Ecology Worksheets for High School
High school students interested in ecology and looking for supplemental material to enhance their understanding of the subject can benefit from engaging with ecology worksheets. These worksheets are designed to present key concepts, reinforce learning, and broaden knowledge about the intricate relationships within ecosystems. Whether students are studying for a test or simply seeking to expand their ecological knowledge, ecology worksheets offer a valuable resource for deepening their understanding of this important field.
Table of Images 👆
- Ecological Succession Worksheet
- Printable Ecology Worksheets
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Middle School
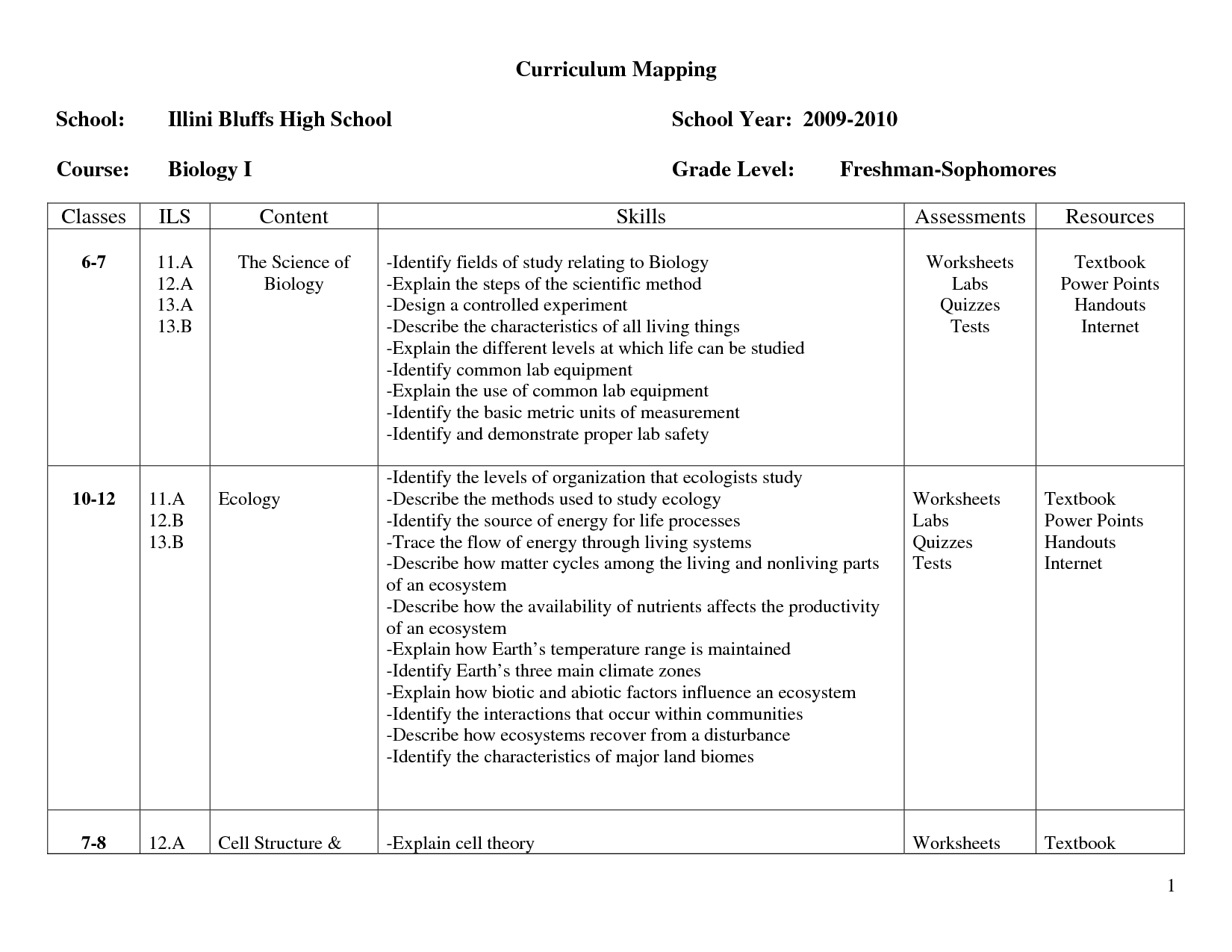
- High School Biology Worksheets and Answers
- Free Printable Reading Worksheets High School
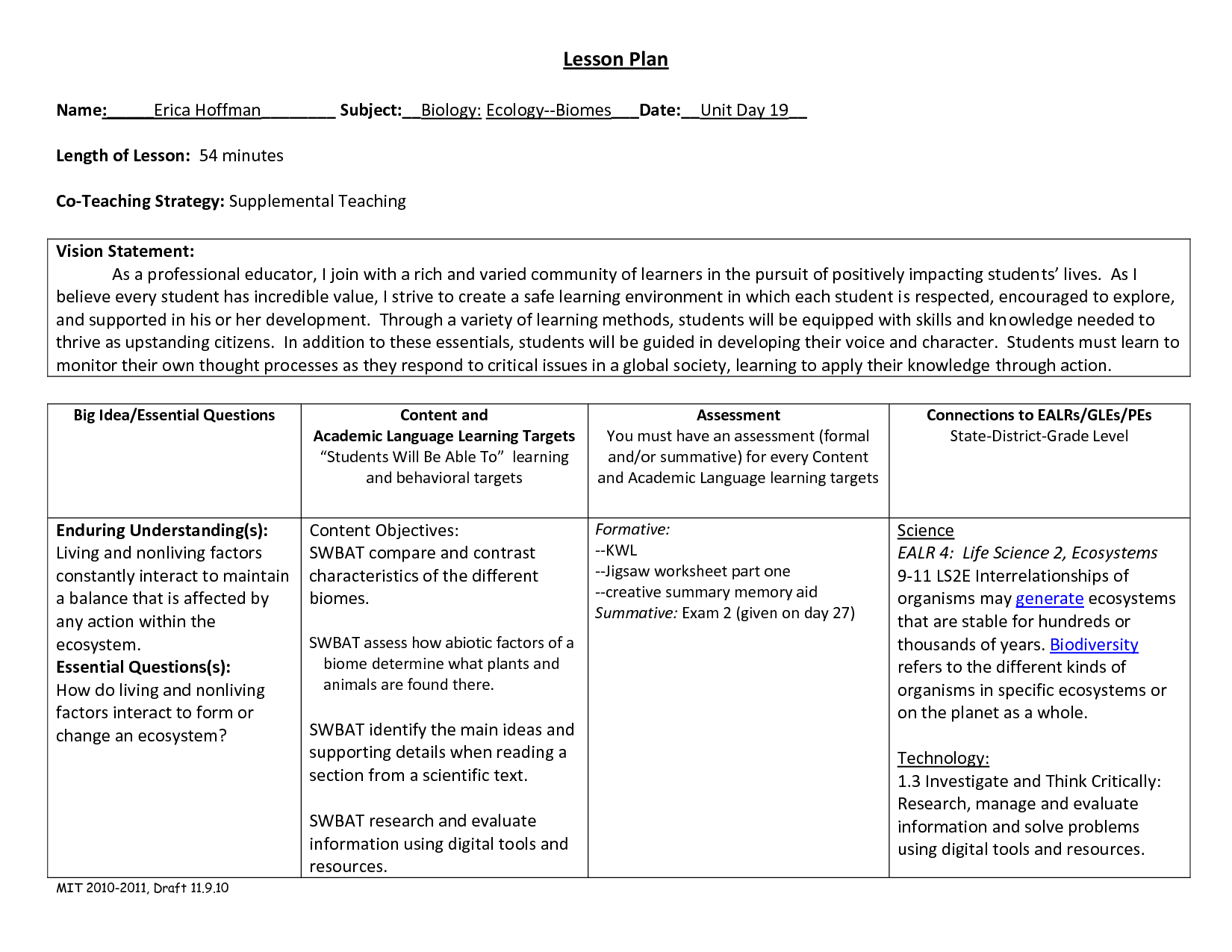
- Biome Worksheets High School
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Main Idea and Supporting Details Worksheets
- Vertebrate Worksheet High School
- Biology Enzyme Worksheet High School
- Symbiosis Worksheet High School Relationship
- High School Chemistry Worksheets
- Population and Community Ecology Worksheet
- Food Web Worksheets Middle School Answers
- High School Biology Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of ecology?
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies the relationships between living organisms and their environment, including how these interactions influence the distribution and abundance of organisms in ecosystems, as well as the flow of energy and matter within these systems.
What are the different levels of ecological organization?
The different levels of ecological organization are individual organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere. These levels represent increasing complexity, from a single living organism to all living organisms on Earth and their interactions with the environment. Each level plays a crucial role in understanding the functioning and dynamics of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
How do autotrophs and heterotrophs differ in how they obtain energy?
Autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own energy from light or inorganic compounds through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, while heterotrophs must obtain energy by consuming other organisms or organic matter. Autotrophs are self-sustaining and do not rely on external sources for energy, whereas heterotrophs depend on consuming other organisms to meet their energy needs.
What are the three main types of ecological pyramids?
The three main types of ecological pyramids are energy pyramid, biomass pyramid, and pyramid of numbers. The energy pyramid shows the flow of energy through trophic levels with energy decreasing as it moves up the food chain, the biomass pyramid represents the total amount of living organic matter in each trophic level, and the pyramid of numbers illustrates the number of organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
Explain the concept of a food chain and provide an example.
A food chain is a series of organisms in an ecosystem where each member is dependent on the one below it for energy. It starts with a primary producer, such as plants, which are then eaten by primary consumers (herbivores), which are in turn eaten by secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on. An example of a food chain is grass (producer) being eaten by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is then eaten by a frog (secondary consumer), which is further consumed by a snake (tertiary consumer).
What is the difference between a food web and a food chain?
A food chain is a linear sequence in which one organism eats another, showing the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem, while a food web consists of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem, showing multiple feeding relationships and interactions between organisms at different trophic levels. In simple terms, a food chain is a single pathway, while a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and its ecological importance.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process involves capturing sunlight with chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of plant cells, and using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen as byproducts. Photosynthesis is crucial for sustaining life on Earth as it is the primary source of energy for most living organisms. It is responsible for producing oxygen, which is essential for respiration in animals, and it forms the base of the food chain by providing organic carbon compounds that are consumed by other organisms. In addition, photosynthesis plays a key role in the global carbon cycle by regulating levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change.
What are the main factors that contribute to population growth or decline?
The main factors that contribute to population growth or decline include fertility rates, mortality rates, immigration, and emigration. Higher fertility rates lead to population growth, while lower mortality rates also contribute to increasing populations. Immigration can also boost population numbers, as individuals move into a region or country. On the other hand, emigration can lead to population decline as people leave a particular area. Additionally, factors such as economic conditions, healthcare access, education, and government policies can also influence population growth or decline.
What is the difference between a habitat and a niche?
A habitat refers to the physical environment where an organism lives, including the biotic and abiotic factors present, while a niche is the particular role or function that an organism plays within its habitat, including how it interacts with other species and resources in that environment. In essence, a habitat is where an organism lives, while a niche is how it lives within that habitat.
Explain the concept of symbiotic relationships and provide examples of each type.
Symbiotic relationships are interactions between two different species that can have a positive, negative, or neutral impact on both organisms. There are three main types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, where both species benefit; commensalism, where one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor helped; and parasitism, where one species benefits at the expense of the other. Examples include mutualism such as bees and flowers, where bees get nectar and flowers get pollinated; commensalism like barnacles living on whales for transportation without harming them; and parasitism like ticks feeding on blood from hosts like dogs.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments