Electricity Worksheets for Students
Electricity worksheets provide a valuable educational tool for students to enhance their understanding of this essential subject. By engaging with these worksheets, students are able to delve into the world of electricity, exploring its various concepts and principles. These worksheets serve as an entity for students to practice and reinforce their knowledge while also fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Whether you are a teacher seeking additional resources or a student eager to explore electricity further, these worksheets offer a comprehensive and interactive learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
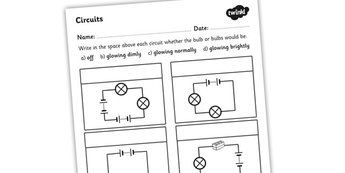
- Electricity Conductors and Insulators Worksheet
- Free Science Worksheets
- Kitchen Safety Hidden Object Worksheets
- Circuits and Conductors Worksheet
- United States Statue of Liberty Coloring Book
- Heat Conductors and Insulators Worksheet
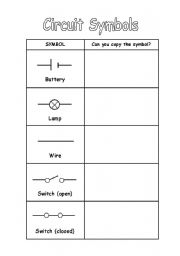
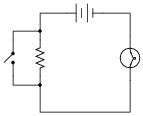
- Circuit Symbols Worksheet
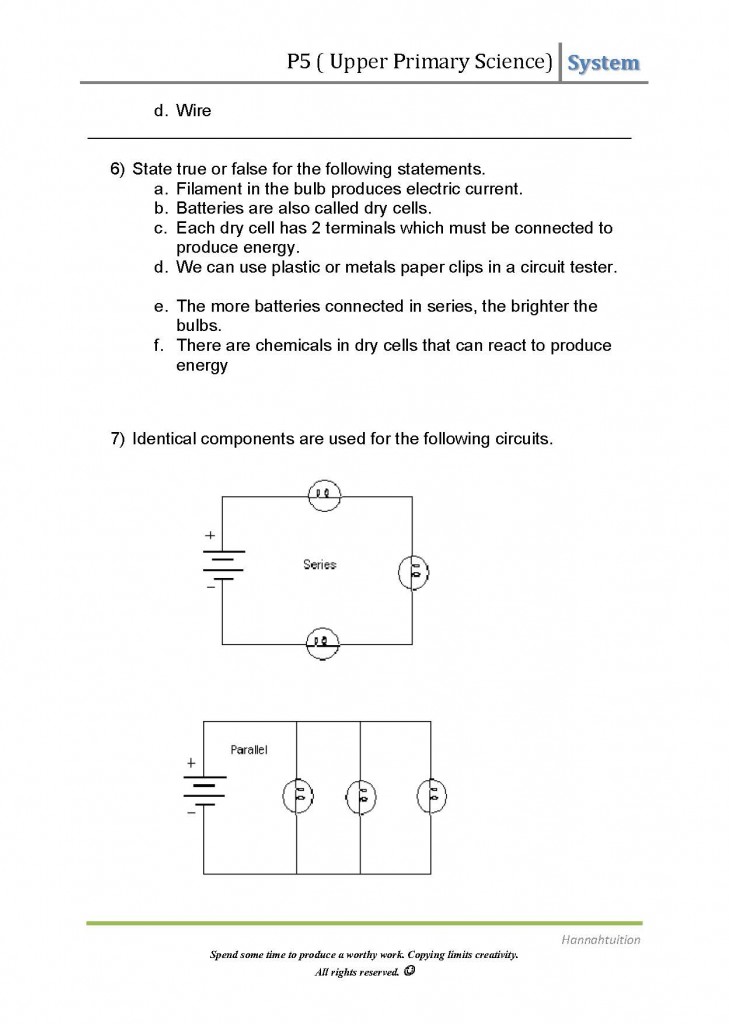
- Simple Circuit Diagram Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets Electricity
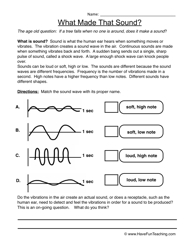
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- Compare and Contrast Reading Comprehension
- Free Bridal Shower Games
- Safety Crossword Puzzles
- War with Grandpa Book
- Free Printable Christmas Crossword Puzzles
More Student Worksheets
Middle School Student Goals WorksheetWho I AM Student Worksheet
High School Student Information Worksheet
Student Art Critique Worksheet
Student Getting to Know You Worksheet
Daily Journal Worksheet for Students
Star Student Printable Worksheet
Self-Esteem Worksheets for Students
What is electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electric charge, typically through a conductor such as a wire. It is a form of energy that powers a wide range of devices and systems in our modern world, from lighting and heating to electronic devices and machinery. The movement of electrons along a circuit generates electrical current, creating the basis for most of our technological and industrial advancements.
How is electricity produced?
Electricity is produced through the conversion of energy from various sources such as coal, natural gas, nuclear reactions, hydroelectric dams, wind turbines, and solar panels. This energy is used to rotate turbines, which in turn generate electricity through electromagnetic induction in power plants. The generated electricity is then transported through power lines to homes, businesses, and other facilities for consumption.
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is a closed loop through which electrons can flow, typically consisting of conductive wires, components such as resistors, capacitors, and switches, and a power source. When connected to a power source, the circuit allows electrons to move through it, producing an electrical current that can power devices or perform specific functions.
What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electricity through them, typically due to the presence of free-moving electrons. Examples of conductors include metals like copper and aluminum. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them easily. They have high resistance to electrical current and are used to protect us from electric shocks. Examples of insulators include rubber, plastic, and glass.
What are the three main components of a circuit?
The three main components of a circuit are a power source, a load, and conductive pathways. The power source provides the electrical energy to the circuit, the load consumes the energy and performs a specific function, and the conductive pathways allow the flow of electricity between the power source and the load.
What is the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC)?
Direct current (DC) flows in one direction at a constant voltage, while alternating current (AC) changes direction periodically. DC is commonly used in batteries and electronic devices, while AC is predominant in homes and businesses because it can be easily transmitted over long distances and transformed to different voltages. AC power is preferred for grid distribution due to its ability to support transformers and accommodate power factor correction.
How does a light bulb work?
A light bulb works by passing an electric current through a filament inside the bulb, which heats up and produces light. The filament is usually made of tungsten, which has a high melting point and doesn't burn out easily. As the filament heats up, it emits light and provides illumination in the surrounding space.
What is resistance in a circuit?
Resistance in a circuit refers to the opposition that electrical current encounters as it flows through a material. It is measured in ohms and is caused by factors such as the material's composition, length, and cross-sectional area. Resistance results in a voltage drop across a component and helps regulate the flow of current within a circuit.
What is the role of a fuse or circuit breaker?
The role of a fuse or circuit breaker is to protect electrical circuits from overloading or short-circuiting by interrupting the flow of electricity. They function as safety devices that automatically cut off the electrical supply when a fault or excessive current is detected in order to prevent damage to the electrical system or appliances and to reduce the risk of fire hazards. This helps to ensure the safety of the building and its occupants.
How does electricity flow through a power grid?
Electricity flows through a power grid starting at power plants where it is generated. The electricity then travels through transmission lines to substations, where the voltage is stepped down before being distributed through distribution lines to homes and businesses. Along this journey, transformers help regulate the voltage to ensure safe and efficient delivery of electricity to end-users.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments