Food Chain Worksheets Free
Food chain worksheets are a valuable educational resource that can help students understand the intricate relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. These worksheets provide a structured and engaging way for students to learn about food chains, focusing on the key concepts of producers, consumers, and decomposers. Whether you are a teacher seeking to supplement your lesson plans or a homeschooling parent looking for educational activities, these free food chain worksheets can aid in your quest to enhance student understanding of this important ecological concept.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
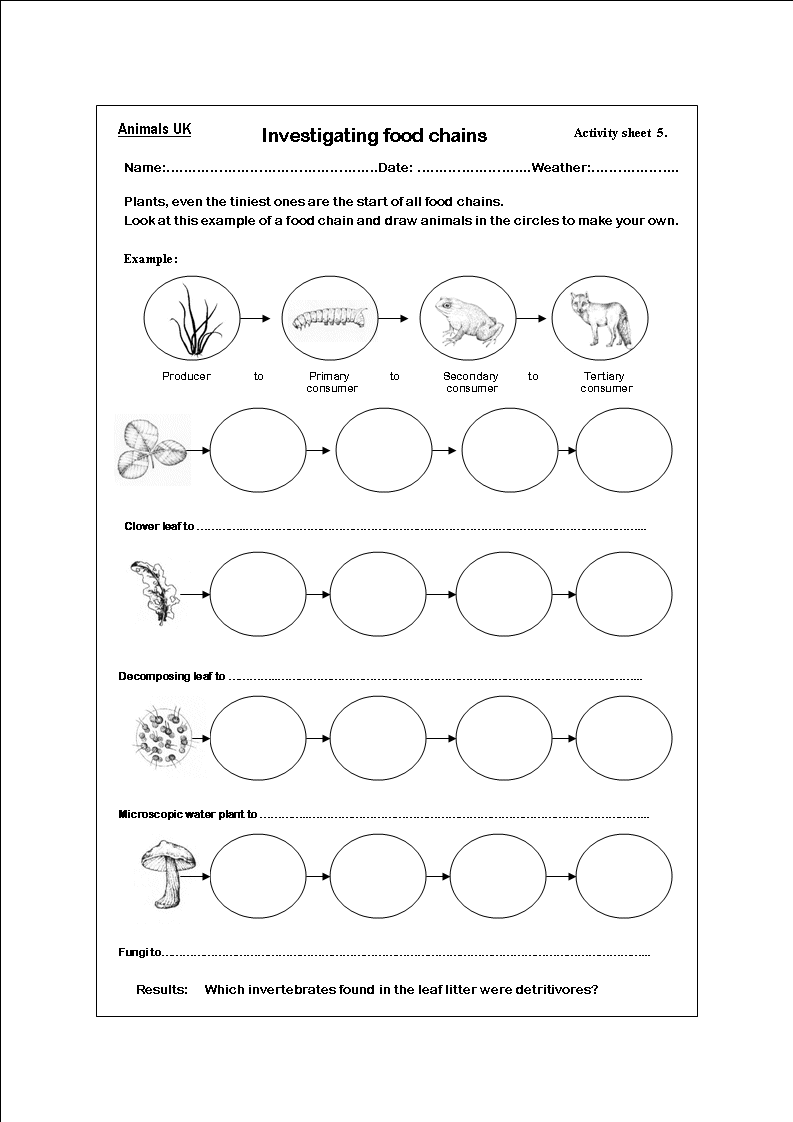
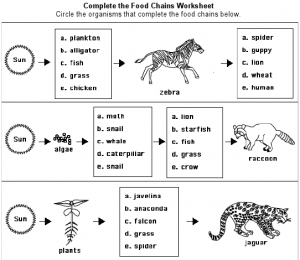
What is a food chain?
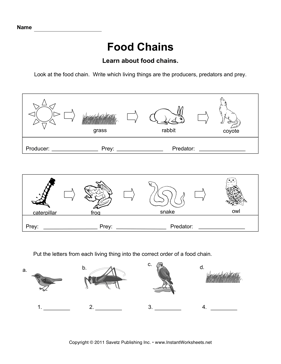
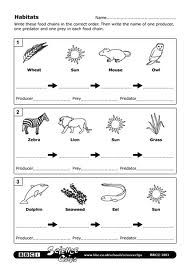
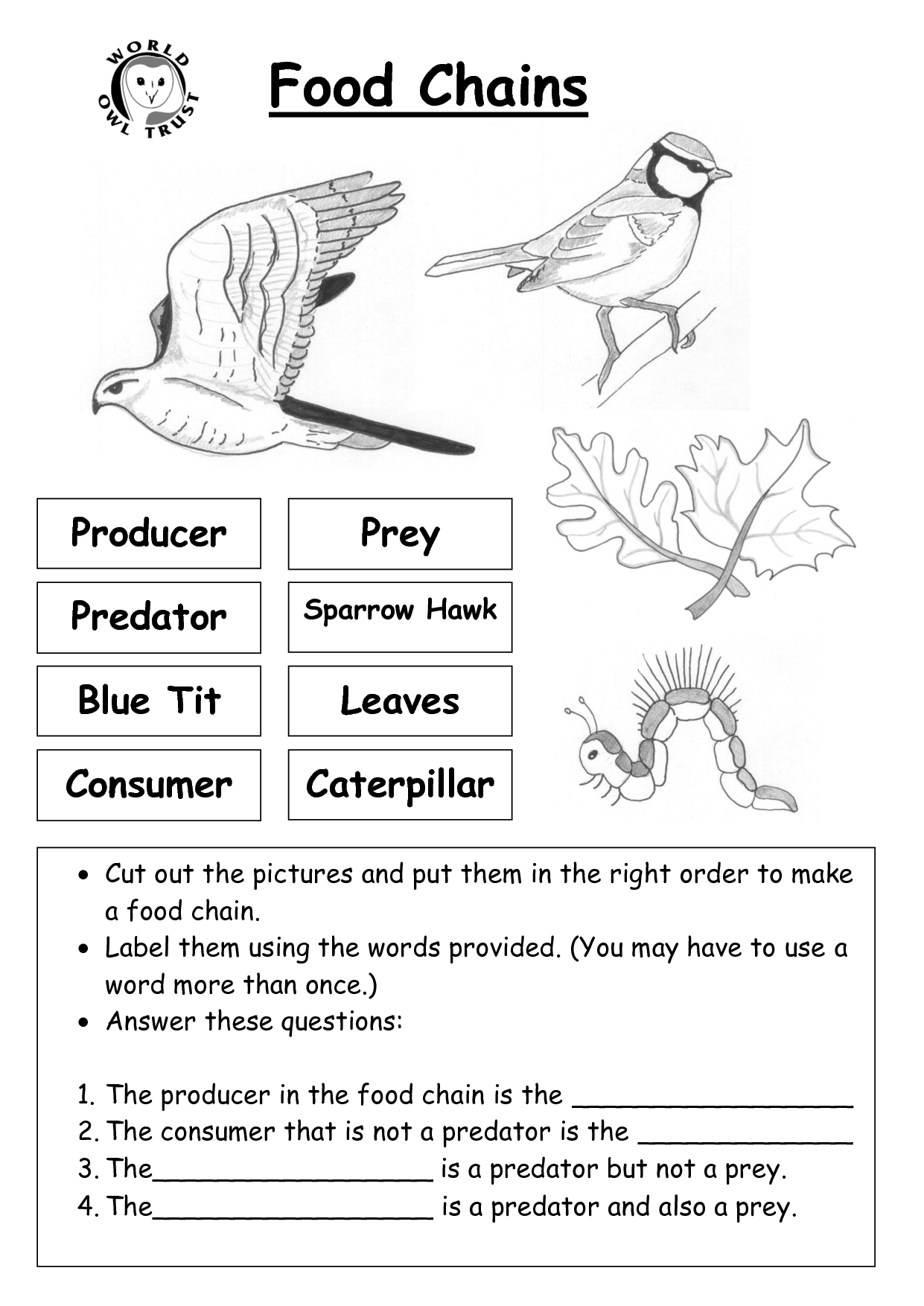
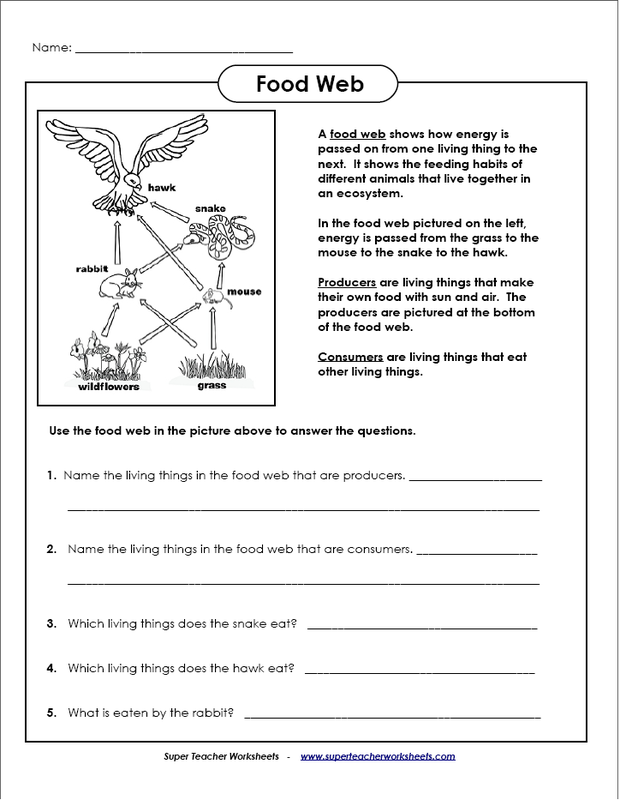
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms in an ecosystem where each organism consumes the one below it and is in turn consumed by the one above it, depicting the flow of energy and nutrients from one level to another. This concept helps understand the interconnectedness of different species and their roles in maintaining the balance of an ecosystem.
What are the different components of a food chain?
The different components of a food chain include producers (plants and algae), primary consumers (herbivores that eat the producers), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat the primary consumers), and sometimes tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat the secondary consumers). Additionally, decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil for producers to use, completing the food chain cycle.
How do organisms in a food chain interact with each other?
Organisms in a food chain interact with each other through the transfer of energy and nutrients. Producers, such as plants, convert sunlight into food through photosynthesis, which is then consumed by primary consumers, such as herbivores. Secondary consumers, like carnivores, then feed on the primary consumers, and so on. This transfer of energy and nutrients between organisms creates a flow of resources within the ecosystem, ultimately supporting the survival and functioning of each organism in the food chain.
What role do producers play in a food chain?
Producers play a crucial role in a food chain as they are the organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, and serve as the primary source of energy for the rest of the ecosystem. They convert sunlight and nutrients into organic compounds that are then consumed by other organisms, ultimately supporting the entire food chain by providing energy and nutrients for consumers at higher trophic levels.
What is the significance of consumers in a food chain?
Consumers play a crucial role in a food chain as they are organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms. They help regulate the population size of prey species and influence the structure of ecosystems by affecting the abundance of other species. Consumers also contribute to the transfer of energy and nutrients throughout the food chain, ultimately sustaining the entire ecosystem. Their interactions with other organisms help maintain a balance in nature and ensure the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
What are the different types of consumers in a food chain?
Consumers in a food chain can be classified into three main categories: primary consumers or herbivores, which feed directly on producers (plants); secondary consumers or carnivores, which feed on the herbivores; and tertiary consumers or top predators, which are at the top of the food chain and feed on other carnivores. Additionally, omnivores are consumers that feed on both plants and animals, while scavengers and decomposers play important roles in ecological systems by consuming dead organisms and breaking down organic matter.
How do decomposers contribute to a food chain?
Decomposers contribute to a food chain by breaking down dead organic matter into nutrients that can be recycled back into the ecosystem. This process helps to sustain the flow of energy and nutrients by releasing essential elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus back into the environment, which can then be absorbed by plants and other organisms higher up in the food chain, completing the cycle of life.
What is the concept of energy transfer in a food chain?
The concept of energy transfer in a food chain refers to the process of energy moving from one organism to another as they consume and are consumed by each other in a linear sequence. In a food chain, energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy by producers (plants) through photosynthesis. This energy is then passed on to consumers (herbivores) when they eat the producers, and further transferred to higher-level consumers (carnivores) when they eat the herbivores. This flow of energy through the food chain is crucial for sustaining life and maintaining balance in ecosystems.
How does the food chain illustrate the concept of interdependence?
The food chain illustrates the concept of interdependence by showing how different organisms rely on one another for survival. Each organism in the chain depends on another for food, and the chain demonstrates the interconnectedness of all living things in an ecosystem. For example, plants rely on sunlight and nutrients from the soil, herbivores rely on plants for food, and carnivores rely on herbivores for food. If one part of the food chain is disrupted, it can have cascading effects on other organisms, highlighting the interdependence that exists within ecosystems.
What are some examples of food chains in different ecosystems?
In a forest ecosystem, a common food chain includes plants (producers) being eaten by insects (consumers), which are then consumed by birds (predators). In a grassland ecosystem, the food chain may consist of grass (producer) being consumed by herbivores like zebras (primary consumers), which are then preyed upon by lions (top predators). In a marine ecosystem, algae (producer) can be eaten by small fish (consumers), which are then preyed upon by larger fish (predators), such as sharks. These examples demonstrate the interconnected relationship between different organisms in various ecosystems through the transfer of energy along the food chain.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments