Elementary Worksheets Plant Life
Are you searching for educational resources to help your elementary students learn about plant life? Look no further! Worksheets can be a valuable tool in engaging young learners and reinforcing key concepts. In this blog post, we will explore how worksheets can be a beneficial entity for teachers and students alike, providing a structured and interactive approach to learning about plant life.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. This crucial biological process not only produces food for the organism but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, making it essential for sustaining life on Earth.
How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil?
Plants obtain nutrients from the soil through their roots, which absorb water and minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are transported within the plant through vascular tissues, allowing them to be distributed to different parts of the plant for growth and development. The process of nutrient absorption is facilitated by root hairs, which increase the surface area for nutrient uptake, as well as mycorrhizal fungi that form symbiotic relationships with the plant roots to enhance nutrient absorption.
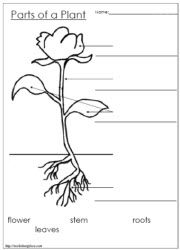
What is the purpose of roots in a plant?
The purpose of roots in a plant is to anchor the plant in the ground, absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and store food reserves. Additionally, roots help support the plant's above-ground structures and enable it to exchange gases with the soil.
Describe the process of pollination in plants.
Pollination is the process in which pollen from the male part of a flower (anther) is transferred to the female part (stigma) of the same or another flower, resulting in fertilization and seed production. This transfer can be facilitated by wind, water, or insects like bees and butterflies. Once pollen lands on the stigma, it travels down to the ovary where fertilization occurs, leading to the formation of seeds. Pollination is crucial for the reproduction of plants and the production of fruits and seeds.
What are the different parts of a flower and their functions?
A flower consists of several parts including petals, which attract pollinators; sepals, which protect the flower bud; stamen, the male reproductive organ producing pollen; pistil, the female reproductive organ containing the stigma, style, and ovary; stigma, receives pollen; style, supports the stigma; ovary, contains ovules that develop into seeds; and ovules, which contain the egg cells. Each part plays a crucial role in the reproduction process of the plant, from attracting pollinators to producing seeds for future generations.
Can plants reproduce asexually? If so, how?
Yes, plants can reproduce asexually through methods such as fragmentation, budding, or producing offspring from specialized plant parts such as roots, stems, or leaves. Fragmentation occurs when a plant's parts break off and develop into new individuals, while budding involves the development of new plants from small growths on the parent plant. Other methods include producing plantlets or bulbils that can grow into new plants without fertilization.
Explain the life cycle of a plant from seed to maturity.
A plant life cycle begins with a seed, which germinates when the conditions are right, such as moisture and warmth. The seed sprouts a root that anchors it and absorbs water and nutrients from the soil. Meanwhile, a shoot emerges, growing towards the sunlight. As the plant continues to grow, it develops leaves, flowers, and fruits through a process called photosynthesis where it converts sunlight into energy. Pollination occurs, leading to fertilization and seed formation within the fruits. Once mature, the plant produces seeds that fall to the ground, starting the cycle anew.
How do plants adapt to their environment?
Plants adapt to their environment through various mechanisms such as altering their physical structure (e.g. root depth, leaf size, and shape) to better capture sunlight or water, changing their reproductive strategies, developing defense mechanisms against predators or harsh conditions, and adjusting their growth and development in response to environmental cues like light, temperature, and water availability. Additionally, plants can form symbiotic relationships with other organisms like fungi or bacteria to enhance nutrient uptake or stress tolerance. Overall, plants exhibit a range of adaptations that allow them to survive and thrive in different ecological niches.
Describe the process of seed dispersal in plants.
Seed dispersal in plants is the method by which seeds are spread away from the parent plant to colonize new areas. This can be achieved through various mechanisms such as wind dispersal, where seeds are carried by the wind; animal dispersal, where seeds are eaten by animals and deposited elsewhere through their feces; water dispersal, where seeds are transported by bodies of water; and explosive dispersal, where seeds are forcefully expelled from the plant. Each method allows for seeds to reach new environments conducive to germination and growth, increasing the plant's chances of survival and reproduction.
What are some common examples of plants that grow in different habitats?
Some common examples of plants that grow in different habitats include cacti which thrive in arid deserts, mangroves that grow along coastal waters, ferns that can be found in moist forests, and succulents that flourish in dry environments like savannas. These diverse plants have adapted to their specific habitats through unique features and characteristics that allow them to survive and thrive in their respective environments.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments