Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade Science
If you're a 4th grade science teacher or a parent looking to supplement your child's learning at home, these electricity worksheets are just what you need. Designed to engage young minds and reinforce key concepts, these worksheets provide a fantastic opportunity to explore the fascinating world of electricity.
Table of Images 👆
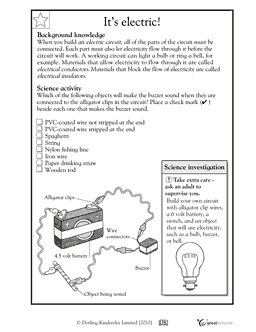
- Electricity Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
- Science Electricity Worksheets 4th Grade
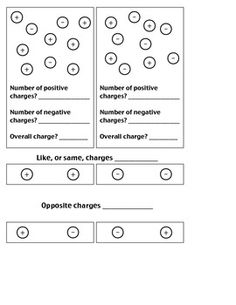
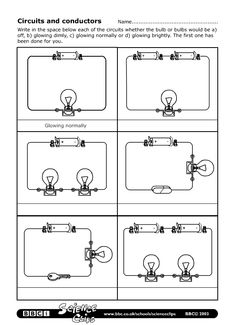
- Conductors and Insulators Worksheet 4th
- 2 Grade English Worksheets for Kids
- Natural Resources Worksheets 3rd Grade
- Types of Clouds Worksheets 2nd Grade Science
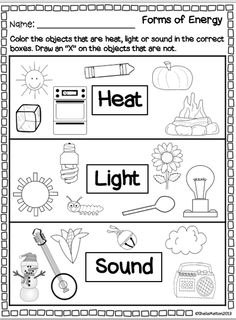
- Sound and Light Energy Worksheet
- Common Core Math Test Examples
- Moon Phases Worksheet Grade 2
- Science Natural Disasters Worksheet
- Electrical Circuit Symbols
More 4th Grade Worksheets
4th Grade Elapsed Time WorksheetsIrregular Plural Worksheets 4th Grade
Rotational Symmetry Worksheets 4th Grade
Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
Long Division with Remainders Worksheets 4th Grade
Fourth Grade Reading Comp Worksheets
Reading Response Worksheets 4th Grade
4th Grade Essay Writing Worksheets
Worksheets 4th Grade Narrative Writing
Long Lined Paper Worksheets 4th Grade Essay-Writing
What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy that is created through the movement of electrons. It is a fundamental force of nature that powers a wide range of devices and systems, from lights and appliances in our homes to electronics and industries.
How is electricity produced?
Electricity is typically produced by converting mechanical energy, generated by sources such as steam, falling water, wind, or the burning of fossil fuels, into electrical energy. This process usually involves rotating a turbine connected to a generator, which produces electricity through electromagnetic induction. Solar panels can also directly convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells. The generated electricity is then transmitted through a power grid to homes, businesses, and other users.
What is a circuit?
A circuit is a closed loop or pathway through which electricity can flow, typically involving interconnected components such as wires, resistors, capacitors, and transistors that work together to perform a specific electrical function.
What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors are materials that allow the flow of electricity through them, such as metals like copper and aluminum. Insulators, on the other hand, are materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them easily, such as rubber and plastic. Conductors have high conductivity and low resistance, while insulators have high resistance and low conductivity. The distinction between conductors and insulators is important in understanding how electricity moves through different materials.
What is a battery and how does it work?
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy through a series of chemical reactions between its components. Inside a battery, there are two electrodes (anode and cathode) that are submerged in an electrolyte solution, which allows for the flow of ions between the electrodes. When the battery is connected to an external circuit, electrons are released from the chemical reactions happening inside the battery, creating an electric current that can power electronic devices. Once the chemical reactions are depleted or the battery is discharged, it needs to be recharged to replenish the chemical energy for future use.
How does a light bulb produce light?
A light bulb produces light through a process called incandescence. When electricity flows through the filament of the bulb, it heats up the tungsten filament, causing it to emit light. As the filament reaches a high temperature, it glows and emits visible light. The combination of electrical current and resistance in the filament generates both heat and light, creating the illumination we see from a light bulb.
What are the different types of switches and how do they control electricity flow?
There are various types of switches, including toggle, rocker, push-button, rotary, and dimmer switches, each with a unique design and purpose. Switches control the flow of electricity by interrupting or completing the circuit. When a switch is turned on, it allows electricity to flow through the connected wires, enabling devices to receive power. Conversely, when the switch is turned off, it breaks the circuit and stops the flow of electricity, effectively shutting off the power supply to the devices.
How do magnets and electricity interact?
Magnets and electricity interact through electromagnetism, which is a fundamental force of nature. When an electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field around it. Likewise, a moving magnetic field can induce an electric current in a wire. This interaction forms the basis of various devices and technologies, such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, and transformers, demonstrating the close relationship between magnets and electricity.
What are some common electrical safety precautions?
Common electrical safety precautions include turning off the power before working on electrical outlets or appliances, using ground fault circuit interrupters in wet areas such as bathrooms and kitchens, avoiding overloading power strips or outlets, keeping electrical cords untangled and in good condition, not using damaged or frayed cords, and ensuring that electrical outlets are properly covered with safety plugs when not in use.
How does electricity power common household appliances?
Electricity powers common household appliances by flowing through wires to the appliance's power cord, where it enters the appliance through an electrical outlet or plug. The electricity then travels through the appliance's internal wiring and circuitry, providing the energy needed to operate the appliance's various functions, such as heating elements, motors, or electronic components. This flow of electricity allows household appliances like refrigerators, televisions, washing machines, and others to perform the tasks for which they are designed.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments