DNA Translation Worksheet
DNA translation is a fundamental process in molecular biology that allows the information encoded in DNA to be converted into functional proteins. If you're a student or a researcher seeking a comprehensive worksheet to enhance your understanding of this crucial topic, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of DNA translation and provide you with a suitable worksheet to delve deeper into this fascinating subject.
Table of Images 👆
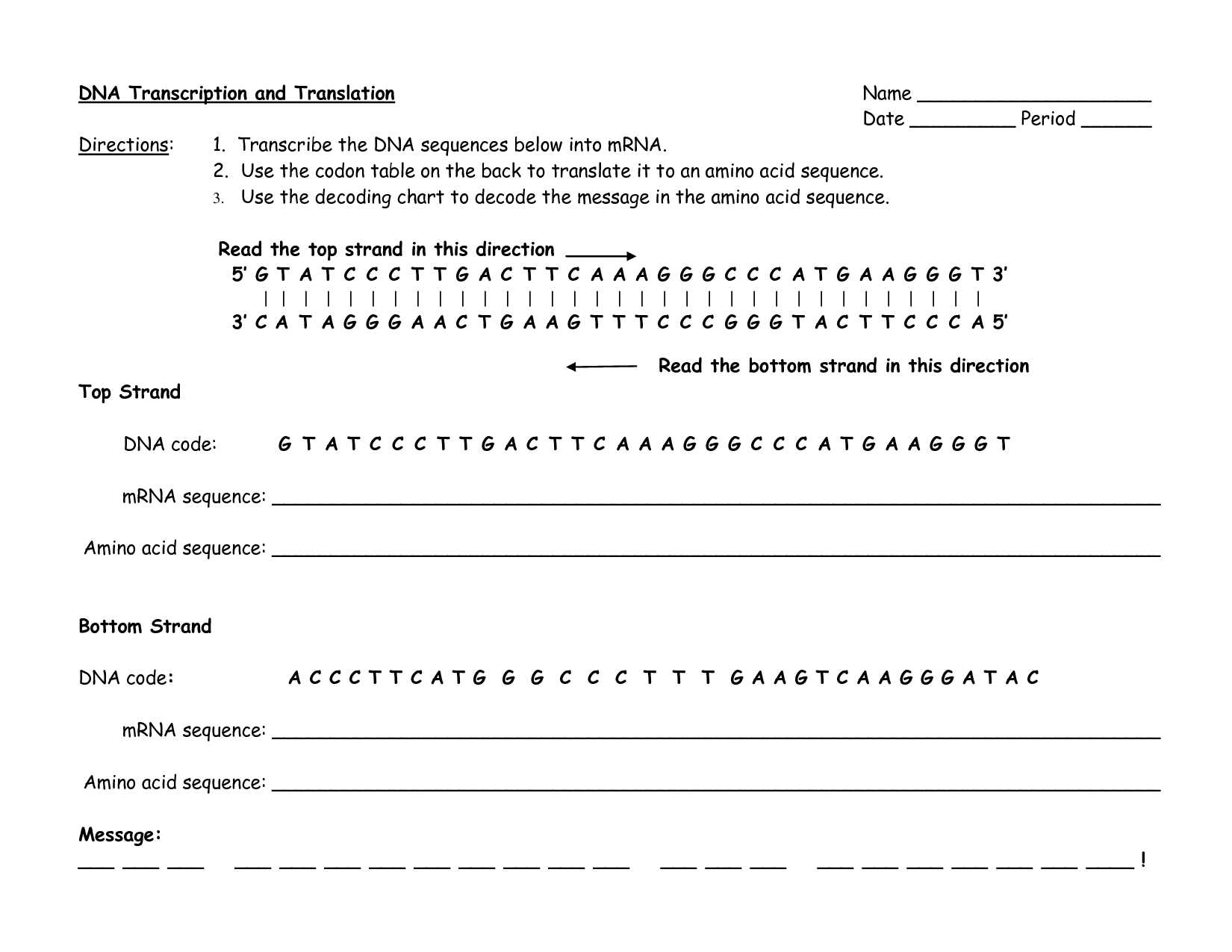
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is DNA translation?
DNA translation is the process in which the information stored in a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to synthesize a protein. This occurs at cellular ribosomes, where transfer RNA molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome based on the codons found on the mRNA. These amino acids are then linked together in a specific order to form a polypeptide chain, which will ultimately fold into a functional protein that carries out various functions within the cell.
Where does DNA translation occur?
DNA translation occurs in the cytoplasm of a cell, specifically at the ribosomes. Ribosomes are the cellular organelles responsible for synthesizing proteins by reading the mRNA molecule and assembling amino acids into a polypeptide chain based on the genetic information encoded in the DNA.
What is the role of mRNA in translation?
mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosome, where protein synthesis occurs during translation. The mRNA strand acts as a template for the ribosome to read and assemble amino acids in the correct order to build a specific protein. In this way, mRNA plays a crucial role in the process of translating the genetic code into functional proteins within the cell.
How is mRNA created in the process of transcription?
mRNA is created in the process of transcription by RNA polymerase enzymes that bind to a specific gene's promoter region on the DNA. The enzyme unwinds and unzips the DNA double helix at the promoter site, then reads the template strand to synthesize a complementary mRNA molecule through base pairing. As RNA polymerase moves down the gene, it continues to elongate the mRNA strand until it reaches a termination signal, at which point transcription ends and the newly formed mRNA molecule is released to be processed and translated into proteins.
What is the purpose of tRNA in translation?
tRNA, or transfer RNA, plays a crucial role in translation by bringing specific amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA sequence during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule is attached to a specific amino acid at one end and has an anticodon sequence at the other end that corresponds to a specific mRNA codon. This matching of codon-anticodon sequences ensures that the correct amino acids are incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain, allowing for the accurate assembly of proteins.
What is an anticodon and how does it relate to tRNA?
An anticodon is a sequence of three nucleotides on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules that base-pair with a complementary codon in mRNA during translation. The anticodon is crucial in ensuring that the correct amino acid is brought to the ribosome to be incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain. By recognizing and binding to specific codons on mRNA, the anticodon acts as a key intermediary in translating the genetic code into proteins.
What is the start codon and what does it signify?
The start codon is the codon "AUG" in mRNA, which codes for the amino acid methionine. It signifies the beginning of translation in protein synthesis, as it marks the initiation point for assembling the amino acid sequence that makes up a protein.
How is the genetic code read to determine the amino acid sequence?
The genetic code is read through a process called translation, where messenger RNA (mRNA) transcribed from DNA is used as a template to assemble amino acids into a protein. Ribosomes, along with transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carrying specific amino acids, bind to the mRNA in a sequence determined by the complementary base pairing between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, it reads the codons and adds the corresponding amino acids, linking them together to form a polypeptide chain that folds into a functional protein.
What happens at the ribosome during translation?
During translation at the ribosome, messenger RNA (mRNA) is read by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules containing specific amino acids. The ribosome decodes the mRNA sequence and assembles the amino acids brought in by tRNA molecules to form a polypeptide chain. This process continues until a stop codon is reached, resulting in the synthesis of a protein based on the genetic information carried by the mRNA.
What is the significance of DNA translation in protein synthesis?
DNA translation is a crucial step in protein synthesis where the information encoded in the DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and then translated into a specific sequence of amino acids to form a protein. This process is essential for the production of proteins, which are the building blocks of cells and perform a wide array of functions within an organism. DNA translation ensures that the genetic information stored in the DNA is effectively used to synthesize the proteins needed for various biological processes, ultimately influencing the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



































Comments