Exponential Graph Worksheet
Are you in need of a comprehensive and user-friendly resource to help your students understand exponential graphs? Look no further than our Exponential Graph Worksheet. Designed specifically for middle and high school mathematics classes, this worksheet provides a perfect blend of theory and practice to engage students and reinforce their understanding of this important mathematical concept.
Table of Images 👆
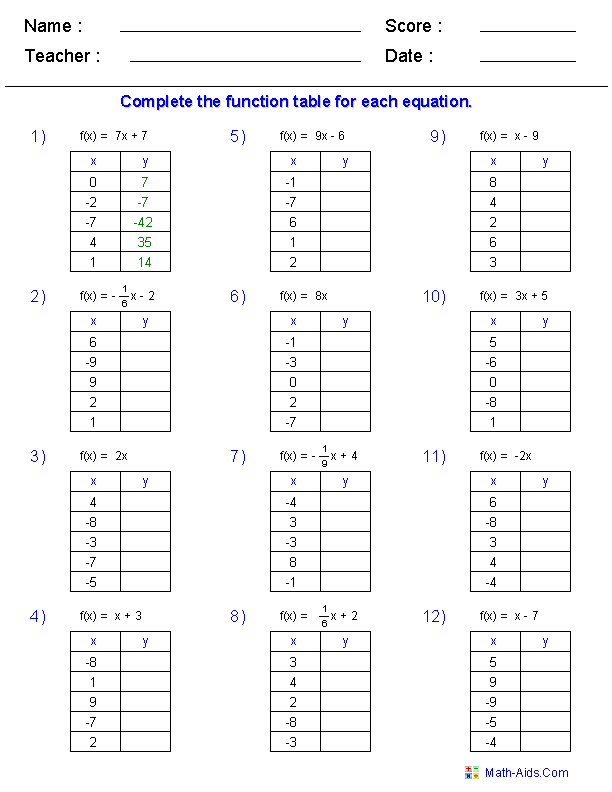
- Graph Function Table Worksheet
- Real Life Examples Exponential Function Graph
- Exponential Growth Worksheets Free Printable
- Function Tables Worksheets
- Exponential Smoothing Formula Example
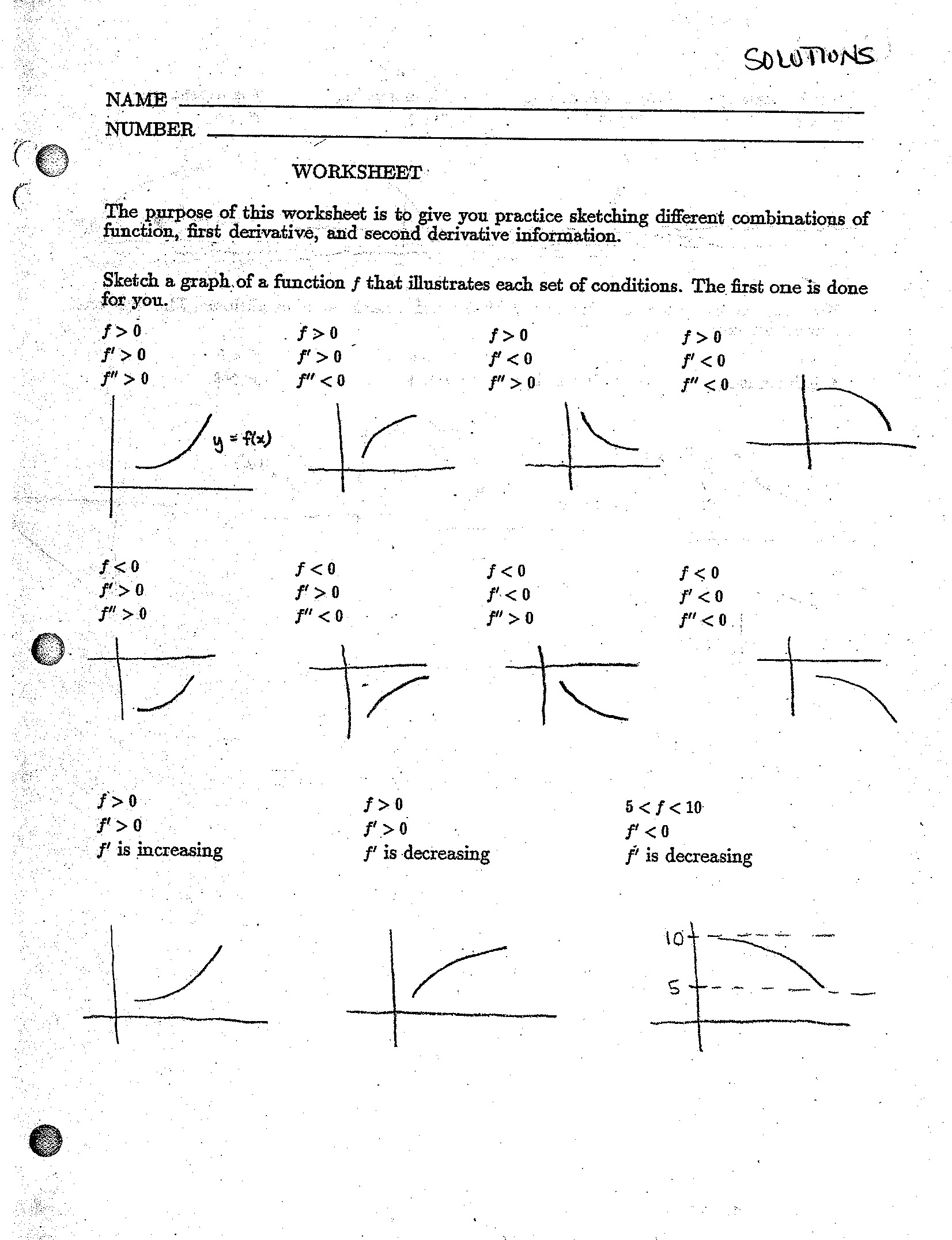
- Function Transformation Worksheet
- Linear or Nonlinear Graph
- Coordinate Plane Graph Paper
- Math Paper Template
- Glencoe Algebra 2 Answer Key Chapter 4
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an exponential graph?
An exponential graph is a type of graph where the rate of change of the dependent variable (y-axis) is proportional to the variable itself. In other words, as the independent variable (x-axis) increases, the dependent variable grows or decays at an increasing rate. Exponential graphs are characterized by a curve that either continuously rises or falls, rather than forming a straight line.
How does an exponential graph differ from a linear graph?
An exponential graph shows a rapid increase in one direction as opposed to a linear graph that shows a constant rate of change in a straight line. In an exponential graph, the y-values grow or decay at an increasing rate, often represented by a curve, while in a linear graph, the y-values increase or decrease steadily and evenly along a straight line.
What is the general form of an exponential function equation?
The general form of an exponential function equation is given by y = a * b^x, where "a" is the initial value or y-intercept, "b" is the base of the exponential function, and "x" is the exponent.
How does the base value affect the shape of an exponential graph?
The base value in an exponential function determines the rate at which the function grows or decays. A base greater than 1 will lead to exponential growth, resulting in a steeply rising graph. Conversely, a base between 0 and 1 will lead to exponential decay, resulting in a graph that decreases rapidly. The base value also affects the location of the asymptote, with a base value of 1 having a horizontal asymptote at y=0.
What is the role of the exponent in an exponential function?
The exponent in an exponential function determines the rate at which the function grows or decays. It represents how many times the base number is multiplied by itself to produce the output value. Positive exponents result in exponential growth, while negative exponents lead to exponential decay. The exponent is a crucial factor in determining the behavior and shape of an exponential function.
How can you identify the domain and range of an exponential graph?
To identify the domain and range of an exponential graph, note that the domain is all real numbers, as exponential functions are defined for all x-values. The range depends on whether the exponential function is increasing or decreasing. For a function where a > 1 (exponential growth), the range will be all positive real numbers, while for a function where 0 < a < 1 (exponential decay), the range will be all positive real numbers greater than 0. Remember that in both cases, the function will approach but never reach zero and will increase or decrease without bound.
What are the key characteristics of an exponential graph?
An exponential graph is characterized by a curve that steadily increases or decreases at an accelerating rate as it moves along the x-axis. It has a constant ratio between the y-values at successive points, and the graph either increases exponentially if the base of the exponential function is greater than 1 or decreases exponentially if it is between 0 and 1. Exponential graphs never intersect the x-axis, and they may have a horizontal asymptote or increase towards positive infinity.
How can you determine the y-intercept of an exponential graph?
To determine the y-intercept of an exponential graph, you need to find the point where the graph intersects the y-axis. The y-intercept occurs at the point where x=0. By substituting x=0 into the exponential function and solving for y, you will find the y-coordinate of the y-intercept. This y-coordinate represents the value of the function when x=0, which is the point where the graph intersects the y-axis.
What is exponential growth?
Exponential growth is a type of growth pattern in which a quantity increases at a constant rate per unit of time, resulting in rapid and accelerating growth. In exponential growth, the growth rate itself is proportional to the current value of the quantity, leading to a continuously compounding increase over time. This type of growth is often seen in natural systems, technology, and financial investments.
What are some real-life applications of exponential graphs?
Exponential graphs are commonly used in fields such as biology to model population growth, in finance to analyze compound interest, in physics to describe radioactive decay, and in telecommunications to represent signal strength over distance. Additionally, exponential growth and decay models are used in epidemiology to predict the spread of diseases and in economics to understand inflation and deflation. Overall, exponential graphs have a wide range of applications across various disciplines due to their ability to depict rapid and continuous change over time.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments