DNA Workshop PBS Worksheet Answers
Worksheets can be a beneficial tool for learners of all ages when it comes to understanding complex subjects. For those seeking a comprehensive guide to DNA workshops, finding the right worksheet answers is crucial. Whether you're an educator, student, or simply someone interested in delving into the fascinating world of DNA, having access to accurate and reliable worksheet answers can help solidify your understanding of this intricate subject.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Middle School
- Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Fingerprinting Worksheet
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet
- WebQuest Answer Key DNA and Protein Synthesis
- Restriction Mapping Problems AP Biology
- Genetics Study Guide Answers
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Pedigree Worksheet Answer Key
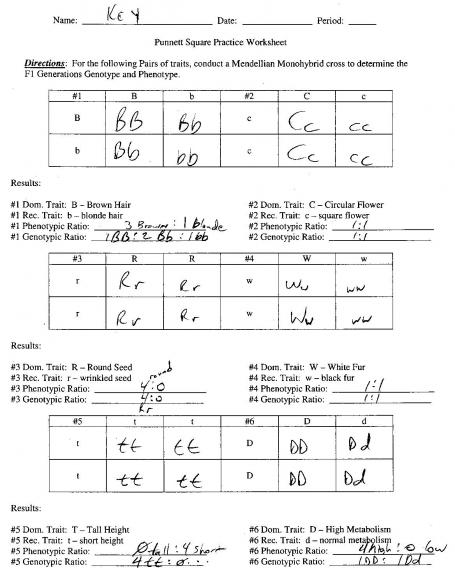
- Punnett Square Practice Problems Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Vocabulary Workshop Level E Unit 11 Answers
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
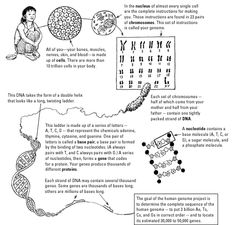
What is DNA made of?
DNA is made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). These nucleotides are arranged in a double helix structure to form the genetic code that carries the instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms.
What is the shape of DNA?
The shape of DNA is a double helix, which is like a twisted ladder. It consists of two strands that coil around each other, with the famous double helix structure being essential for the storage and transfer of genetic information in living organisms.
What are the four bases found in DNA?
The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up in specific combinations - A with T and C with G - to form the rungs of the DNA double helix, which carries the genetic information in living organisms.
How do the bases pair up in DNA?
In DNA, the bases pair up in complementary fashion with adenine (A) always pairing with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairing with guanine (G). This base pairing is fundamental to the structure of DNA and its ability to accurately store genetic information through replication and transcription processes.
What is the function of DNA polymerase during DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the complementary strand during DNA replication. It essentially reads the existing DNA strand and creates a new strand that is complimentary to the template, ensuring accurate replication of genetic information. DNA polymerase also has proofreading capabilities to correct any errors that may occur during replication, helping to maintain the integrity of the genetic code.
What is the purpose of DNA sequencing?
DNA sequencing is a crucial scientific technique used to determine the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. It helps researchers understand genetic information, gene variations, mutations, and relationships between genes and diseases. This information is vital for various fields such as genetics, biological research, personalized medicine, forensics, and evolutionary biology, contributing to advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and understanding of various diseases and conditions.
How does DNA transcription differ from DNA replication?
DNA transcription is the process in which a segment of DNA is used as a template to generate a complementary RNA molecule, while DNA replication is the process of copying an entire strand of DNA to create an identical daughter DNA molecule. In transcription, only a specific segment of DNA is transcribed into RNA, whereas in replication, the entire DNA molecule is duplicated. Additionally, transcription produces an RNA molecule as the end product, while replication results in two identical DNA molecules.
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
mRNA, or messenger RNA, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This genetic information is then used by the ribosomes to direct the synthesis of specific proteins through a process called translation. During translation, mRNA is read by ribosomes in groups of three nucleotides called codons, which correspond to specific amino acids. As the ribosome reads the mRNA, it catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, ultimately leading to the production of a specific protein based on the genetic code carried by the mRNA.
How are DNA mutations caused?
DNA mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including errors made during DNA replication, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, and environmental factors such as UV light. Mutations can also be inherited from parents or occur due to viral infections. Ultimately, mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to variations in traits or the development of diseases.
What is the importance of DNA in inheritance?
DNA is crucial in inheritance because it carries the genetic information that is passed down from parents to offspring. It determines traits, such as physical appearance, behavior, and susceptibility to diseases. The sequence of DNA in an individual's genes determines their unique characteristics and plays a key role in the transmission of genes from one generation to the next, making it the fundamental molecule for inheritance and passing on genetic information.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments