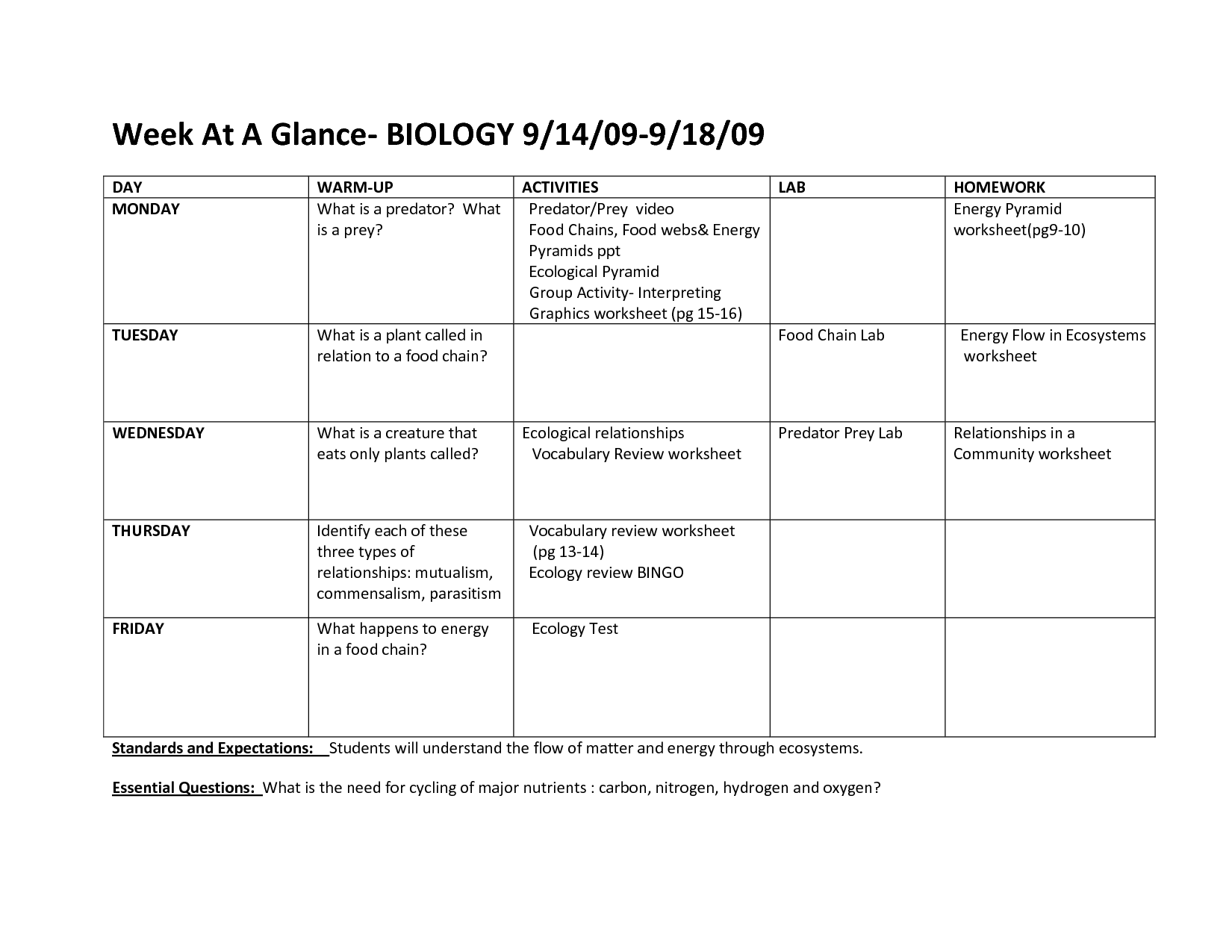
Ecosystem Organization Pyramid Worksheet Template
Are you in need of a comprehensive and easy-to-use worksheet to help your students understand the concept of ecosystem organization? Look no further! Our Ecosystem Organization Pyramid Worksheet Template is designed to provide a clear and concise overview of the different levels and entities within an ecosystem. This worksheet is suitable for biology or environmental science classes and is an ideal resource for teachers seeking a structured and organized way to present this complex subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- My Activity Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecosystem Organization Pyramid
- Food Chain Pyramid Worksheets
- Ecosystem Levels of Organization Worksheet
- Biomass Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
- Organism Trophic Levels Ecosystem
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Blank
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms, together with the non-living components of their environment, interacting as a system. This includes plants, animals, and microorganisms interacting with one another and with their physical environment. Ecosystems can vary in size and complexity, ranging from a small pond to a vast rainforest, but they all function to create a balance through the interdependence of its living and non-living components.
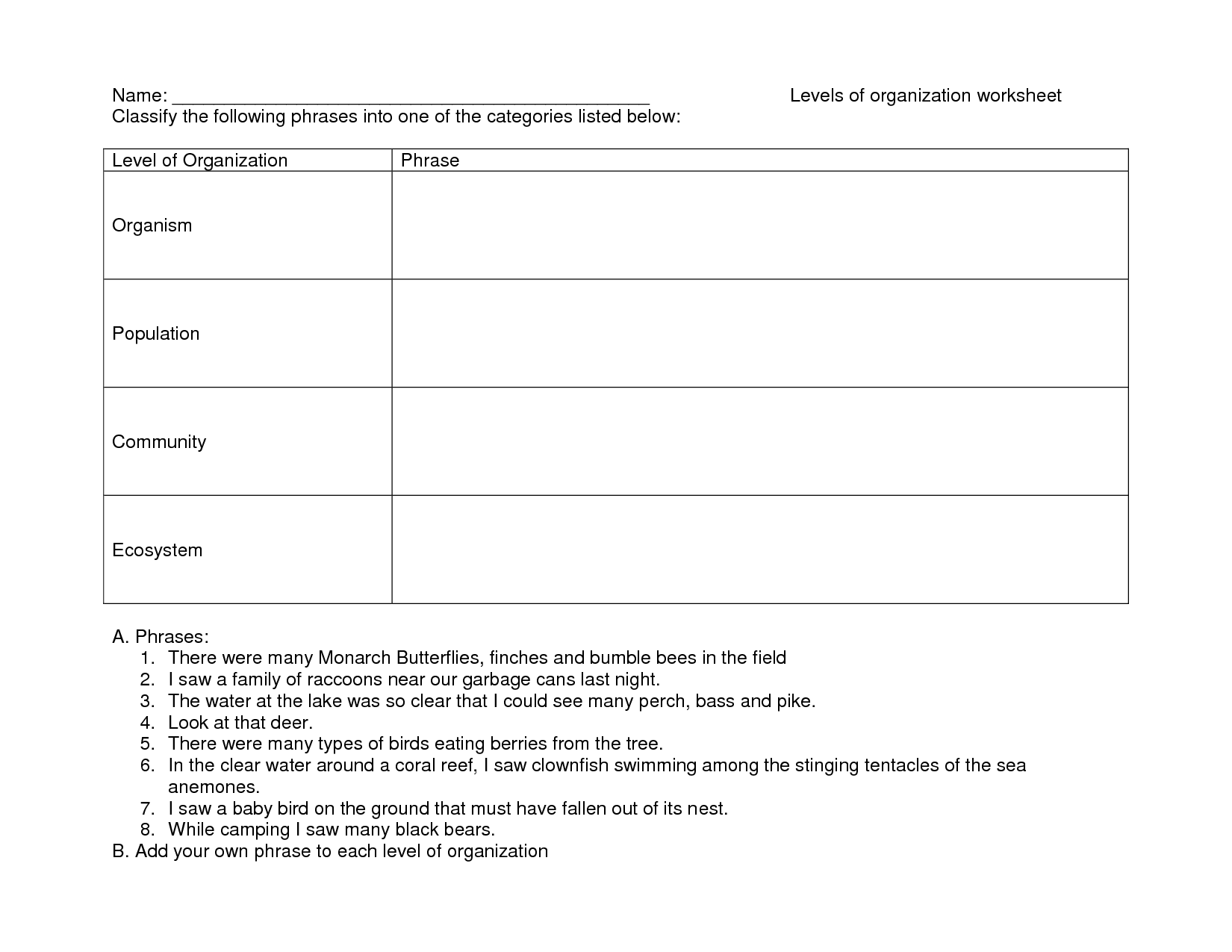
What are the different levels of organization in an ecosystem?
The different levels of organization in an ecosystem are individual organisms, populations of the same species, communities of different species interacting in a particular area, and the entire ecosystem comprising all living organisms and their physical environment. These levels work together to create a complex web of interactions and relationships that sustain life within the ecosystem.
What is the primary source of energy in an ecosystem?
The primary source of energy in an ecosystem is the sun. Solar energy is converted by green plants through the process of photosynthesis into chemical energy that is then transferred to other organisms through the food chain.
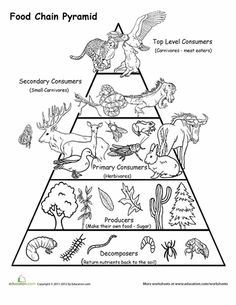
What are primary producers and what role do they play in the ecosystem?
Primary producers are organisms such as plants, algae, and some bacteria that are capable of photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem as they form the base of the food chain by producing organic compounds that serve as food for other organisms. Without primary producers, higher trophic levels would not have a source of energy, leading to the collapse of the entire ecosystem. Additionally, primary producers also play a vital role in oxygen production and carbon cycling, making them essential for the balance and sustainability of ecosystems.
What are primary consumers and what is their relationship with primary producers?
Primary consumers are organisms that feed directly on primary producers, typically plants and algae. They are the herbivores of the ecosystem, forming the second trophic level. The relationship between primary consumers and primary producers is a vital part of the food chain, as primary consumers rely on primary producers for energy and nutrients. By consuming plants, primary consumers transfer energy from the producers to higher trophic levels, such as secondary consumers. This relationship plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
What are secondary consumers and what is their role in the ecosystem?
Secondary consumers are organisms that feed on primary consumers (herbivores) in an ecosystem. They primarily eat plant-eating animals to obtain energy and nutrients for their survival. By consuming primary consumers, secondary consumers help regulate and balance the populations of these animals, preventing overgrazing or overpopulation of certain species. This ultimately maintains the overall health and diversity of the ecosystem by controlling the flow of energy and nutrients through the food chain.
What are decomposers and what is their function in the ecosystem?
Decomposers are organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and insects that break down dead organic matter into simpler substances. Their function in the ecosystem is to recycle nutrients back into the environment, making them available for other living organisms to use. Decomposers play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by breaking down organic matter and returning essential nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus to the soil for plants to absorb and use for growth.
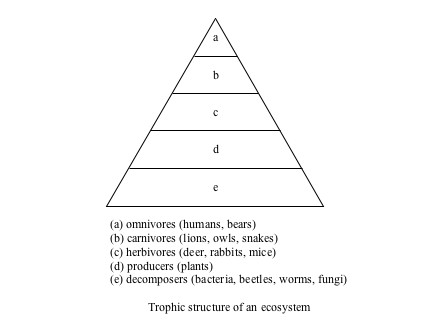
How does energy flow through the different levels of the ecosystem pyramid?
Energy flows through the different levels of the ecosystem pyramid through a process known as trophic levels. Primary producers, such as plants, convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which is then consumed by primary consumers, such as herbivores. The energy is then transferred to higher-level consumers, such as carnivores, as they consume lower trophic level organisms. As energy moves up the pyramid, some energy is lost through respiration, waste, and heat production, leading to a decrease in available energy at higher trophic levels. This process continues throughout the ecosystem, with energy passing from one organism to another in a linear flow.
How does the number of organisms change from one level to the next in the pyramid?
The number of organisms generally decreases from one trophic level to the next in a pyramid-shaped ecosystem. This is because energy is lost as heat as it passes from one trophic level to the next, so less energy is available to support a large number of organisms at higher levels. This results in fewer predators than prey, leading to a pyramid shape where the base, containing producers, has the highest number of organisms, with successive trophic levels having fewer organisms as you move up the pyramid.
Why is the ecosystem pyramid important for understanding the balance and stability of an ecosystem?
The ecosystem pyramid is important for understanding the balance and stability of an ecosystem because it visually represents the flow of energy and matter through different trophic levels within a given ecosystem. It shows the hierarchical structure of energy transfer from producers to consumers to decomposers, highlighting the interdependence of organisms in maintaining the ecosystem's health. By analyzing the ecosystem pyramid, ecologists can assess the distribution of biomass, energy, and nutrients, helping them identify potential vulnerabilities or disruptions that may impact the overall balance and stability of the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments