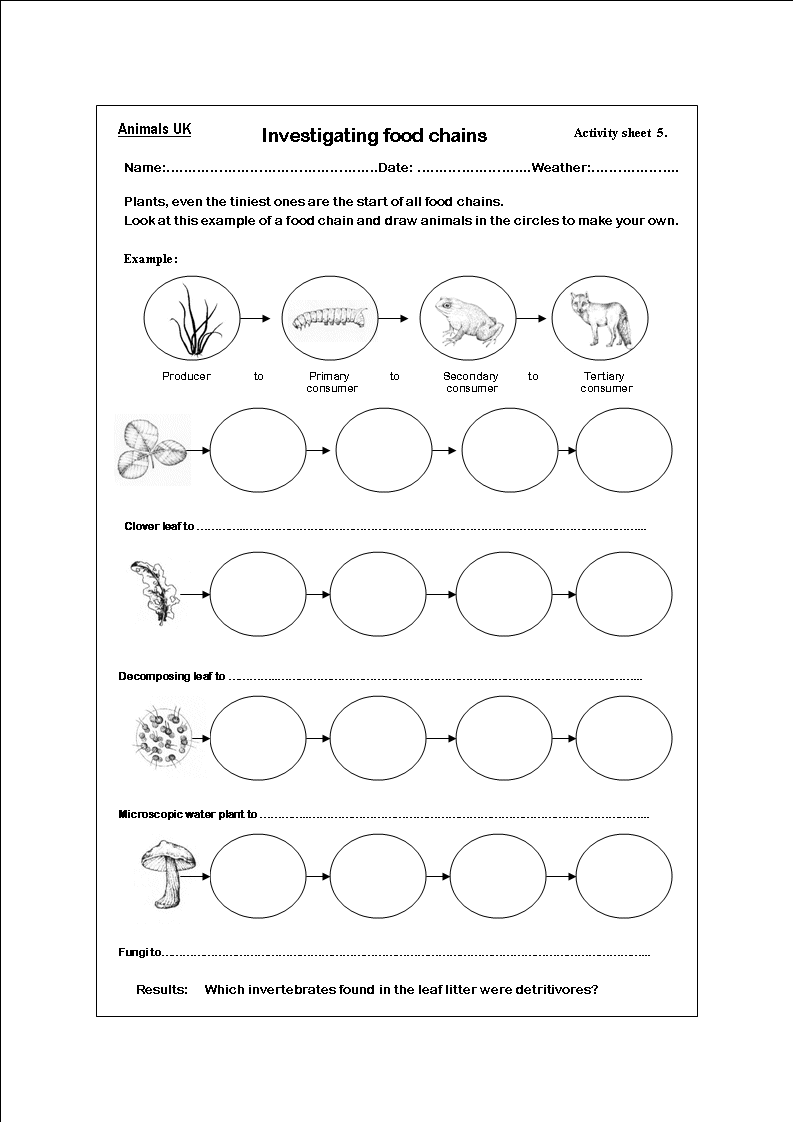
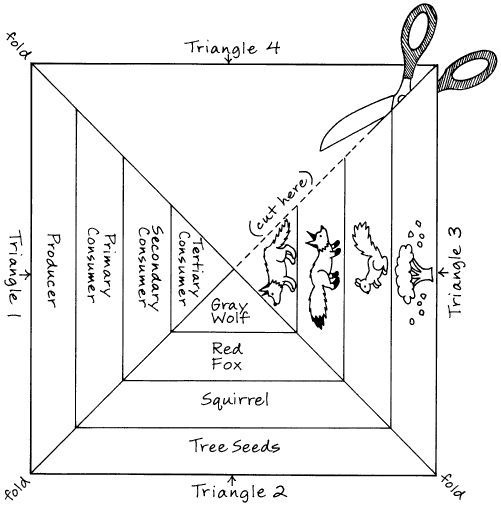
How are food chains different from food webs?
Food chains are a linear sequence that shows a specific feeding relationship between different organisms in an ecosystem, where energy and nutrients flow from one organism to another. In contrast, food webs illustrate a more complex network of interconnected food chains, demonstrating multiple feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem. While a food chain focuses on a single pathway of energy transfer, a food web depicts the interconnected nature of an ecosystem's food relationships, encompassing a broader picture of how organisms interact with one another in an ecosystem.
What are producers in a food web?
Producers are organisms, often green plants or algae, that are able to convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. They are found at the base of a food web and provide energy and nutrients for other organisms in the ecosystem. By creating their own food, producers play a vital role in supporting the entire food chain by making energy available for consumers at higher trophic levels.
Name three different types of consumers in a food web.
In a food web, three different types of consumers are herbivores (such as rabbits, deer, and cows that eat plants), carnivores (like lions, wolves, and hawks that eat other animals), and omnivores (such as bears, humans, and rats that consume both plants and animals).
What is the role of decomposers in a food web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food web as they break down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler nutrients that can be absorbed by plants. This process of decomposition releases essential nutrients back into the soil, allowing for the recycling of matter in the ecosystem and providing a source of energy for other organisms higher up in the food chain. Ultimately, decomposers help maintain the balance and sustainability of the ecosystem by facilitating the cycling of nutrients.
How do predators and prey interact in a food web?
Predators and prey interact in a food web through a dynamic relationship where predators consume prey for energy and prey populations are regulated by predation. This interaction plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within ecosystems by controlling population sizes, influencing species diversity, and impacting the overall health of the ecosystem. Predators help control the population of prey species, preventing overpopulation, which can lead to resource depletion and environmental degradation. In turn, prey species have adaptations to avoid predators, such as camouflage or defensive behaviors, which further shapes the predator-prey relationship in the ecosystem.
What happens if there is a disruption in a food web?
A disruption in a food web can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. If a species at a lower trophic level is greatly impacted or eliminated, it can lead to a decrease in population numbers or extinction of species higher up in the food web that depend on them for food. This can cause imbalances in the ecosystem, affect biodiversity, disrupt energy flow, and ultimately impact the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem.
How do energy and nutrients flow through a food web?
Energy flows through a food web from one trophic level to another as organisms consume and transfer energy through consumption. Nutrients, on the other hand, are cycled within the food web as they are taken up by organisms, released back into the environment through decomposition, and then taken up again by other organisms. Both energy and nutrients flow through a food web in a continuous cycle, sustaining the ecosystem's functioning and productivity.
Can the same organism occupy multiple trophic levels in a food web? Explain.
Yes, the same organism can occupy multiple trophic levels in a food web. This phenomenon is known as omnivory, where an organism consumes both plants as primary producers and other animals as consumers, allowing them to occupy more than one level in the food chain. For example, a human can be a primary consumer when eating plants and a secondary consumer when eating meat, demonstrating the flexibility and complexity of food webs in nature.
How can changes in one population affect other populations in a food web?
Changes in one population can have a cascading effect on other populations in a food web. For example, if a predator population declines due to factors such as hunting or habitat loss, the prey population might increase in number. This can then lead to overgrazing of vegetation, impacting other species that rely on that vegetation for food or habitat. Similarly, if a prey population decreases, the predator population may suffer from lack of food, potentially leading to their decline as well. Overall, changes in one population can disrupt the balance of the food web and have ripple effects on the entire ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments