Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a student or teacher looking for an answer key to the Ecological Pyramids Worksheet? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the essential key to completing this worksheet successfully. With a focus on the entity and subject of ecological pyramids, this answer key will help you understand the intricacies of this fundamental ecological concept.
Table of Images 👆
- Photosynthesis Biology Answer Key POGIL
- Ecosystem Worksheet Answer Key
- Ecological Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Ecological Pyramids Worksheet Answers
- Membrane Structure and Function Answer Key POGIL
- Ecological Succession Worksheet Answer Key
- Blank Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Energy Flow through Ecosystem Worksheet Answers
- Biomass Energy Pyramid Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an ecological pyramid?
An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation that shows the transfer of energy and matter within an ecosystem. It consists of different trophic levels, with primary producers at the base, followed by herbivores, then carnivores, and finally, top predators at the top. The pyramid shape represents the decreasing energy available at each higher trophic level due to energy loss as it flows through the food chain. This concept helps to demonstrate the structure and function of ecosystems and the interdependencies of different organisms within them.
What are the different types of ecological pyramids?
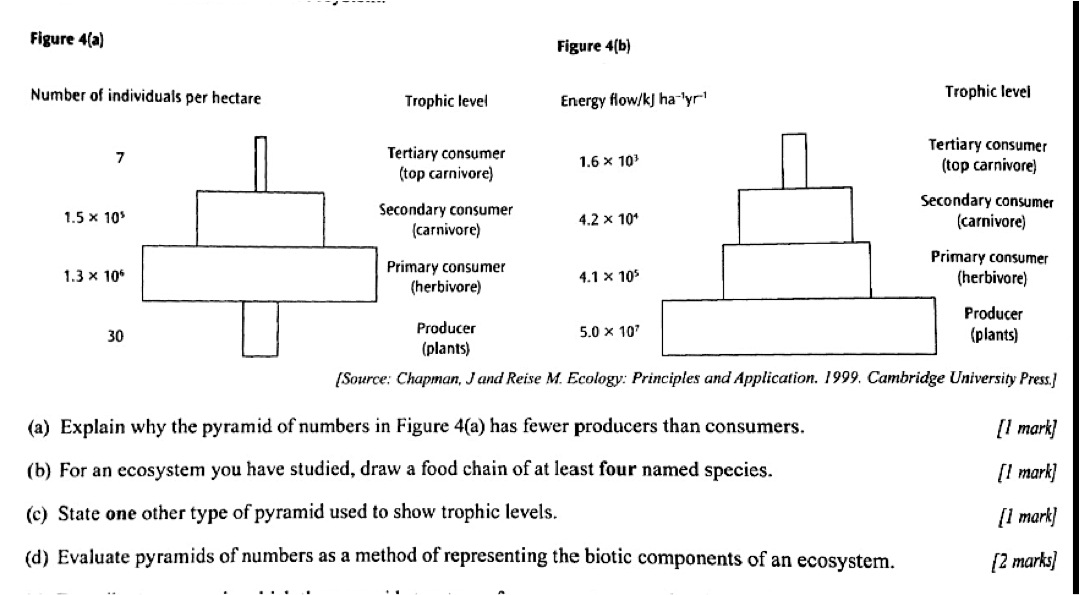
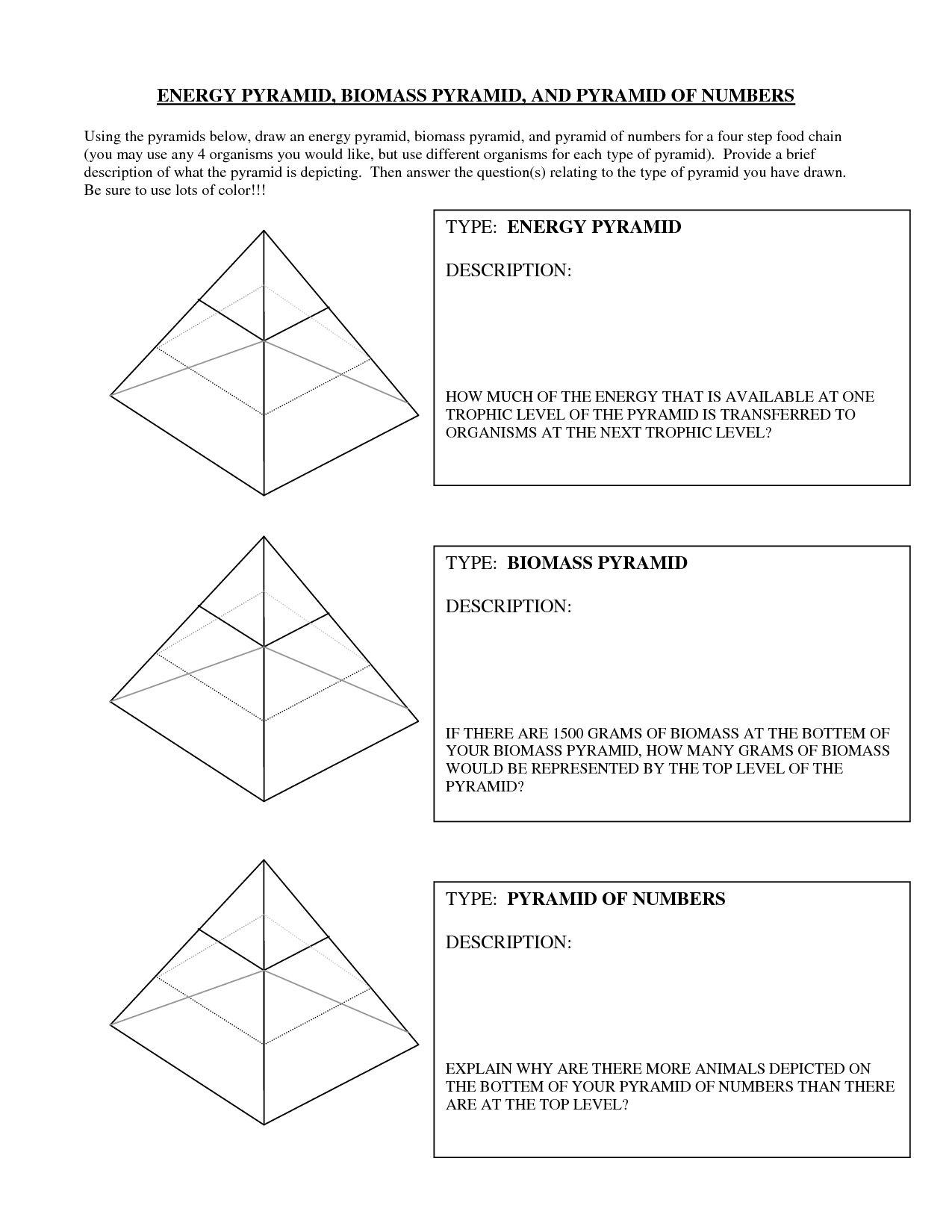
The different types of ecological pyramids include pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy. The pyramid of numbers quantifies the number of organisms at each trophic level, the pyramid of biomass represents the total biomass of organisms at each trophic level, and the pyramid of energy illustrates the flow of energy through different trophic levels with energy decreasing as it moves up the pyramid. These pyramids help us understand the structure and functioning of ecosystems and the relationships between organisms within them.
Describe the pyramid of numbers.
The pyramid of numbers is a graphical representation of the number of individual organisms present in each trophic level of an ecosystem. In this pyramid, producers, such as plants, form the base with the highest number of organisms, followed by herbivores, then carnivores at the top with the fewest individuals. This pyramid helps illustrate the energy flow and biomass distribution within an ecosystem, showing the decreasing number of organisms as you move up the trophic levels.
Explain the pyramid of biomass.
The pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the standing crop of various trophic levels in an ecosystem, illustrating the amount of living organic matter present in each level. It typically shows that the biomass decreases as you move up the food chain, with producers at the bottom having the highest biomass and top consumers having the lowest. This pyramid helps to visualize the energy transfer and efficiency within an ecosystem, demonstrating that energy is lost as it moves through different trophic levels due to metabolic processes and heat loss.
How does the energy pyramid work?
An energy pyramid illustrates the flow of energy within an ecosystem, showing the transfer of energy from one trophic level to another. At the base of the pyramid are producers, like plants, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores consume the producers, transferring some of this energy to the next trophic level. The process continues up the pyramid as energy is passed along to higher trophic levels, with each level containing less energy than the one below it due to heat loss and inefficiencies in energy transfer. This hierarchy helps to visualize the distribution of energy within an ecosystem and the dependency of organisms on each other for energy.
What is the significance of the producers in an ecological pyramid?
Producers play a crucial role in an ecological pyramid as they are at the base, providing the foundational energy source for the entire ecosystem. Through photosynthesis, producers convert sunlight into organic materials, which then serve as food for consumers and decomposers in the ecosystem. Without producers, the rest of the pyramid would collapse, highlighting their significance in sustaining energy flow and supporting biodiversity within the ecosystem.
Describe the relationship between trophic levels in an ecological pyramid.
The relationship between trophic levels in an ecological pyramid is hierarchical, with each level representing a different position in the food chain based on energy transfer. At the base are producers, such as plants, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Above them are primary consumers, which feed on the producers, followed by secondary and tertiary consumers that eat the primary consumers. Each trophic level represents a transfer of energy from lower levels, with only about 10% of energy being passed on to the next level. This relationship highlights the dependence and interconnectedness of different organisms in an ecosystem.
How does the size of each trophic level change from one level to the next?
The size of organisms generally decreases as you move up the trophic levels in an ecosystem. This is because each trophic level feeds on the level below it, so there is less energy available at higher levels to sustain larger organisms. As a result, top predators tend to be smaller in size compared to the organisms they consume at lower trophic levels.
Explain the concept of ecological efficiency in an energy pyramid.
Ecological efficiency in an energy pyramid represents the percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next. It signifies the amount of energy that is actually passed on as organisms consume each other in the food chain. Typically, only about 10% of the energy is transferred to the next trophic level, while the rest is lost as heat during metabolism or used for growth and reproduction. This efficiency concept helps illustrate the energy flow within ecosystems and highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced and diverse food web to sustain life.
What can ecological pyramids tell us about the stability and productivity of an ecosystem?
Ecological pyramids provide valuable information about the structure of an ecosystem by illustrating the relationships and energy flow between different trophic levels. A stable and productive ecosystem is typically characterized by a large base of producers, such as plants or phytoplankton, supporting a smaller number of herbivores and an even smaller number of top predators. A well-defined pyramid with a large base and progressively smaller higher trophic levels indicates a balanced ecosystem with efficient energy transfer and a healthy abundance of species at each level. In contrast, inverted or irregular pyramids may suggest ecosystem instability, with potential issues like overgrazing or overfishing disrupting the natural flow of energy and resources.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments