Food Chain Worksheets Ecosystems
Food chain worksheets are incredibly useful resources for students learning about ecosystems. They provide a structured and organized way for learners to understand the intricate relationships between organisms within a specific environment. By focusing on the entity and subject of food chains, these worksheets engage students in activities that reinforce their understanding of how energy flows and nutrients are transferred from one organism to another in different ecosystems.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
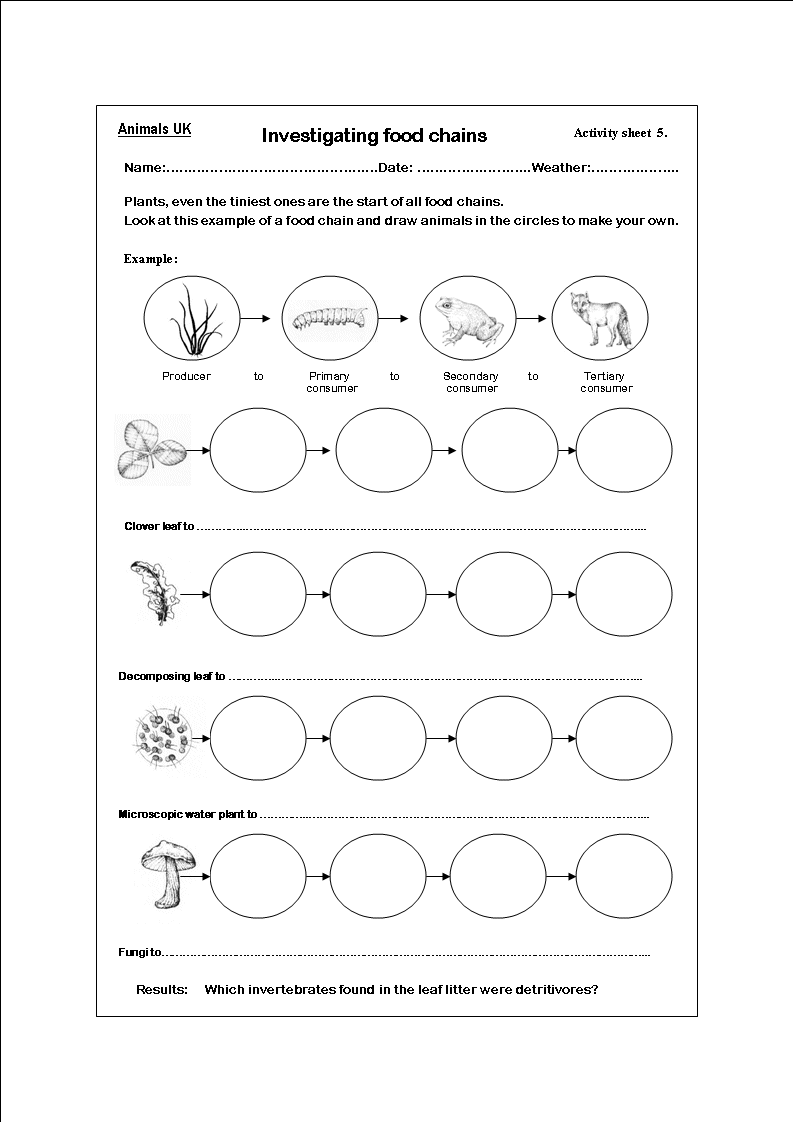
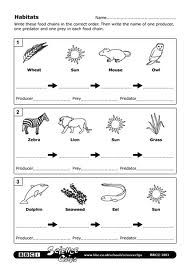
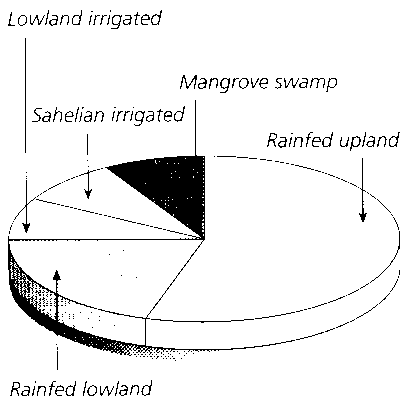
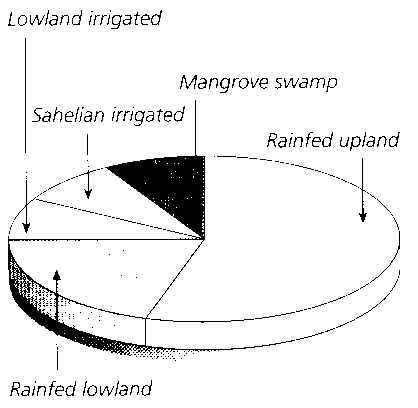
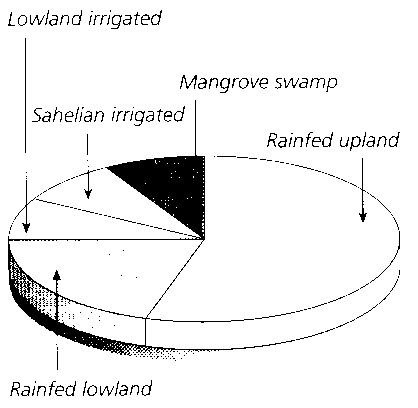
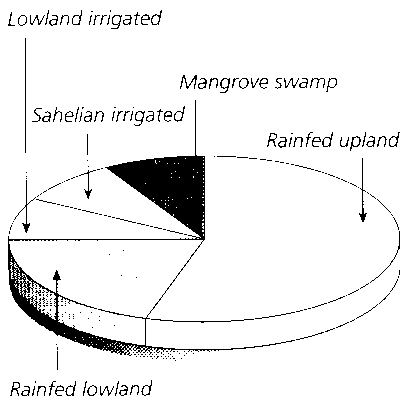
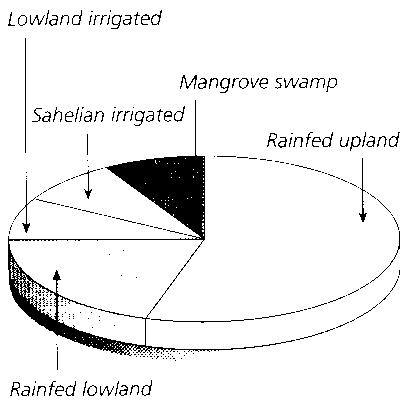
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each organism is consumed by the next organism in the chain, transferring energy and nutrients from one organism to another in an ecosystem. It illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients through different trophic levels, starting with producers (plants), then primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on, culminating with apex predators at the top of the chain.
What are producers in a food chain?
Producers in a food chain are organisms that are capable of photosynthesis, such as plants, algae, and certain bacteria. They are able to convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and serve as the foundation of the food chain by producing organic compounds that are consumed by other organisms in higher trophic levels.
Give an example of a primary consumer.
An example of a primary consumer is a rabbit that feeds on plants and grass in a grassland ecosystem.
Explain the role of decomposers in a food chain.
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food chain by breaking down dead organic matter such as plants and animals into simpler substances. Through this process of decomposition, they release nutrients back into the ecosystem, which can then be utilized by producers like plants to grow. Essentially, decomposers help recycle nutrients and organic matter, ensuring the sustainability and balance of the food chain and ecosystem overall.
What is a trophic level?
A trophic level is a hierarchical level in an ecosystem, indicating an organism's position in a food chain. Organisms that share the same trophic level have a similar function in the transfer of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem. The trophic level of an organism is determined by its feeding behavior and how it obtains energy.
Define herbivore.
An herbivore is an organism that primarily feeds on plants and vegetation for its nutritional needs. This dietary choice distinguishes herbivores from carnivores and omnivores, which primarily consume meat and a combination of both plant and animal matter, respectively. Herbivores play a vital role in ecosystems by helping regulate plant populations and nutrient cycling.
How does energy flow through a food chain?
Energy flows through a food chain in a linear fashion from one organism to another. It begins with producers, such as plants, that capture sunlight and convert it into energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to herbivores that eat the producers, and then to carnivores that eat the herbivores. As each organism consumes another, energy is passed along the chain until it eventually reaches decomposers that break down dead organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the environment to start the cycle over again.
Describe the relationship between predators and prey in a food chain.
The relationship between predators and prey in a food chain is one of interdependence, where predators rely on consuming prey for food to survive, while prey serve as a food source for predators. This dynamic interaction is crucial for maintaining a balance in the ecosystem, as predation helps control the population of prey species, preventing overpopulation, and ultimately promoting the health and stability of the ecosystem.
What happens when there is a disruption in a food chain?
When there is a disruption in a food chain, it can have far-reaching consequences on the entire ecosystem. The imbalance caused by the disruption can lead to overpopulation of certain species, decline in others, and potential collapse of the food chain. This can result in a cascade effect where the ecosystem struggles to maintain its equilibrium, affecting biodiversity, populations, and overall ecosystem health.
Explain the concept of a food web.
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that shows the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. It consists of multiple organisms linked together based on who eats whom in order to survive. Each organism in a food web is both a predator (consumer) and prey (food source), demonstrating the interconnectedness and interdependence of different species within an ecosystem. This intricate web illustrates the relationships and dependencies among various organisms, highlighting the balance and dynamics of energy exchange in nature.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments