Food Web Worksheets 7th Grade
In 7th grade, understanding the intricate relationships between different organisms in a food web can be a challenging concept. Luckily, there are worksheets available that focus on this topic and provide valuable practice for students. These worksheets delve into the entity and subject of food webs, allowing 7th graders to grasp the complex dynamics and interactions within ecosystems.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
What is a food web?
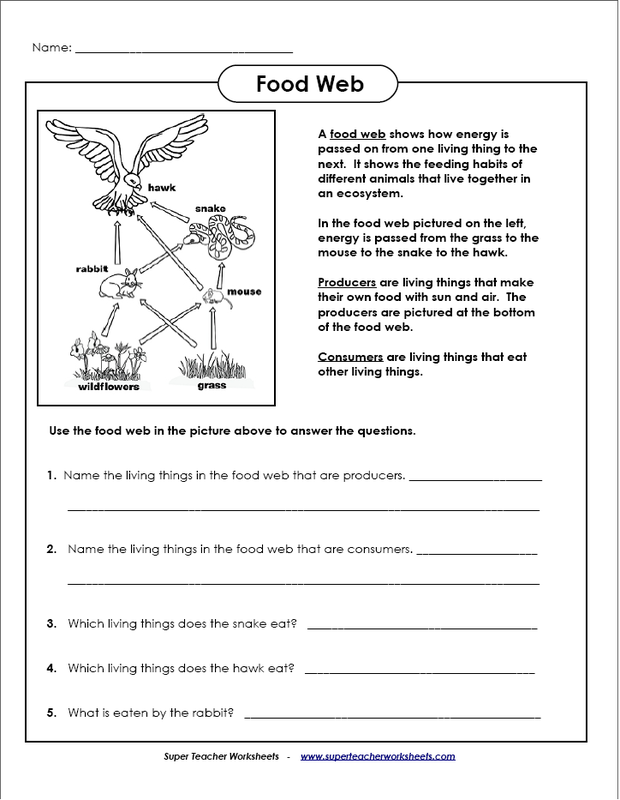
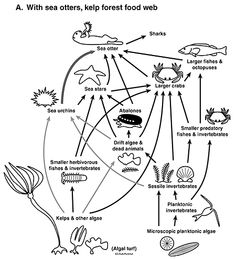
A food web is a system of interlocking and overlapping food chains that shows the feeding relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem. It illustrates how energy and nutrients are transferred and recycled through various species in a given habitat, demonstrating the complex web of connections that exist between producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem.
What are the primary producers in a food web?
Primary producers in a food web are organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis, such as plants, algae, and certain types of bacteria. These organisms are essential at the base of the food chain as they convert sunlight into energy, which is then passed on to the primary consumers that feed on them.
What are the primary consumers?
Primary consumers are organisms that feed on producers, such as plants and algae, in an ecosystem. They are also known as herbivores and play a crucial role in transferring energy from producers to higher trophic levels in the food chain. By consuming plant materials, primary consumers help regulate plant populations and maintain a balanced ecosystem.
Give an example of a secondary consumer.
A fox is an example of a secondary consumer as it feeds on primary consumers like rabbits and mice.
Explain the role of decomposers in a food web.
Decomposers play a critical role in a food web by breaking down dead organisms and organic matter into simpler nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. This process, called decomposition, releases these nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for producers like plants to use for growth. Ultimately, decomposers help to recycle nutrients, maintain the balance of an ecosystem, and ensure the sustainability of life within the food web.
How does energy flow in a food web?
Energy flows in a food web from one organism to another as they consume and are consumed. It begins with producers, such as plants, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Primary consumers, such as herbivores, then consume producers, transferring the energy up the food chain. Secondary consumers feed on primary consumers, continuing the flow of energy. Eventually, energy is passed on to higher level consumers until reaching decomposers, which break down organisms and release nutrients back into the environment. This continuous flow of energy ensures the functioning and stability of ecosystems.
Describe the difference between a predator and a prey in a food web.
A predator is an organism that hunts, kills, and feeds on other organisms, known as prey, to obtain energy. Predators are usually carnivores that rely on consuming other animals as their primary food source. On the other hand, prey are the organisms that are hunted and eaten by predators as a source of food. Prey organisms have adaptations such as camouflage, speed, or defense mechanisms to avoid being captured by predators. In a food web, predators are typically higher up in the trophic levels, while prey organisms are lower down in the food chain.
What happens to the energy as it moves up the food chain?
As energy moves up the food chain, some of it is lost at each trophic level through metabolic processes such as respiration and movement, resulting in less energy being available to higher trophic levels. This phenomenon is known as the 10% energy rule, where only about 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next. This explains why there are typically fewer organisms at higher trophic levels, as there is less available energy to support them.
How can changes in one population in a food web affect other populations?
Changes in one population in a food web can have a cascading effect on other populations within the same web. For example, a decline in a prey population can lead to food scarcity for predators higher up the food chain, causing a decline in their population as well. Conversely, an increase in a prey population can lead to an increase in predator populations. These interactions and dependencies within a food web result in a delicate balance where any changes in one population can have a significant impact on the overall ecosystem.
How does a balanced food web contribute to the overall health of an ecosystem?
A balanced food web contributes to the overall health of an ecosystem by promoting stability and resilience. Each organism plays a specific role in the food chain, regulating the population sizes of other species and maintaining biodiversity. This balance helps prevent the overabundance of any one species, which can lead to negative impacts on the rest of the ecosystem. Additionally, a diverse food web ensures that energy and nutrients are efficiently transferred throughout the ecosystem, supporting the survival and growth of all organisms within it.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments