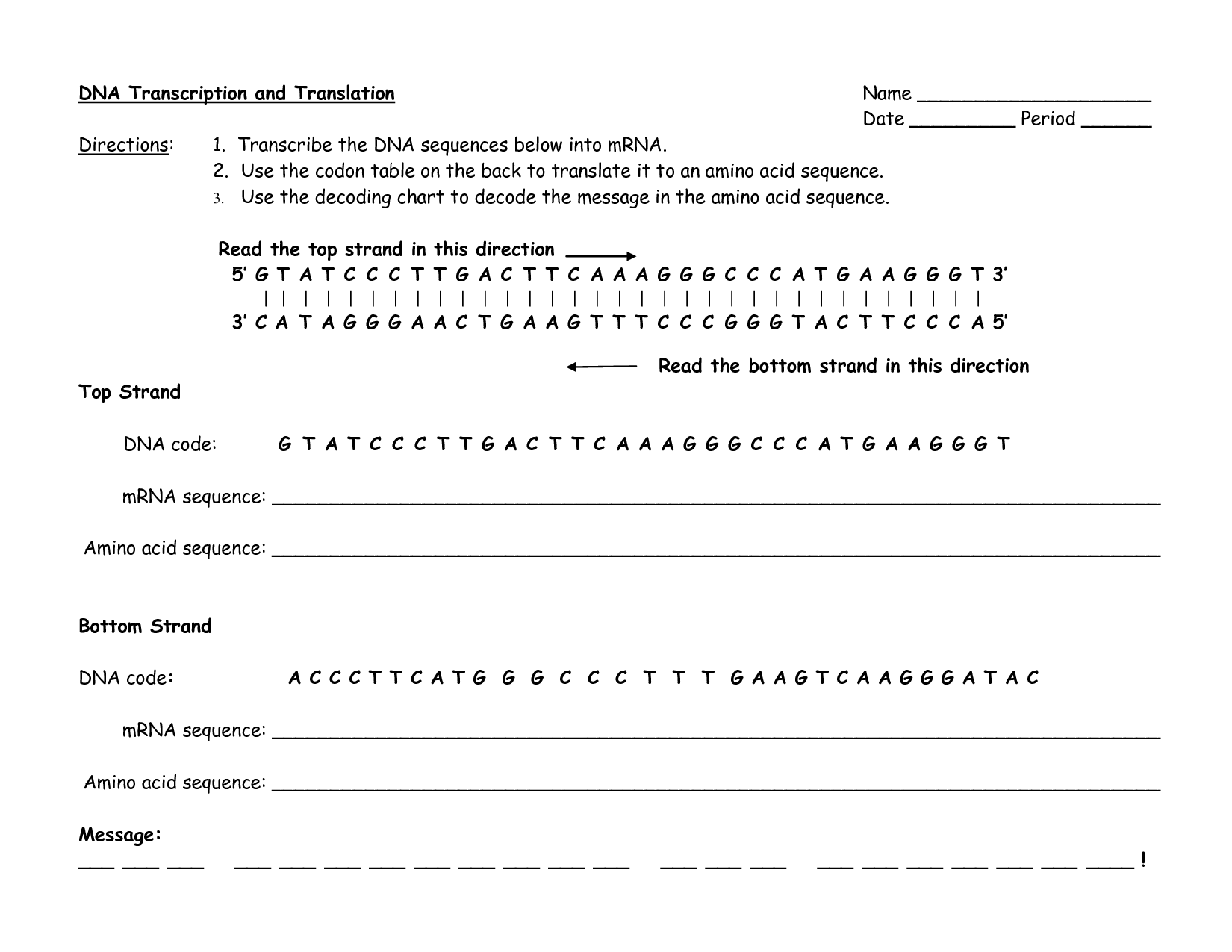
DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
Are you an aspiring biologist or a student studying genetics? If so, we have just the resource for you! Introducing our DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet, designed to help you grasp the intricate processes involved in gene expression. With its comprehensive content and engaging exercises, this worksheet provides a valuable tool for understanding the connection between DNA and protein synthesis.
Table of Images 👆
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is DNA transcription?
DNA transcription is the process where a specific segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme RNA polymerase. This is an essential step in gene expression, as the RNA copy, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), can then be used by the cell to direct the synthesis of proteins through the process of translation.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template during the process of transcription. It binds to the DNA at specific regions called promoters and unwinds the double helix, allowing the RNA polymerase to read the DNA sequence and synthesize a complementary RNA strand. This enzyme plays a crucial role in gene expression by transcribing the genetic information stored in the DNA into functional RNA molecules, such as messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), which are essential for protein synthesis and various cellular processes.
What are the three main steps of transcription?
The three main steps of transcription are initiation, where the RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region on the DNA, elongation, where the RNA polymerase synthesizes the mRNA by adding nucleotides complementary to the DNA template, and termination, where the RNA polymerase reaches the termination sequence and releases the newly formed mRNA molecule.
What is the function of the promoter region in transcription?
The promoter region in transcription serves as the site where RNA polymerase binds to initiate the process of transcription. It contains specific DNA sequences that help regulate the initiation of gene expression by recruiting transcription factors and other regulatory proteins. The promoter region plays a crucial role in determining when and how strongly a gene is transcribed into RNA, making it a key element in regulating gene expression.
What is the purpose of the terminator sequence in transcription?
The terminator sequence in transcription serves as a signal to the RNA polymerase to stop transcribing the DNA template. It marks the end of the gene being transcribed and helps in the proper termination of transcription, ensuring that the RNA molecule is accurately and fully synthesized.
What is RNA splicing and why is it important in transcription?
RNA splicing is the process in which non-coding regions of mRNA molecules, known as introns, are removed and the remaining protein-coding regions, known as exons, are joined together to form a mature mRNA molecule. This process is crucial in transcription because it allows for the production of multiple protein variants from a single gene. By removing introns and joining exons in different combinations, cells can generate a diverse array of proteins that play different roles in various cellular processes. This helps increase the functional complexity and diversity of the proteome, allowing organisms to carry out complex biological functions.
How is RNA different from DNA in terms of structure and function?
RNA differs from DNA in structure as it is typically single-stranded while DNA is double-stranded. RNA uses the sugar ribose, as opposed to deoxyribose used in DNA. Additionally, RNA contains uracil instead of thymine found in DNA. Functionally, RNA is primarily involved in protein synthesis, serving as a messenger between DNA and the ribosomes where proteins are made, while DNA carries the genetic information that is passed down from one generation to the next.
What is the genetic code and how is it related to translation?
The genetic code is a set of rules that determine how RNA sequences (specifically messenger RNA) are translated into proteins by the ribosomes. The code consists of codons, which are three-nucleotide sequences that correspond to specific amino acids. These codons are read by the ribosomes during protein synthesis, with each codon directing the insertion of a particular amino acid into the growing protein chain. Therefore, the genetic code serves as the bridge between the sequence of nucleotides in an mRNA molecule and the sequence of amino acids in a protein, playing a crucial role in the process of translation.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes play a crucial role in translation by acting as the site where messenger RNA (mRNA) is translated into proteins. They bind to the mRNA strand and "read" the genetic code, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to bring amino acids to the ribosome. The ribosome then links the amino acids together in the correct order to form a protein chain, based on the instructions encoded in the mRNA. Ultimately, ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins, which are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of cells.
What are the three main stages of translation?
The three main stages of translation are initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, the ribosome assembles around the start codon on the mRNA. During elongation, the ribosome moves along the mRNA, matching tRNA anticodons to mRNA codons and forming a growing polypeptide chain. Finally, termination occurs when a stop codon is reached, signaling the release of the completed polypeptide and disassembly of the ribosome complex.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments