Energy Flow through an Ecosystem Worksheet Answers
Are you a science teacher searching for an effective tool to assess your students' understanding of energy flow in ecosystems? Look no further! We have compiled a set of well-crafted worksheet answers that focus on the entity and subject matter of energy flow through an ecosystem. With these accurate and concise answers, you can easily evaluate your students' comprehension of this crucial ecological concept.
Table of Images 👆
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is energy flow in an ecosystem?
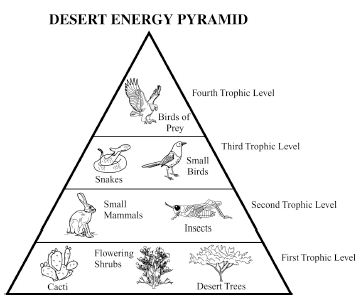
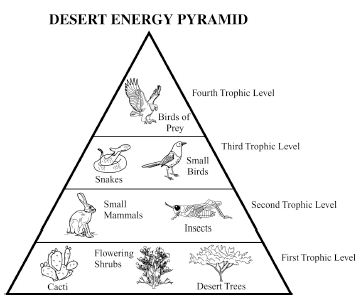
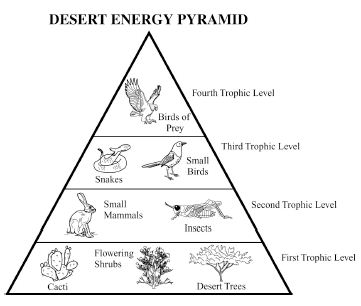
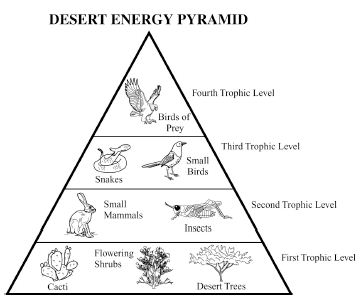
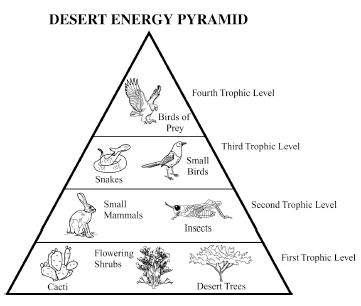
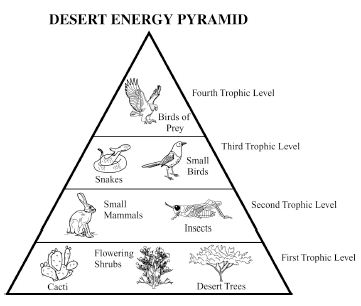
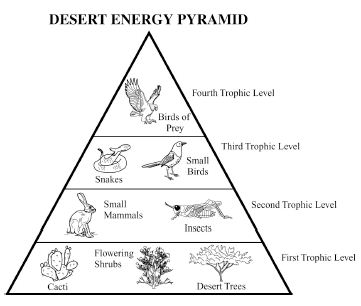
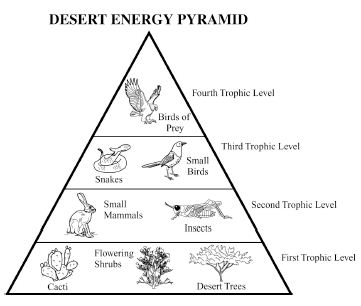
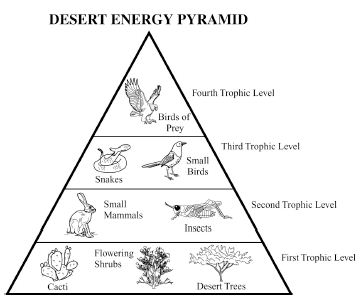
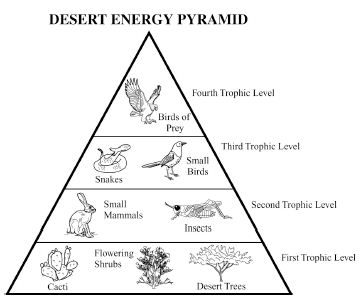
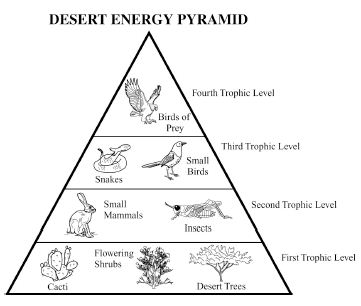
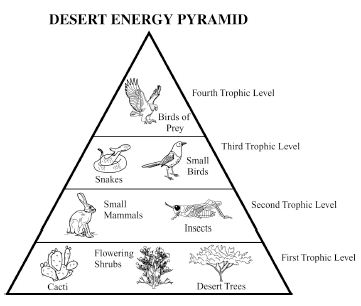
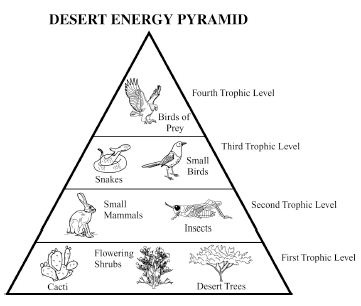
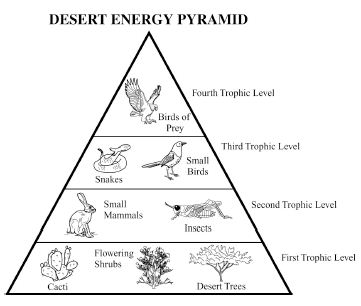
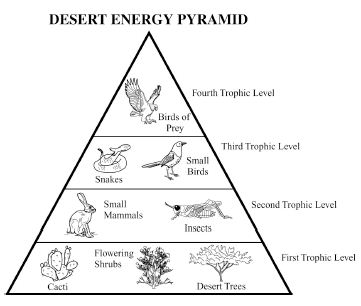
Energy flow in an ecosystem refers to the transfer of energy from one organism to another through a series of feeding relationships. It begins with producers, such as plants, converting sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then passed on to consumers, like herbivores, then to carnivores, and finally to decomposers. As each organism consumes another, energy is transferred along the food chain. However, not all energy is passed on; some is lost as heat at each trophic level. Overall, energy flow is crucial for sustaining life within an ecosystem and is a key component of the nutrient cycle.
How does energy enter an ecosystem?
Energy enters an ecosystem primarily through sunlight, which is captured by plants during the process of photosynthesis. Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, which is then passed on to other organisms when they are consumed. This energy flow continues as organisms are eaten by other organisms, transferring energy throughout the ecosystem in a complex food web. Ultimately, energy is constantly cycling and being redistributed within the ecosystem to sustain life processes.
What is a producer in an ecosystem?
A producer in an ecosystem is an organism, usually a plant, that produces organic compounds through photosynthesis using sunlight as an energy source. These organic compounds serve as a food source for other organisms in the ecosystem, forming the base of the food chain. Producers play a vital role in converting energy from the sun into a form that can be utilized by other organisms in the ecosystem.
How do producers obtain energy?
Producers obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis, in which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. This glucose serves as the primary source of energy for the cells of these organisms, allowing them to carry out essential biological functions and sustain their growth and reproduction.
What is a consumer in an ecosystem?
A consumer in an ecosystem is an organism that obtains energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms. Consumers play a crucial role in the food chain by consuming producers (plants or algae) or other consumers (animals) to obtain the energy needed for growth, metabolism, and reproduction. They are categorized based on their position and relationship in the food chain, such as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and decomposers.
What is the difference between a herbivore and a carnivore?
The main difference between a herbivore and a carnivore lies in their dietary preferences. Herbivores primarily consume plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and grains, while carnivores mainly eat meat and other animal products. This distinction impacts their digestive systems, dental structures, and overall behavior in terms of hunting or foraging for food.
How do consumers obtain energy?
Consumers obtain energy through various sources such as electricity from power plants, natural gas for heating and cooking, gasoline for vehicles, and renewable sources like solar or wind energy. Energy can be purchased from utility companies, obtained through self-generation methods like solar panels, or acquired indirectly through products and services that require energy for production and operation. Overall, consumers access energy through a combination of sources that meet their needs and preferences.
What is a decomposer in an ecosystem?
A decomposer in an ecosystem is an organism that breaks down dead organisms and organic matter into simpler substances, releasing nutrients back into the environment. These organisms play a crucial role in the recycling of nutrients, facilitating the decay and decomposition process that helps sustain the overall balance of the ecosystem. Examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi, and certain insects.
What role do decomposers play in energy flow?
Decomposers play a crucial role in energy flow by breaking down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler compounds. Through this process of decomposition, energy stored in the organic matter is released and recycled back into the ecosystem. This enables nutrients to be returned to the soil, making them available for plants to grow and for other organisms to consume, ultimately sustaining the flow of energy through food webs and ecosystems.
How is energy lost in an ecosystem?
Energy is lost in an ecosystem through various processes such as heat loss during metabolic activities, inefficiency in energy transfer between trophic levels, and incomplete consumption of organisms by predators. When organisms consume food for energy, only a portion of that energy is assimilated and used for growth, movement, and reproduction, while the rest is lost as heat during biochemical reactions. As energy moves up the food chain, each trophic level utilizes only a fraction of the energy from the previous level, leading to further loss. This energy loss continues as organisms die and decompose, with decomposers releasing energy back into the environment in a form that is unusable for higher trophic levels.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments