Food Chain Worksheet.pdf
Worksheets are a valuable educational tool that help reinforce learning and foster engagement in a wide range of subjects. From math to science, worksheets provide a structured and interactive way for students to practice and apply their knowledge. If you are an educator or a parent looking for a comprehensive and effective resource to teach about food chains, this Food Chain Worksheet is precisely what you need.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheet 3rd Grade
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Chain Vocabulary Worksheet
- Free Printable Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Chain Worksheet and Answers
- Producers Consumers and Decomposers Worksheet
- Food Chain Printable Worksheets
- Food Chain Worksheets Answers for BrainPOP
- Desert Food Web Worksheet
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
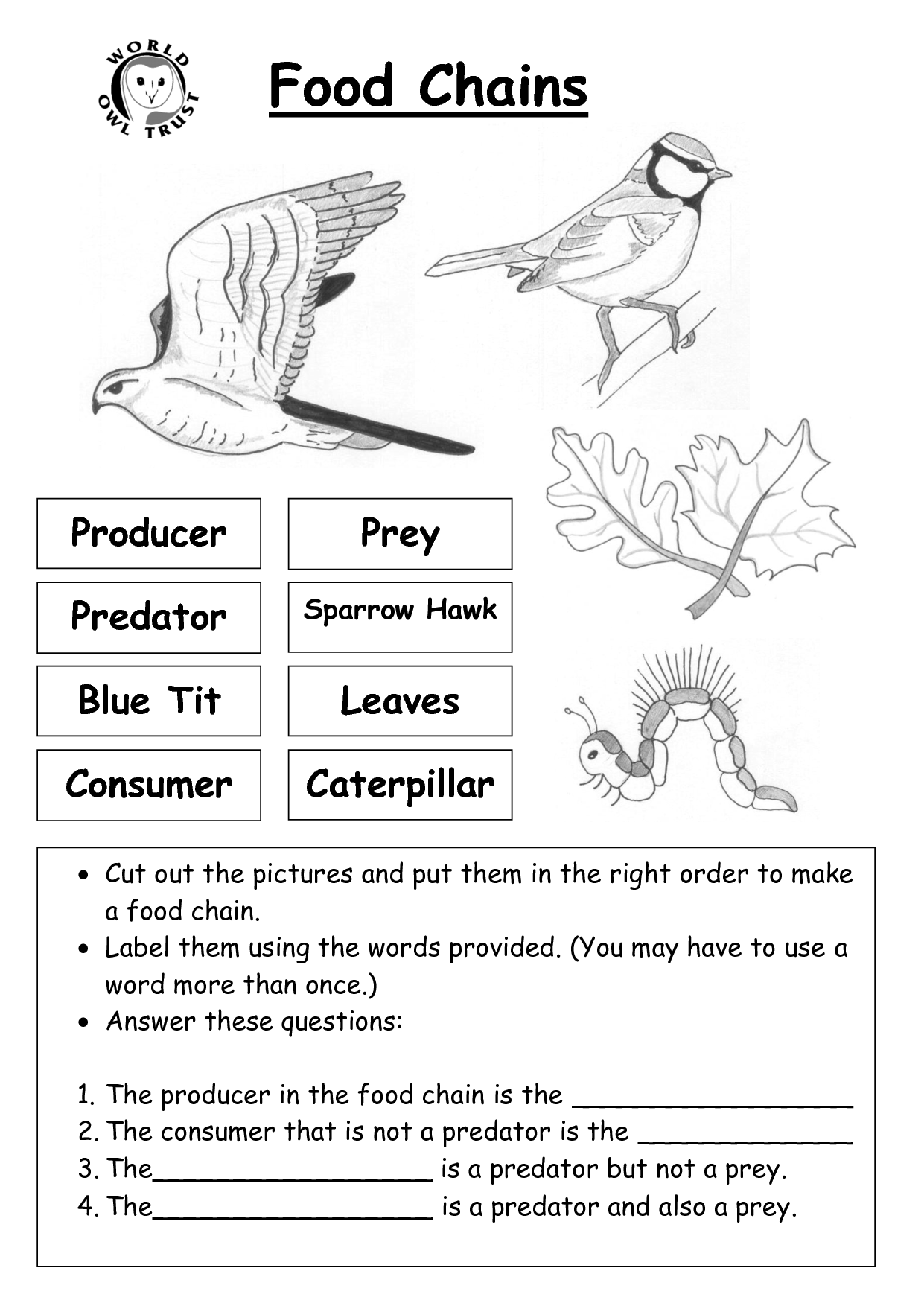
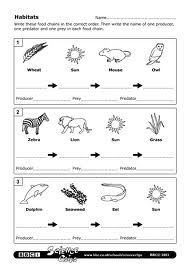
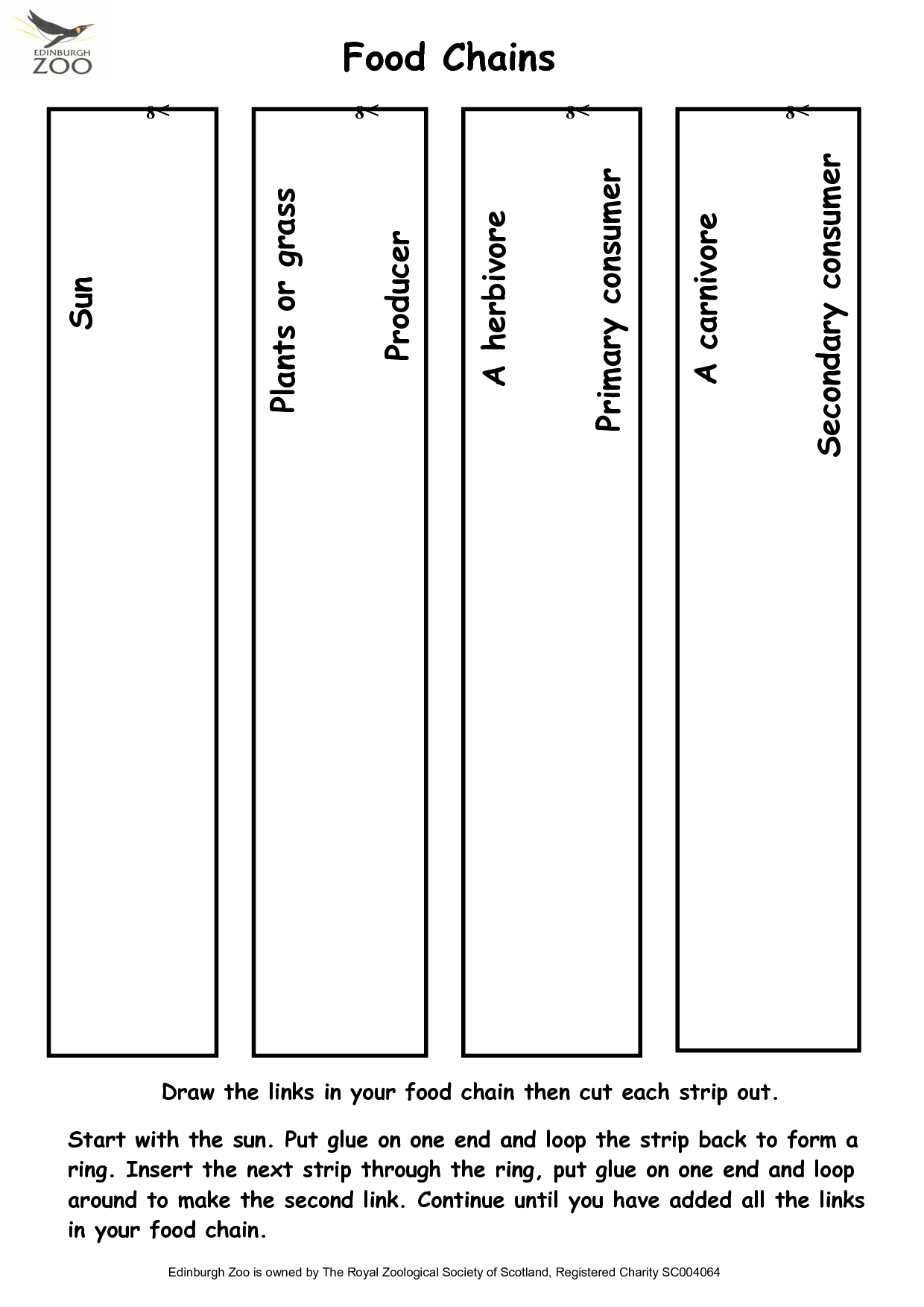
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a series of linked feeding relationships in an ecosystem, where organisms transfer energy by consuming and being consumed by others. It starts with producers, such as plants, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores then eat the producers, followed by carnivores that eat the herbivores. Decomposers break down the remains of all organisms, returning nutrients to the soil. Food chains show the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem.
Describe the role of producers in a food chain.
Producers play a crucial role in a food chain as they are responsible for converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. These organisms, such as plants and algae, are able to manufacture their own food, providing a source of energy for other organisms in the ecosystem. Producers are the primary source of nutrients for all other organisms in the food chain, serving as the foundation upon which the entire ecosystem depends for sustenance and energy.
Explain the difference between herbivores and carnivores.
Herbivores are animals that primarily consume plants and plant-based foods as their main source of nutrition, while carnivores are animals that primarily feed on other animals as their main source of nutrition. This fundamental difference in diet shapes their digestive systems, teeth, and hunting or foraging strategies to best suit their preferred food sources, highlighting the contrasting evolutionary adaptations between the two dietary groups.
What are decomposers, and what is their role in a food chain?
Decomposers are organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, into simpler substances. Their role in a food chain is to recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem by breaking down organic matter, which helps to enrich the soil and provides nutrients for plants to grow. Without decomposers, dead matter would accumulate, and essential nutrients would not be released back into the environment, disrupting the balance of the food chain.
Give an example of a complete food chain, including producers, consumers, and decomposers.
An example of a complete food chain is as follows: grass (producer) is consumed by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is in turn eaten by a frog (secondary consumer), and the frog is decomposed by bacteria and fungi (decomposers). This exemplifies the flow of energy within an ecosystem, starting with producers converting sunlight into energy and nutrients, consumers feeding on producers, and decomposers breaking down dead organisms to recycle nutrients back into the environment.
How do primary consumers obtain their energy?
Primary consumers obtain their energy by consuming producers (plants or algae) through a process called herbivory. They feed on these plants and algae to obtain the nutrients and energy needed for their survival and growth. By consuming plants, primary consumers transfer the energy stored in plants to themselves, forming the basis of the food chain in ecosystems.
Describe the relationship between predators and prey in a food chain.
Predators and prey have a direct relationship in a food chain where predators hunt and consume the prey. Predators rely on the prey for their survival by feeding on them, regulating their populations, and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Prey, on the other hand, have evolved different strategies to avoid being caught by predators, such as camouflage, speed, or defensive mechanisms. This dynamic interaction between predators and prey plays a crucial role in shaping the structure and functioning of ecosystems.
Explain how energy flows through a food chain.
Energy flows through a food chain in a unidirectional manner, starting from the sun and moving through various organisms. Plants absorb sunlight and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores then consume plants, transferring this stored energy into their bodies. Carnivores, in turn, consume herbivores, passing on the energy further up the chain. At each trophic level, energy is lost as heat through metabolic processes, limiting the amount of energy available to higher-level consumers. Ultimately, energy is eventually lost as heat at each trophic level, highlighting the importance of maintaining a balanced ecosystem for energy sustainability.
What happens if one part of a food chain is disrupted or removed?
If one part of a food chain is disrupted or removed, it can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, if a predator is removed, the prey population may increase dramatically, leading to overgrazing or other negative impacts on the environment. On the other hand, if a primary producer is disrupted, it can affect the entire chain up to the top predators. This disruption can lead to imbalances in population sizes, changes in species composition, and overall ecosystem instability.
Why is it important to maintain a balanced food chain in an ecosystem?
Maintaining a balanced food chain in an ecosystem is crucial because it helps to ensure the stability and sustainability of the ecosystem. Each organism in a food chain plays a specific role in controlling the population of species below it, which helps to prevent overpopulation of certain species and ensure that resources are distributed equitably. Disruption of the food chain can lead to cascading effects, such as population explosions of certain species or the decline of others, ultimately destabilizing the entire ecosystem. A balanced food chain is essential for maintaining biodiversity, promoting ecosystem resilience, and supporting the overall health of the environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments