Electromagnetic Waves Worksheet Answers 1
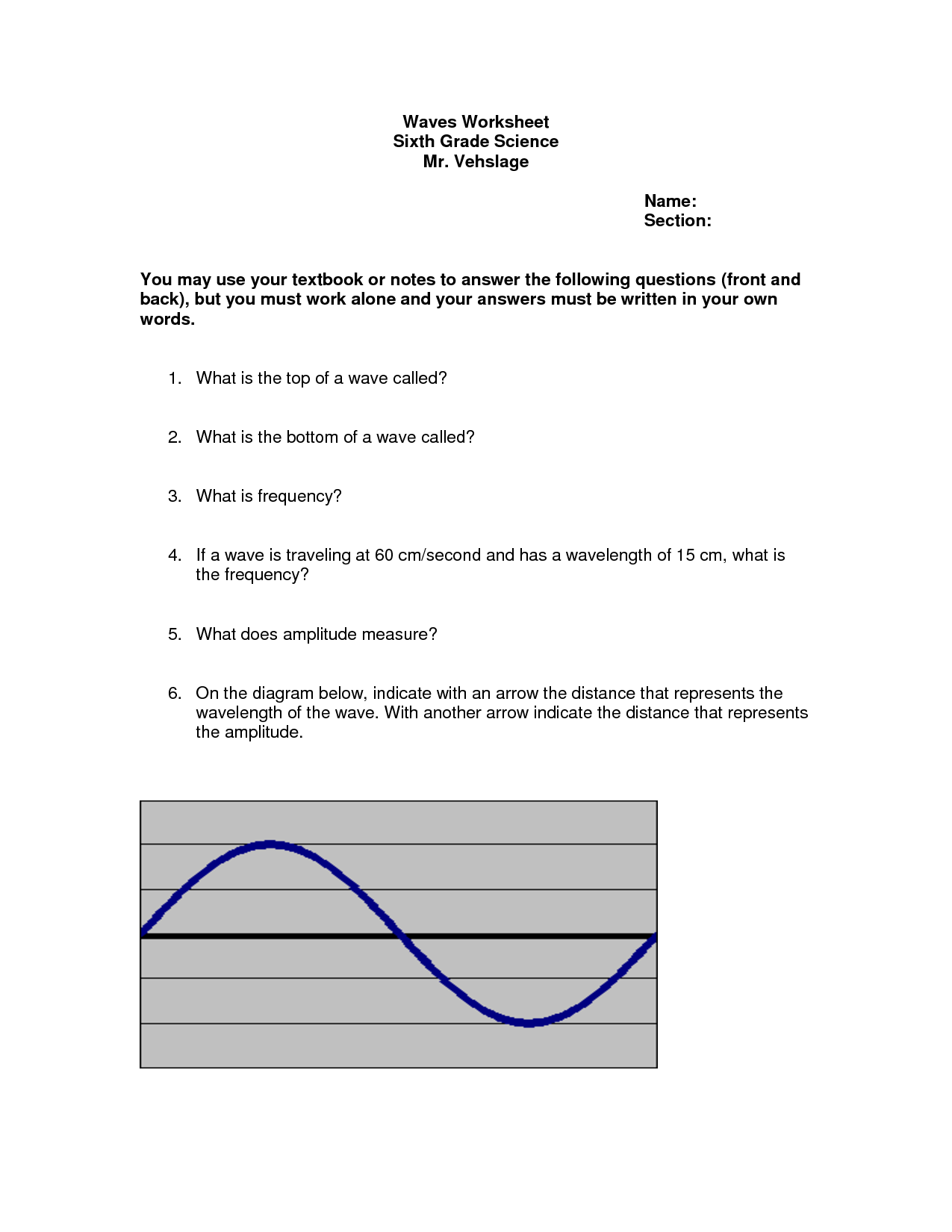
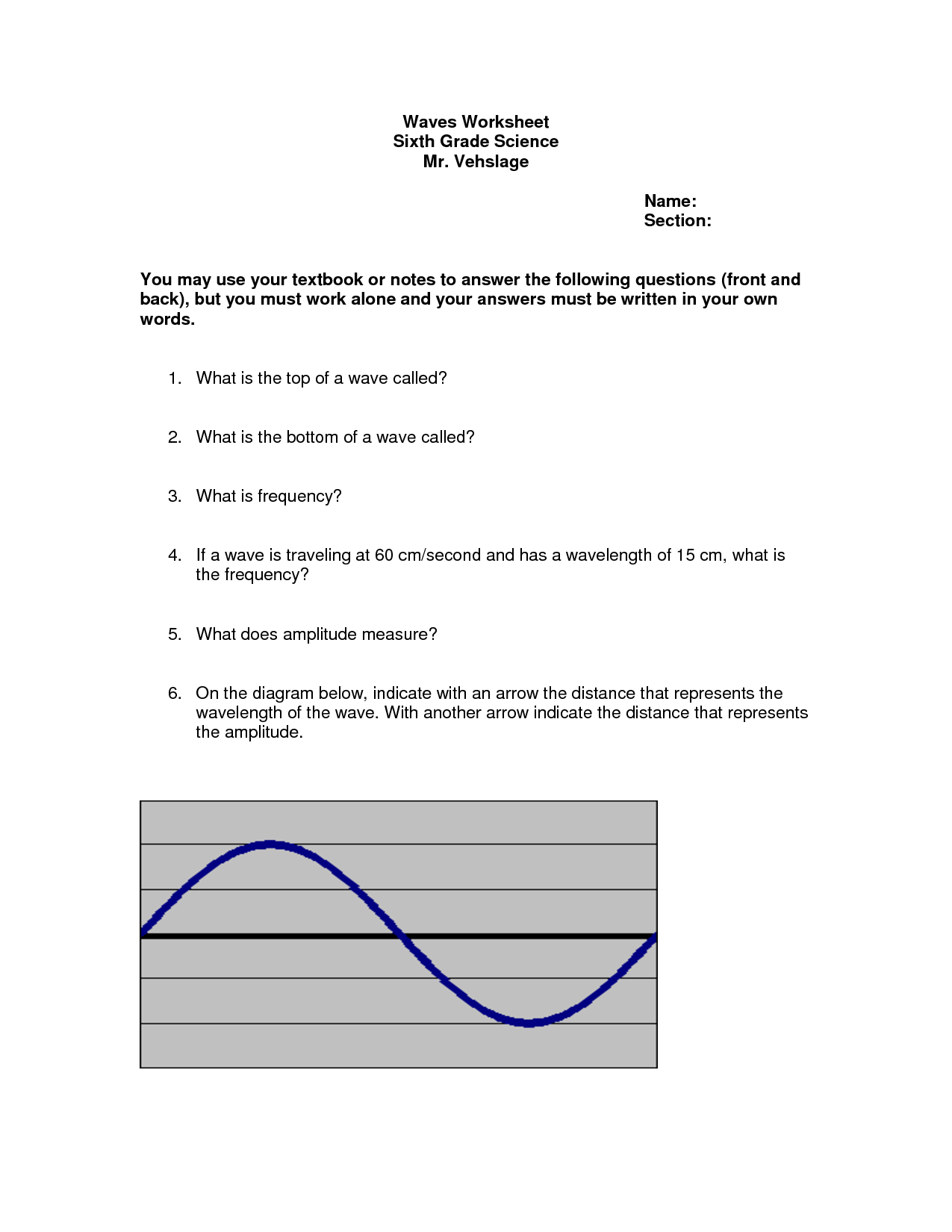
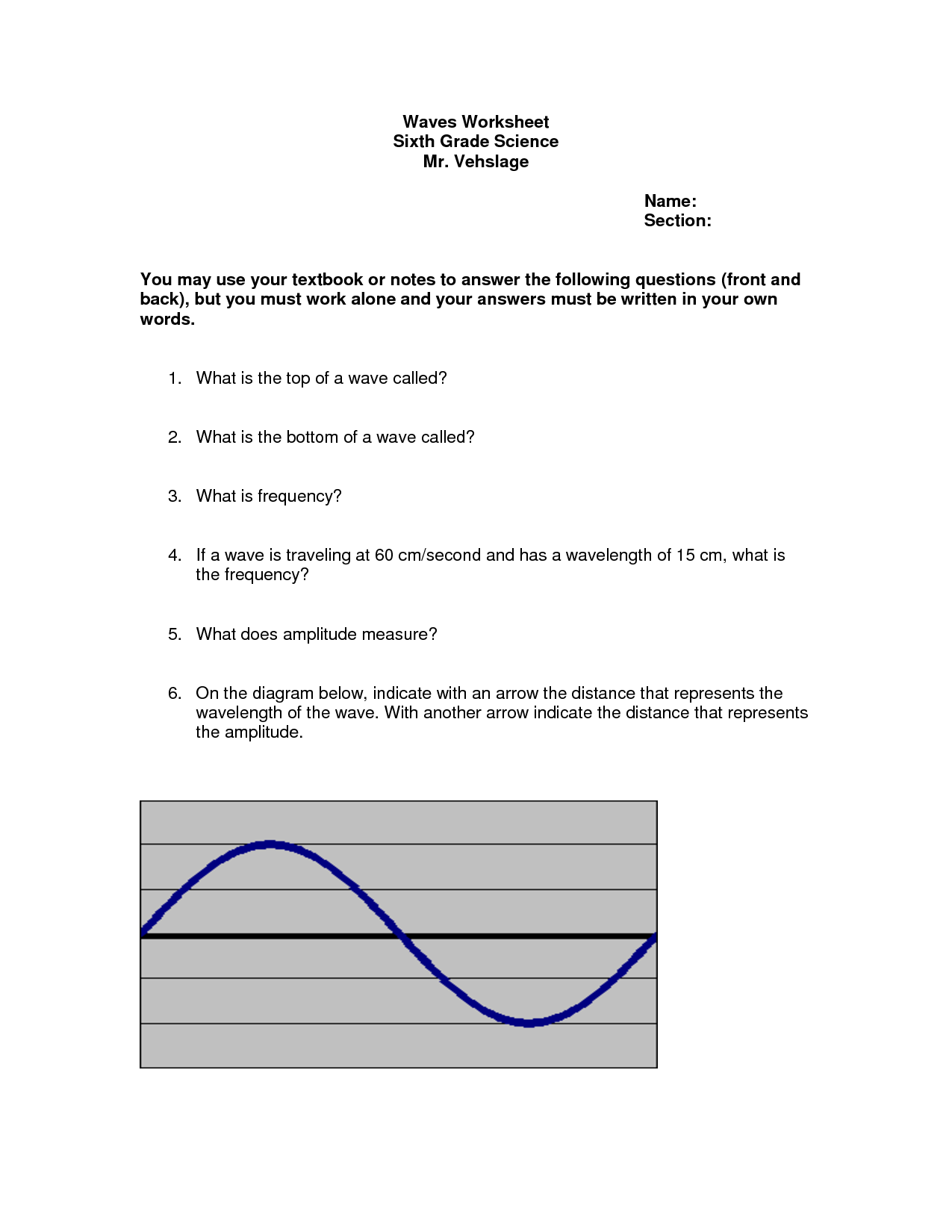
The electromagnetic waves worksheet provides a comprehensive review of the principles and characteristics of electromagnetic waves. This worksheet is designed for individuals who are studying or interested in physics and want to enhance their understanding of the properties and behavior of electromagnetic waves.
Table of Images 👆
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
- Waves & Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
- Speed Frequency Wavelength Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Video Worksheet Answer Key to Sound Waves
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Middle School
- Wave Properties Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, propagating through space at the speed of light. They include a wide range of frequencies, from radio waves to gamma rays, and are responsible for phenomena such as light, radio communication, and X-rays.
What are the different types of electromagnetic waves?
The different types of electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves vary in frequency and energy levels, with radio waves having the lowest frequency and energy, and gamma rays having the highest frequency and energy.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves?
The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second, which is equivalent to 186,282 miles per second.
How are electromagnetic waves generated?
Electromagnetic waves are generated when electrically charged particles, such as electrons, accelerate. This acceleration can occur in various ways, such as when an electric current flows through a wire or when an electron moves from one energy level to another in an atom. The changing electric field produced by the movement of these charged particles creates a magnetic field, which in turn generates electromagnetic waves that propagate through space.
How do electromagnetic waves propagate through space?
Electromagnetic waves propagate through space as a combination of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that self-generate and move through the vacuum at the speed of light. As these waves travel, they do not require a medium to oscillate through, which differentiates them from mechanical waves such as sound waves. The interaction between the changing electric and magnetic fields creates a self-sustaining wave that can travel vast distances, allowing electromagnetic waves to propagate through the vacuum of space.
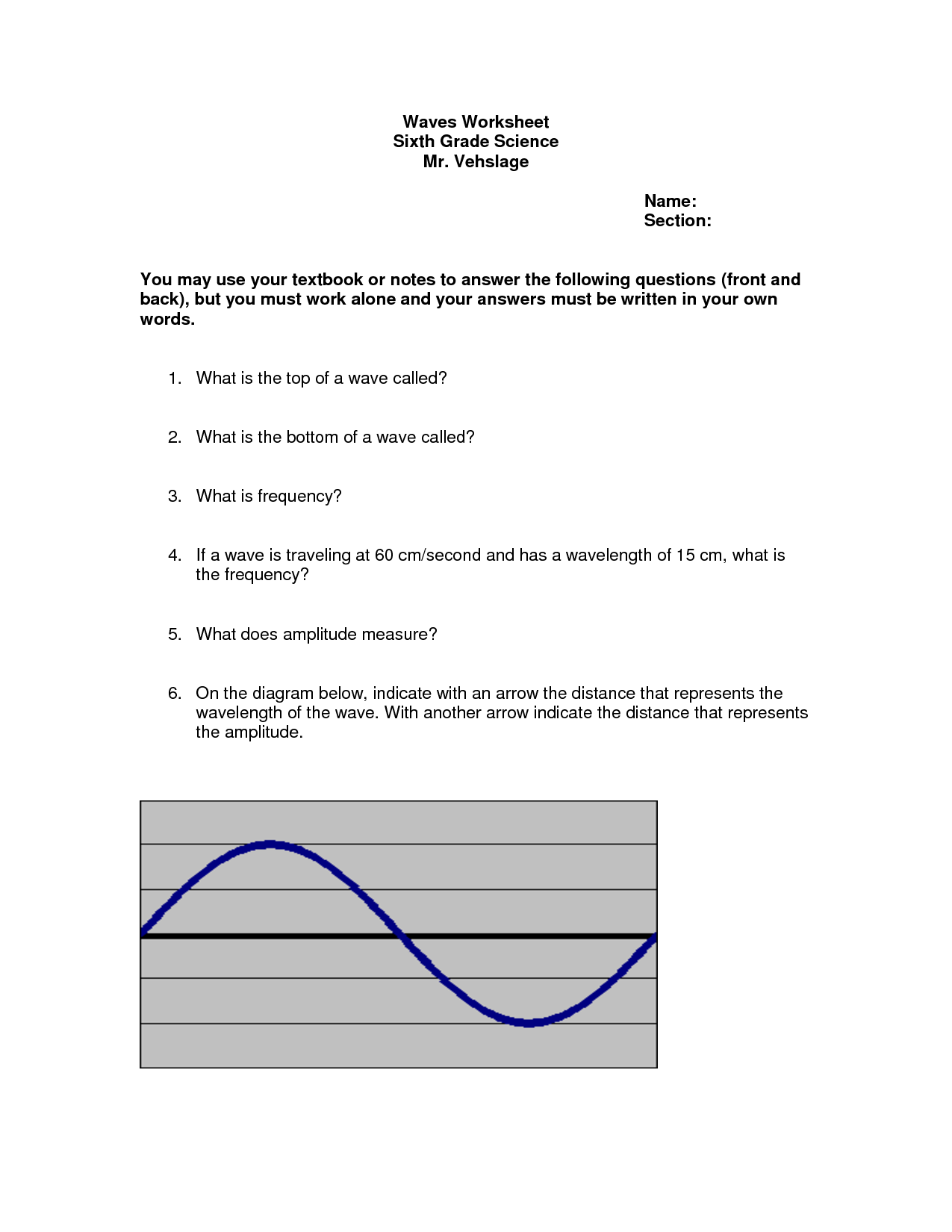
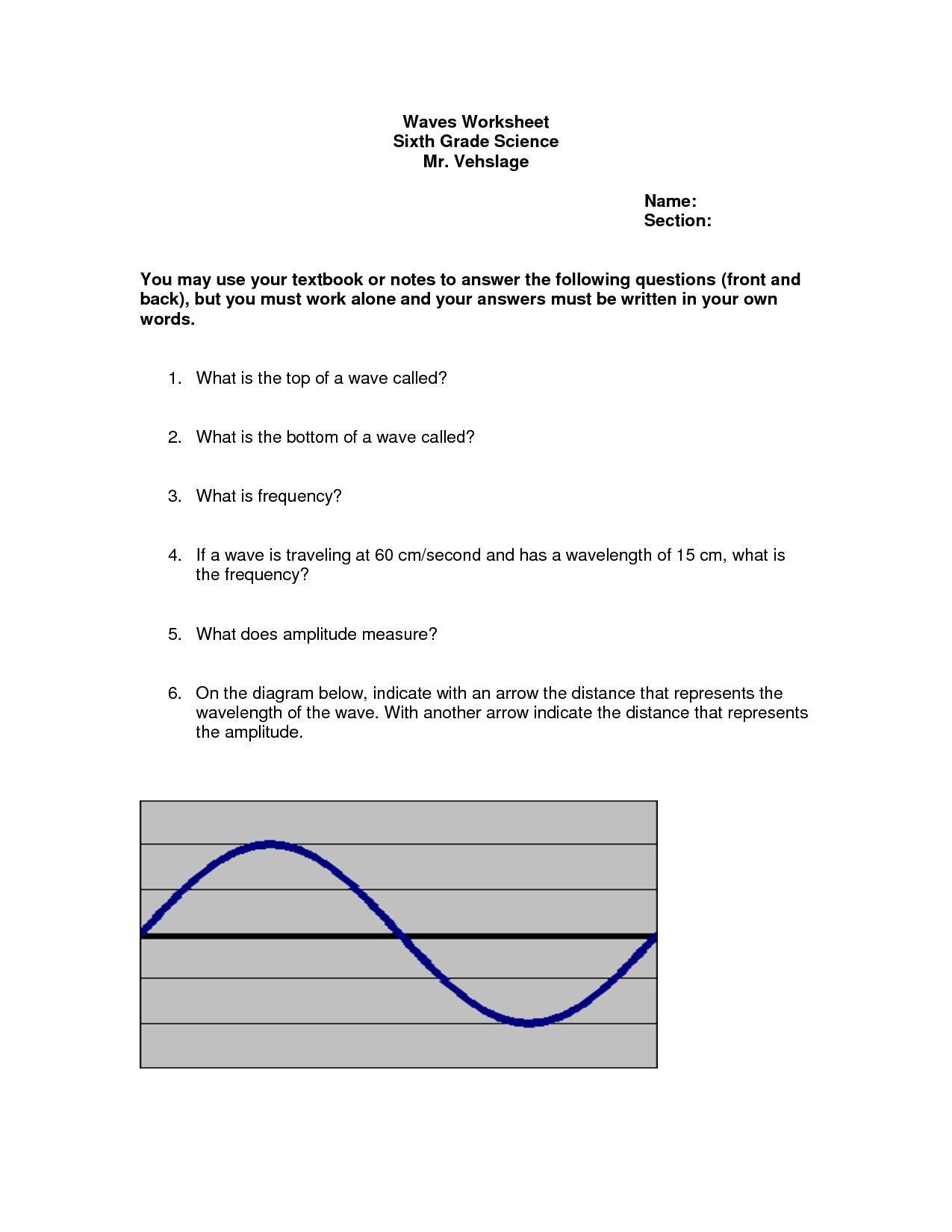
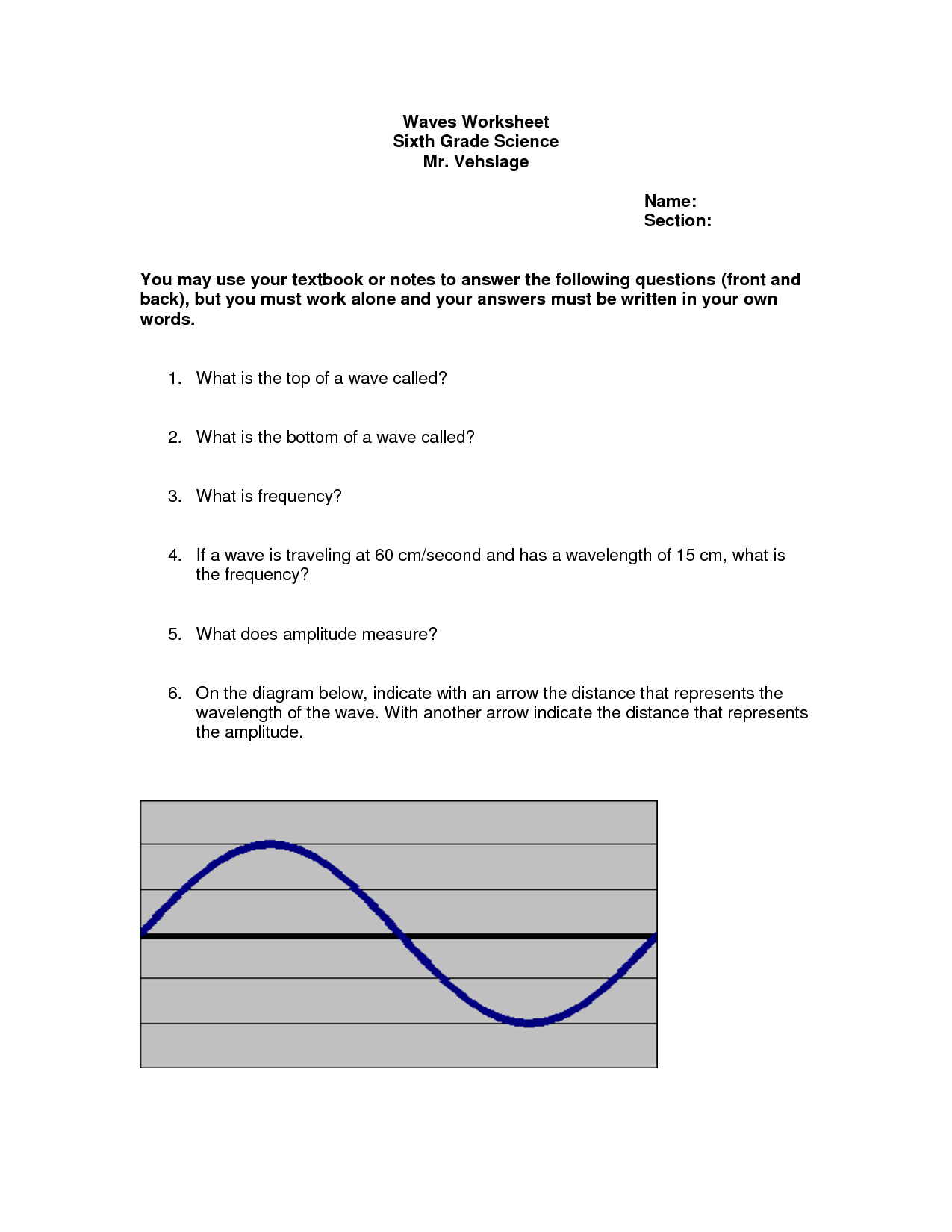
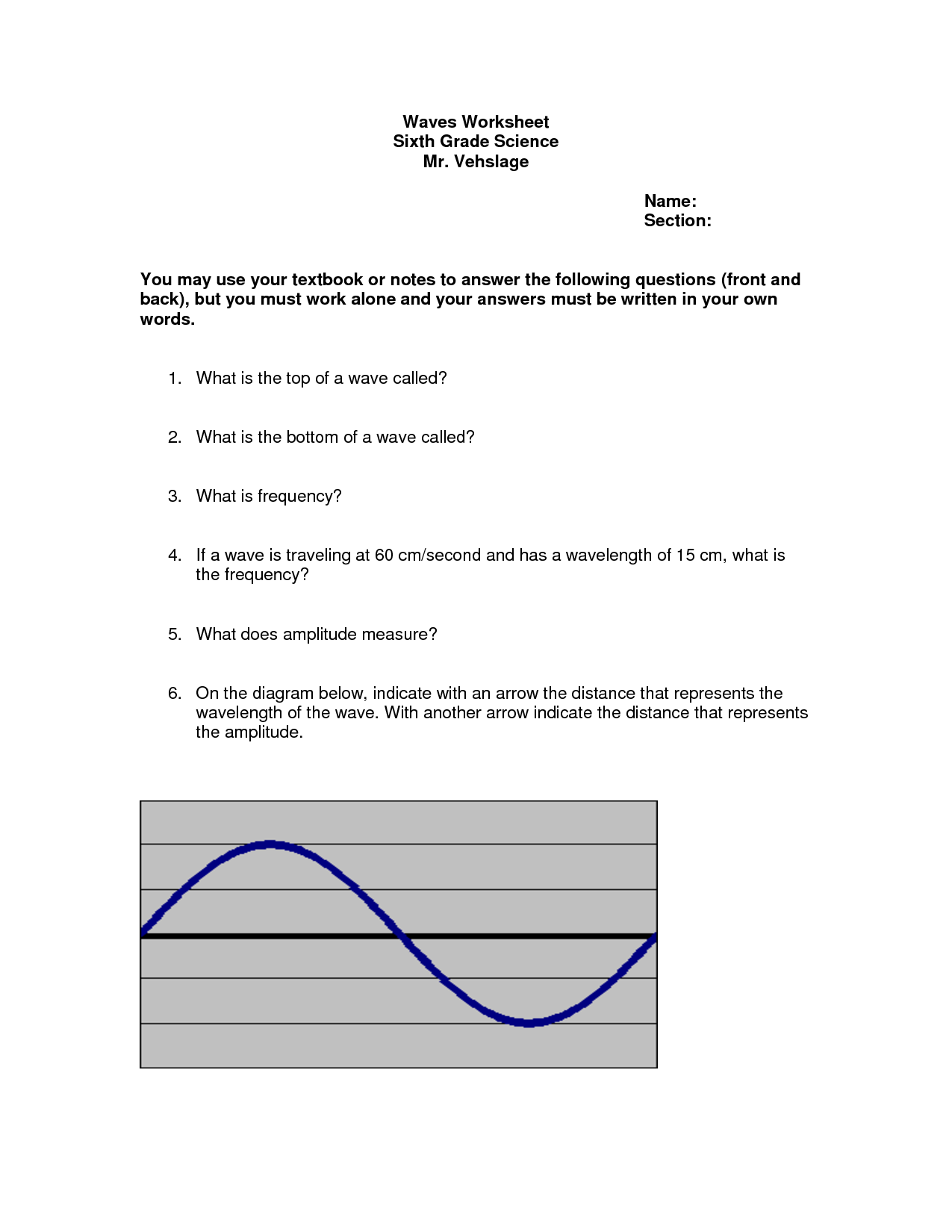
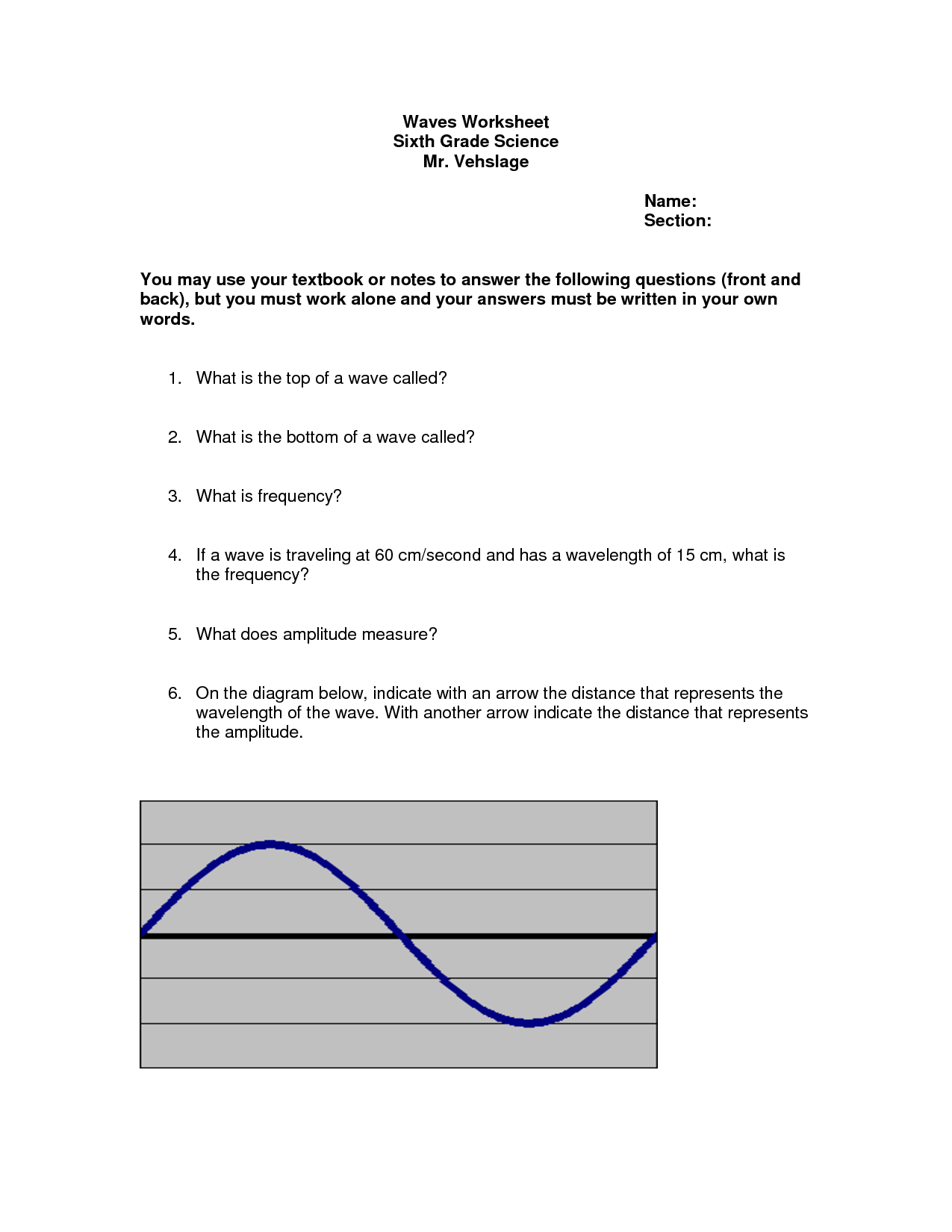
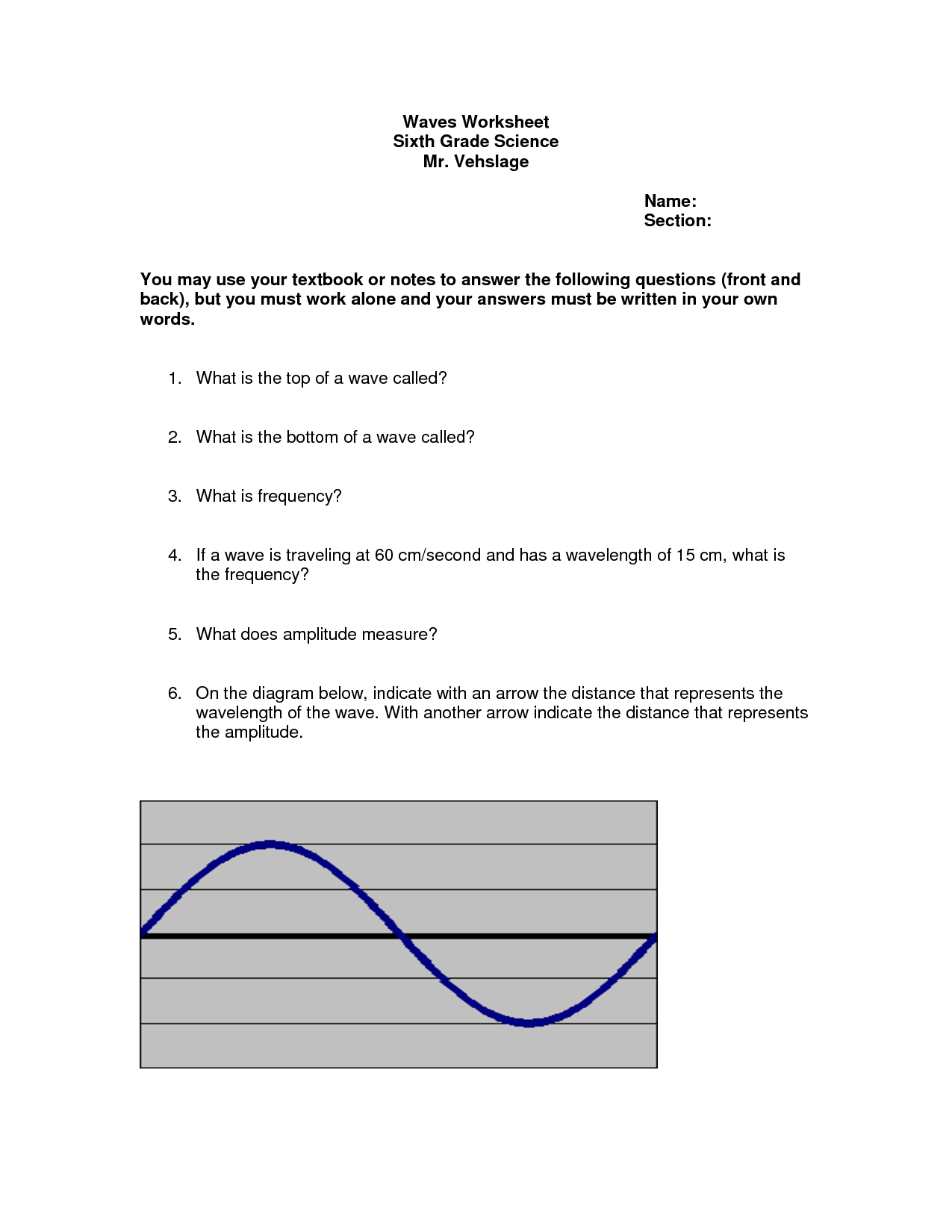
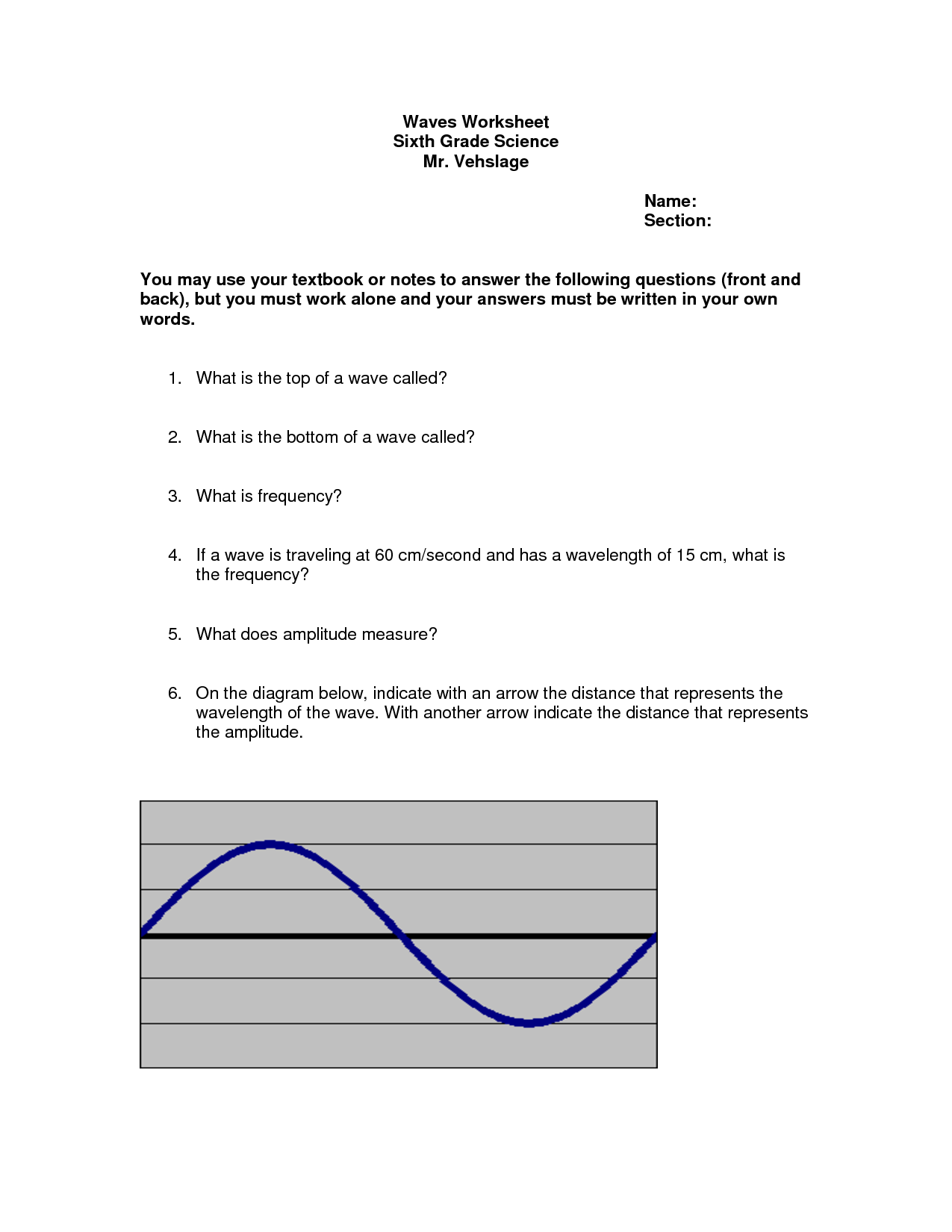
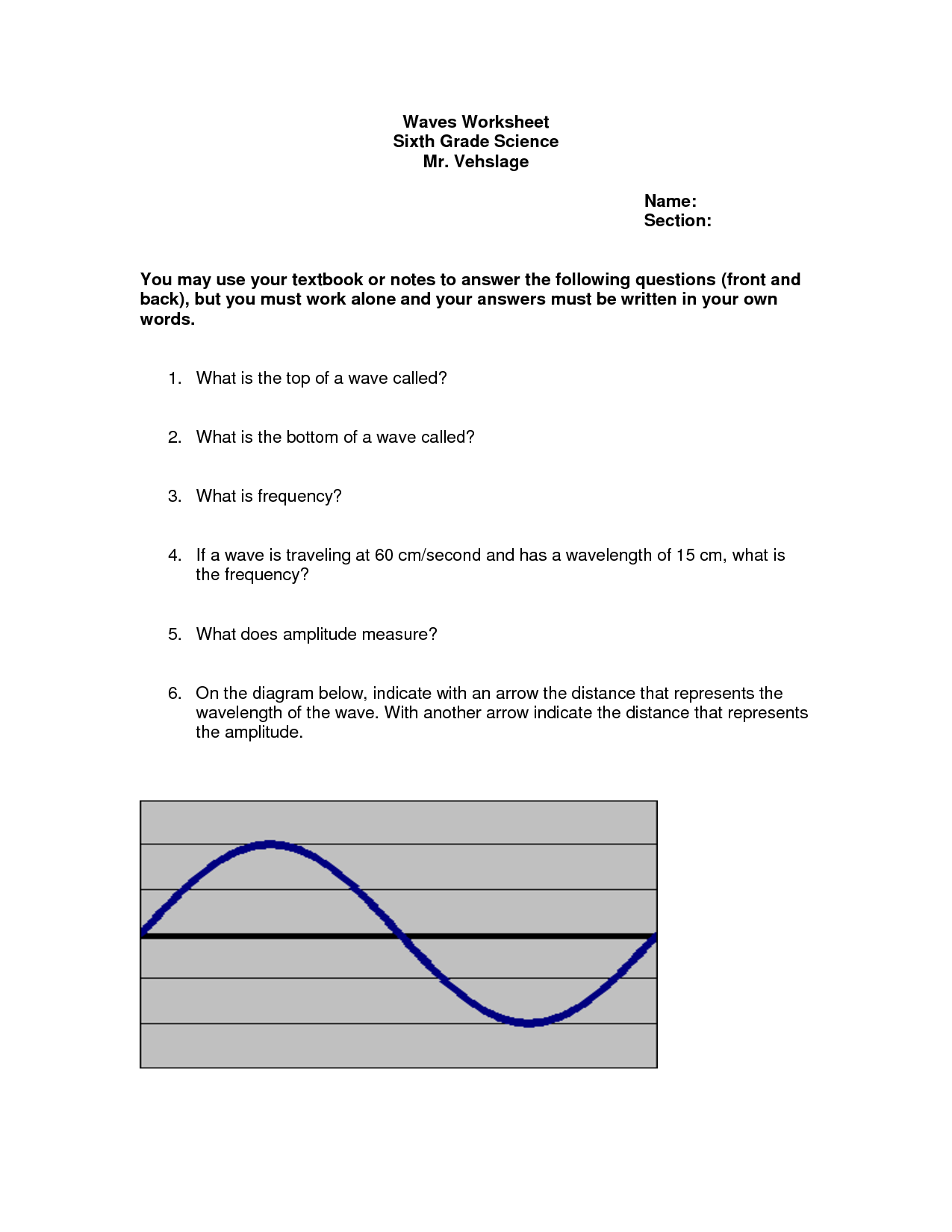
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic waves?
The relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic waves is inverse; as the wavelength of a wave decreases, its frequency increases, and vice versa. This means that shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies and longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies. This relationship is governed by the wave equation c = ??, where c is the speed of light, ? is the wavelength, and ? is the frequency.
How do electromagnetic waves interact with matter?
Electromagnetic waves interact with matter through processes such as absorption, reflection, transmission, and scattering. When electromagnetic waves encounter matter, they can be absorbed by the material, causing an increase in its energy level. Reflection occurs when waves bounce off the surface of the material. Transmission involves the waves passing through the material without being absorbed. Scattering occurs when waves change direction due to interactions with particles in the material. These interactions depend on the properties of both the electromagnetic waves and the matter they are interacting with.
How are electromagnetic waves used in everyday life?
Electromagnetic waves are used in everyday life in a variety of ways, from providing energy to power our homes and devices (through electricity and radio waves) to enabling communication and entertainment through radio and TV broadcasting, Wi-Fi, and cell phone signals. They are also used in medical equipment such as MRI machines and in security systems like metal detectors and X-ray scanners. Additionally, electromagnetic waves are utilized in cooking appliances like microwaves to heat up food quickly and efficiently, demonstrating their importance and usefulness in our daily lives.
How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel through and can travel through vacuum, while mechanical waves require a medium (such as water or air) to propagate. Additionally, electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, whereas mechanical waves involve the vibration of particles in the medium they are traveling through. Also, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum (about 300,000 km/s), while the speed of mechanical waves depends on the properties of the medium they are traveling through.
What are some examples of applications of electromagnetic waves in technology and communication?
Some examples of applications of electromagnetic waves in technology and communication include radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, cell phone communication, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth devices, radar, medical imaging (such as X-rays and MRI), satellite communication, and microwave ovens. These technologies all rely on the transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves to enable communication, data transfer, and various types of imaging.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments