Ecosystem Organization Pyramid Worksheet
Are you a biology teacher searching for a comprehensive and engaging worksheet to teach your students about ecosystem organization pyramids? Look no further! This worksheet is designed to help your students grasp the concept of energy transfer and the relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
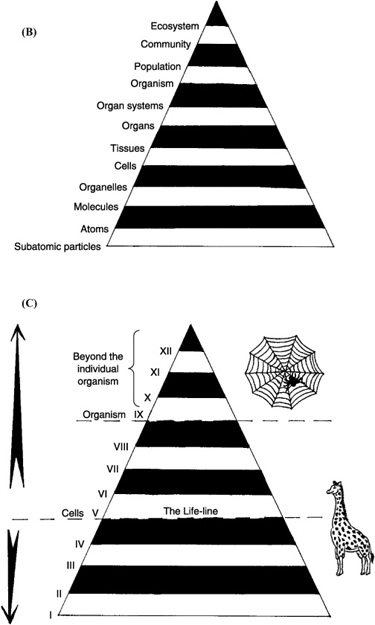
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. This includes plants, animals, microorganisms, soil, water, sunlight, and air, all working together in a complex web of relationships to create a sustainable and balanced environment.
What is the primary source of energy in an ecosystem?
The primary source of energy in an ecosystem is the sun. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy that fuels the entire ecosystem. This energy is then transferred through the food chain as organisms consume one another, ultimately sustaining all life within the ecosystem.
What are producers?
Producers are organisms, typically plants and other photosynthetic organisms, that create their own food by converting light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. They are the foundation of most ecosystems as they provide energy and nutrients for other organisms in the food chain.
What role do consumers play in an ecosystem?
Consumers play a crucial role in an ecosystem as they obtain energy by consuming other organisms. They help regulate the population of other species, maintain the balance of the ecosystem, and transfer energy through the food chain. By feeding on producers and other consumers, they help control the distribution of resources and prevent one species from dominating the ecosystem. Ultimately, consumers contribute to the overall health and stability of the ecosystem by participating in the flow of energy and matter.
Define herbivores.
Herbivores are animals that primarily feed on plants and vegetation as their main source of food, rather than consuming meat or other animals.
Define carnivores.
Carnivores are animals that primarily feed on the flesh of other animals for their nutrition and energy needs. They are classified as secondary consumers in the food chain, preying on herbivores or other carnivores. Carnivores possess adaptations such as sharp teeth, strong jaws, and keen senses to hunt, capture, and consume their prey efficiently.
What are decomposers?
Decomposers are organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and insects that break down dead organic material into simpler substances like nutrients and minerals, recycling them back into the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in the process of decomposition, which helps to release essential nutrients back into the environment for new plant growth and sustains the balance of nutrients in the ecosystem.
Explain the concept of trophic levels in an ecosystem.
Trophic levels in an ecosystem represent the hierarchical levels of organisms based on their position in the food chain and energy transfer. Producers, like plants, occupy the first trophic level and convert sunlight into energy; primary consumers, such as herbivores, consume producers and are at the second trophic level; secondary consumers, like carnivores, feed on primary consumers and are at the third trophic level; and so on, until the top predators, which occupy the highest trophic level. Energy is transferred between trophic levels through eating and being eaten, with each level typically containing less energy than the one below it due to energy loss in metabolic processes, leading to a pyramid-shaped energy flow in ecosystems.
What is a food chain?
A food chain is a sequence of organisms in an ecosystem, where each organism consumes the one below it and is in turn consumed by the one above it. It depicts the flow of energy and nutrients through organisms in an ecosystem, illustrating how they are interdependent on one another for survival.
How does energy flow through an ecosystem?
Energy flows through an ecosystem in a linear manner, starting with producers such as plants who convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to primary consumers like herbivores who eat the producers, and then to secondary consumers like carnivores who eat the herbivores. Energy is continuously transferred through the food chain up to higher trophic levels but is also lost as heat at each step, leading to the eventual decomposition of organisms by decomposers which returns nutrients to the soil for the cycle to begin again.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments