Earthquake Worksheets for Students
Earthquake worksheets are valuable educational tools designed to help students understand and engage with the subject of seismic events. These worksheets provide a variety of exercises and activities that explore the science behind earthquakes, their causes and effects, and emergency preparedness measures. Whether you are a teacher searching for classroom resources or a homeschooling parent looking to supplement your child's education, earthquake worksheets can offer an engaging and informative learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
- 3rd Grade Volcano Worksheets
- Volcano Crossword Puzzles Worksheets
- Worksheets On Earthquakes and Volcanoes
- Printable Volcano Worksheets
- Natural Disaster Comprehension Worksheets
- Natural disasters
- Cartoon Mazes Printable
- Stone Age Word Search
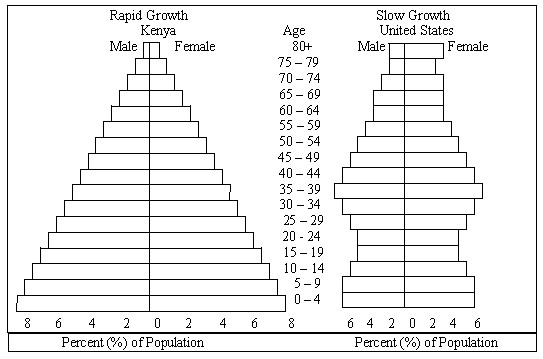
- Population Pyramid Worksheet
- Rock Cycle Reading Worksheet
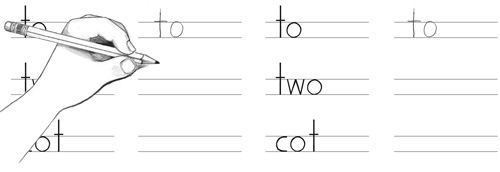
- Left-Handed Letter Formation
More Student Worksheets
Middle School Student Goals WorksheetWho I AM Student Worksheet
High School Student Information Worksheet
Student Art Critique Worksheet
Student Getting to Know You Worksheet
Daily Journal Worksheet for Students
Star Student Printable Worksheet
Self-Esteem Worksheets for Students
What is an earthquake?
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the ground caused by the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth's surface. This movement releases energy in the form of seismic waves, which can result in the shaking and displacement of the Earth's surface, leading to potential damage to buildings, infrastructure, and landscapes.
How are earthquakes caused?
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, which creates seismic waves. This release of energy is typically the result of tectonic plates shifting and sliding past each other along faults in the Earth's crust. The stress and pressure that build up along these faults eventually reach a breaking point, causing movement that generates seismic waves and results in an earthquake.
What are the three main types of faults?
The three main types of faults are normal faults, reverse faults, and strike-slip faults. Normal faults occur when tensional stresses cause the hanging wall to move downward relative to the footwall. Reverse faults occur when compressional stresses cause the hanging wall to move upward relative to the footwall. Strike-slip faults occur when horizontal stresses cause rocks on either side of the fault to slide horizontally past each other.
How does the Richter scale measure the magnitude of an earthquake?
The Richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake based on the logarithm of the amplitude of seismic waves recorded on seismographs. The scale assigns a single number to quantify the energy released during an earthquake, with each whole number increase representing a tenfold increase in amplitude and approximately 31.6 times more energy released.
What is the difference between the epicenter and the focus of an earthquake?
The epicenter of an earthquake is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus, or hypocenter, which is the point within the Earth where the earthquake originates. In other words, the focus is where the seismic energy is released, while the epicenter is the point on the surface closest to the focus.
How do seismographs detect and record earthquakes?
Seismographs detect and record earthquakes by measuring the seismic waves generated by the shaking of the Earth's crust. When an earthquake occurs, it sends out different types of seismic waves that travel through the Earth at different speeds. Seismographs consist of a mass attached to a spring, which moves in response to ground motion. This movement is then recorded on a rotating drum or digitally, creating a seismogram that shows the amplitude and arrival times of the seismic waves. By analyzing these seismograms, scientists can determine the location, magnitude, and depth of an earthquake.
What are the primary effects of earthquakes on the Earth's surface?
The primary effects of earthquakes on the Earth's surface include ground shaking, which can cause buildings and infrastructure to collapse or be damaged; ground rupture, where the ground shifts along a fault line, potentially causing displacement and changes in land elevation; landslides and avalanches triggered by the shaking of the ground; and tsunamis if the earthquake occurs under the ocean, leading to massive waves that can inundate coastal areas.
What are the secondary effects of earthquakes on human communities?
The secondary effects of earthquakes on human communities include landslides, tsunamis, flooding, fires, infrastructure damage, and disrupted utilities such as electricity, water, and communication systems. These effects can lead to injuries, fatalities, displacement of populations, economic loss, and long-term mental health issues. Additionally, the destruction of homes and buildings can result in a lack of shelter and access to essential services, exacerbating the impact on communities already facing challenges from the initial earthquake.
How can people prepare for and stay safe during an earthquake?
To prepare for an earthquake and stay safe during one, people should secure heavy furniture, appliances, and objects that may fall, create an emergency kit with food, water, first aid supplies, and important documents, practice drop, cover, and hold on drills, have a communication plan with family and neighbors, and know safe spots in every room like under sturdy furniture or against an interior wall. During an earthquake, people should stay indoors if possible, move away from windows, and drop to the ground, take cover under furniture, and hold on until shaking stops. If outdoors, stay away from buildings, trees, and powerlines. After the quake, check for injuries, damages, and gas leaks, and follow authorities' instructions for evacuation or sheltering in place.
What are some famous earthquakes in history and what were their impacts?
Some famous earthquakes in history and their impacts include the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, which resulted in widespread fires destroying most of the city and over 3,000 deaths; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, causing over 230,000 fatalities in multiple countries; and the 2010 Haiti earthquake, causing over 200,000 deaths and catastrophic damage to infrastructure. These earthquakes have left lasting impacts on the affected regions, causing loss of life, displacement of populations, and long-term economic and social consequences.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments