Drug Addiction Brain Worksheet
Drug addiction is a complex phenomenon that affects both the mind and the body. For individuals who want to delve deeper into understanding this subject, a drug addiction brain worksheet can prove to be a valuable tool. Designed to highlight the intricate relationship between drugs and the brain, this worksheet can assist individuals in grasping the impact of drug addiction on various aspects of cognitive function, behavior, and overall well-being.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
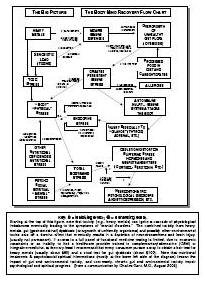
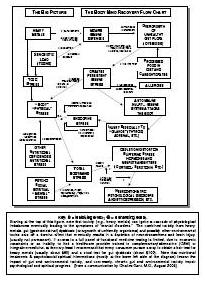
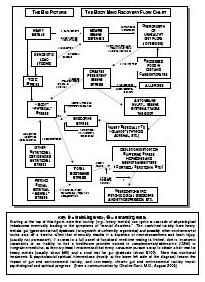
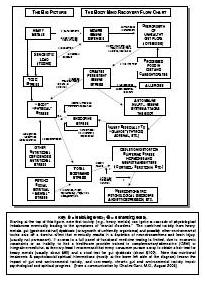
What is drug addiction?
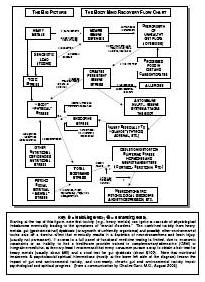
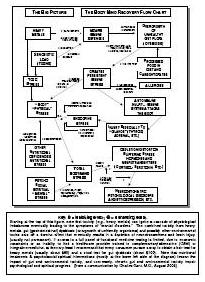
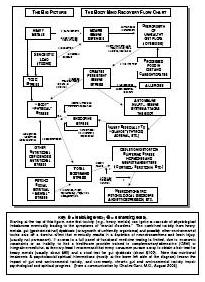
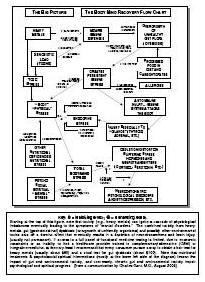
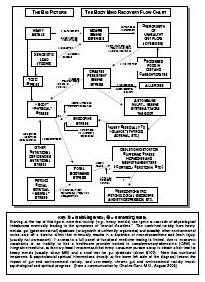
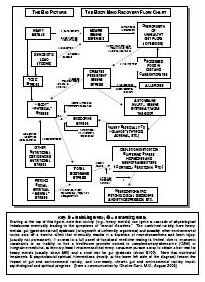
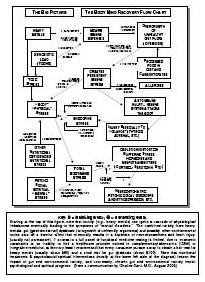
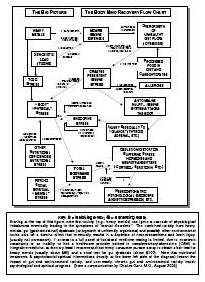
Drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking, use, and continued use despite harmful consequences. It is a complex condition that affects the brain's reward, motivation, and memory functions, leading to uncontrollable and harmful behaviors related to drug use. Treatment often involves a combination of therapy, medication, and support to help individuals overcome the physical and psychological effects of addiction.
How does drug addiction affect the brain?
Drug addiction can greatly impact the brain by altering its structure and function. Drugs can hijack the brain's reward system, leading to a surge of dopamine that reinforces drug use. Over time, this can lead to changes in brain chemistry and circuitry, impairing decision-making, impulse control, and stress regulation. The brain may also adapt to the presence of drugs, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. These changes can persist even after drug use stops, making it difficult for individuals to resist cravings and maintain sobriety.
What are the long-term effects of drug addiction on the brain?
Long-term drug addiction can have severe effects on the brain, including changes in brain structure and function. It can lead to impaired decision-making, memory loss, decreased ability to regulate emotions, and increased risk of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Drug addiction can also disrupt the brain's natural reward system, leading to cravings and compulsive drug-seeking behavior, making it harder for individuals to quit the substance.
What is the reward system in the brain and how does it relate to drug addiction?
The reward system in the brain is a complex network of structures that regulate pleasure, motivation, and reinforcement. It involves the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine in response to rewarding stimuli, signaling the brain to seek out that behavior or substance again. Drug addiction can hijack this reward system by causing an unnatural surge of dopamine levels, leading to the reinforcement of drug-seeking behaviors and the development of addiction. Over time, the brain's natural reward system becomes dysregulated, leading to compulsive drug use despite negative consequences. This highlights the powerful role of the reward system in driving addictive behaviors.
How does drug addiction impact decision-making processes in the brain?
Drug addiction can significantly impact decision-making processes in the brain by altering the functioning of the brain's reward system. Chronic drug use can lead to changes in the brain's dopamine pathways, causing an imbalance between impulse control and reward-seeking behavior. This imbalance can result in individuals prioritizing drug use over rational decision-making, leading to a cycle of addiction where the brain continues to seek out the drug despite negative consequences. Additionally, drug addiction can impair cognitive functions such as judgement, memory, and self-control, further exacerbating poor decision-making processes in individuals with substance use disorders.
What are the changes in neurotransmitter levels that occur with drug addiction?
Drug addiction can lead to changes in the levels of various neurotransmitters in the brain. For example, drugs like cocaine and amphetamines increase levels of dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. Opioids can increase the release of endorphins, which also contribute to feelings of pleasure and euphoria. Over time, chronic drug use can disrupt the natural balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when the drug is not present. Additionally, repeated drug use can impair the functioning of neurotransmitter systems involved in decision-making, impulse control, and stress regulation, contributing to the cycle of addiction.
How does drug addiction affect memory and learning abilities?
Drug addiction can have a detrimental impact on memory and learning abilities by disrupting the brain's normal functioning. Chronic drug use can impair memory formation, recall, and cognitive flexibility, leading to difficulties in learning new information, problem-solving, and decision-making. This is because drugs interfere with the communication between neurons in the brain, particularly in areas crucial for memory and learning, such as the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Additionally, drug-seeking behaviors and compulsive drug use can further exacerbate these cognitive deficits, making it challenging for individuals to break the cycle of addiction and engage in healthy, adaptive behaviors.
What are the structural changes that take place in the brain due to drug addiction?
Drug addiction results in significant structural changes in the brain, including alterations in brain circuits that regulate decision-making, impulse control, and reward processing. Chronic drug use can lead to the remodeling of neural pathways, changes in the release and uptake of neurotransmitters like dopamine, and modifications in the size and functioning of brain regions such as the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system. These changes contribute to the compulsive drug-seeking behavior and the difficulty in stopping drug use that are hallmark characteristics of addiction.
Which areas of the brain are most affected by drug addiction?
The areas of the brain most affected by drug addiction include the prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala. The prefrontal cortex regulates decision-making, impulse control, and judgment, while the nucleus accumbens is involved in reward processing and motivation. The amygdala plays a crucial role in processing emotions and forming memories related to drug use, contributing to the reinforcing effects of addictive substances.
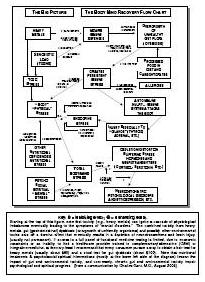
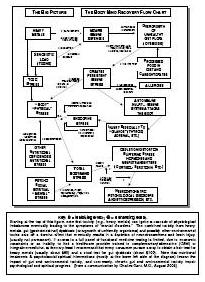
Can the brain recover from drug addiction-related damage?
Yes, the brain has a remarkable ability to recover from drug addiction-related damage through processes known as neuroplasticity and neurogenesis. With the cessation of drug use and appropriate treatment, structural and functional changes can occur in the brain that promote healing, reorganization, and the building of new neural pathways. Rehabilitation, therapy, and support can aid in this recovery process, allowing individuals to regain cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall well-being over time.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments