DNA Structure Worksheet
The DNA structure worksheet provides an engaging and informative tool for students to delve into the intricacies of this essential molecule. Designed to captivate young minds, this worksheet serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the entity and subject of DNA, enabling students to grasp its fundamental structure and functions in a concise and clear manner.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
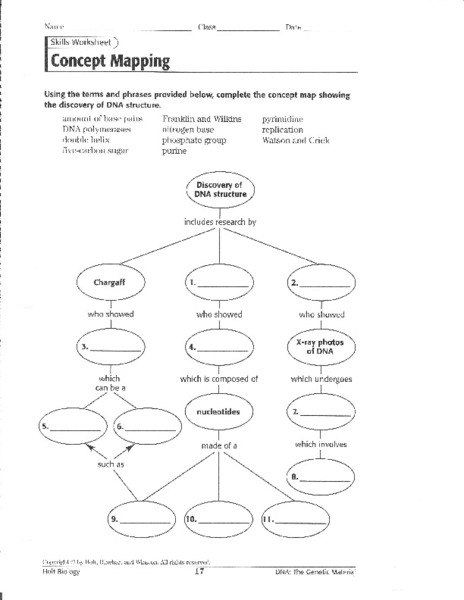
- DNA Structure Concept Map Worksheet
- DNA Replication Activity Worksheet
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Replication Structure Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Model Worksheet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
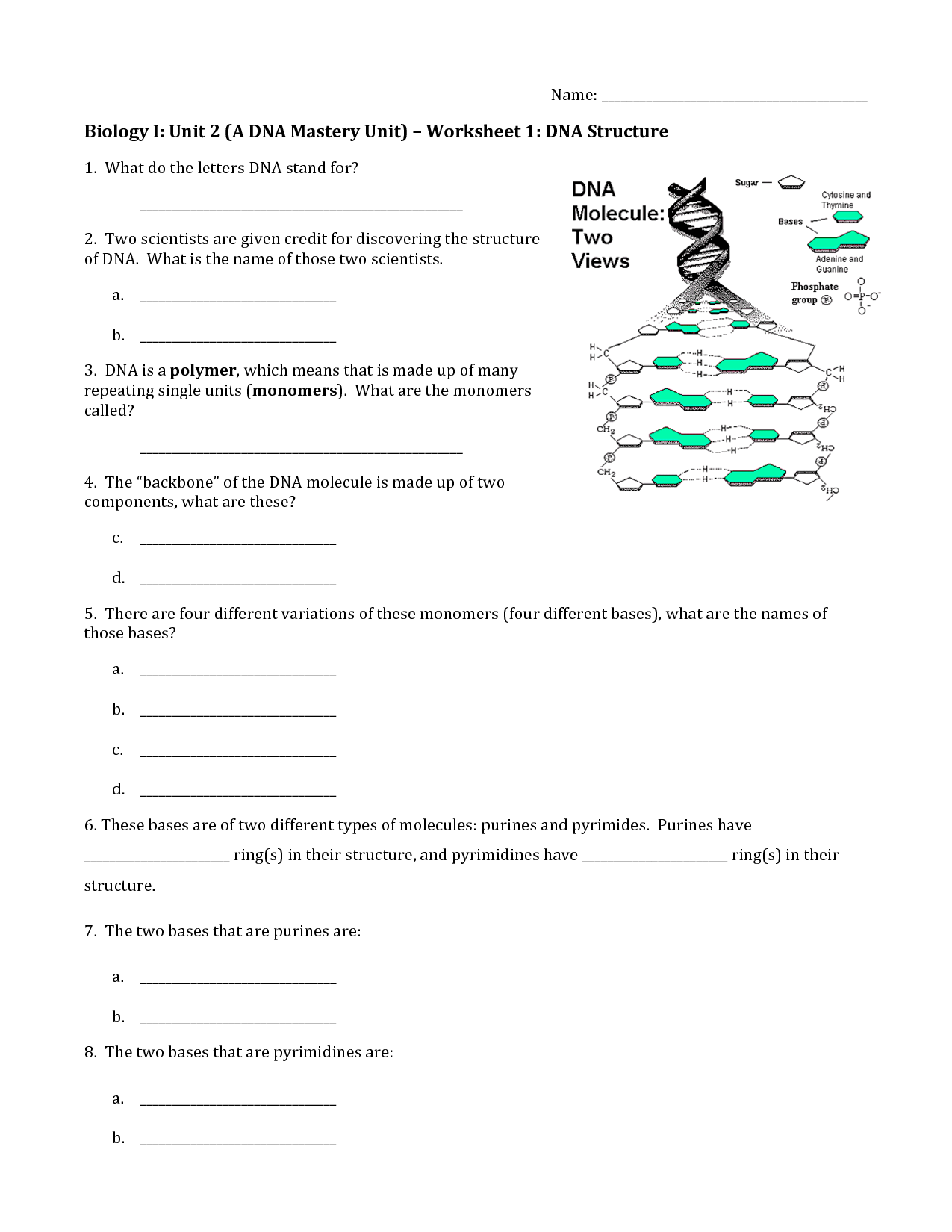
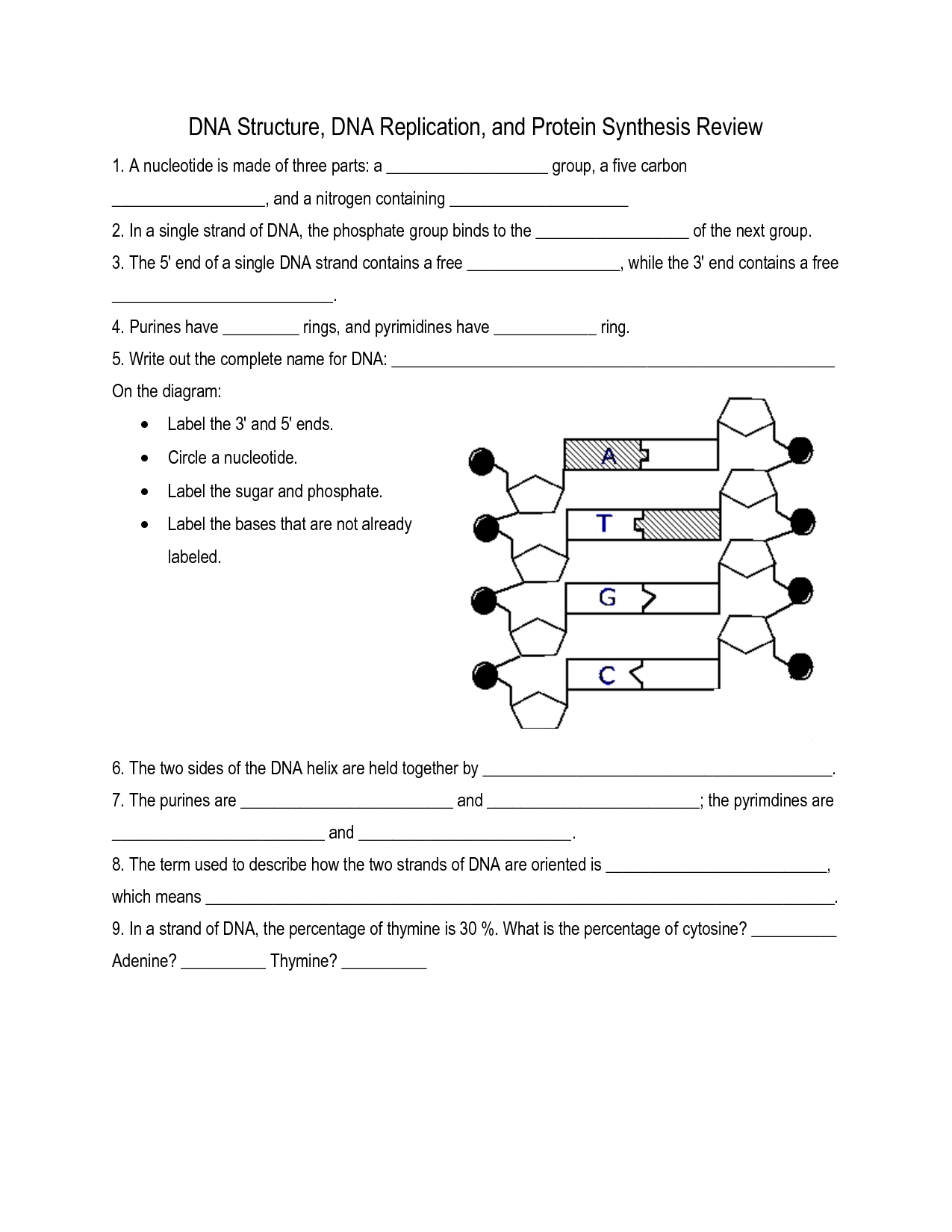
What is the overall shape of DNA?
The overall shape of DNA is a double helix, where two long strands of nucleotides intertwine to form a twisted ladder-like structure.
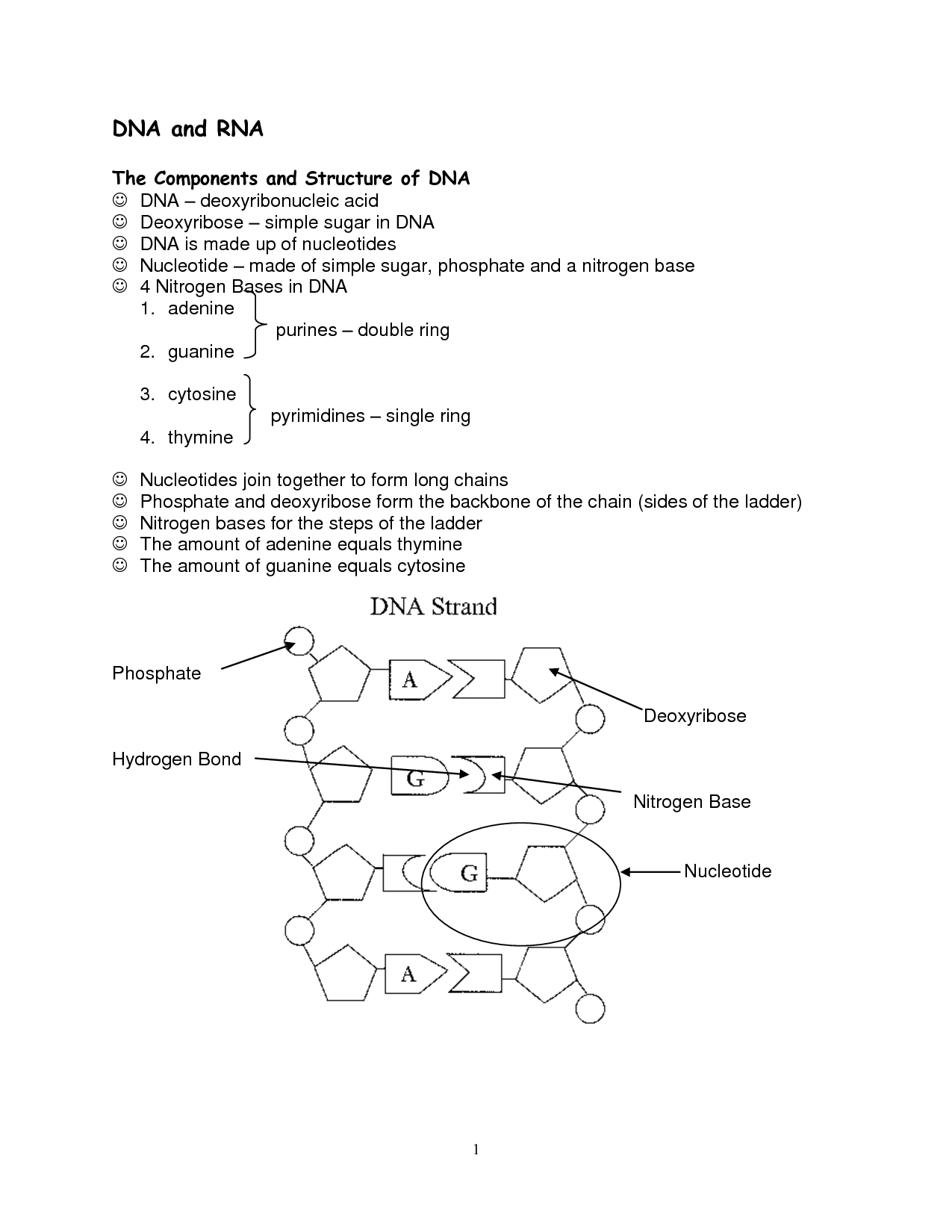
What are the building blocks of DNA?
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). These nucleotides are arranged in a specific sequence to form the double helix structure of DNA, where adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What are the two components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base.
What type of bond holds the two strands of DNA together?
Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands of DNA together. These bonds form between the nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides on each strand, specifically between adenine and thymine, and guanine and cytosine. The hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds but are crucial for stabilizing the double helix structure of DNA.
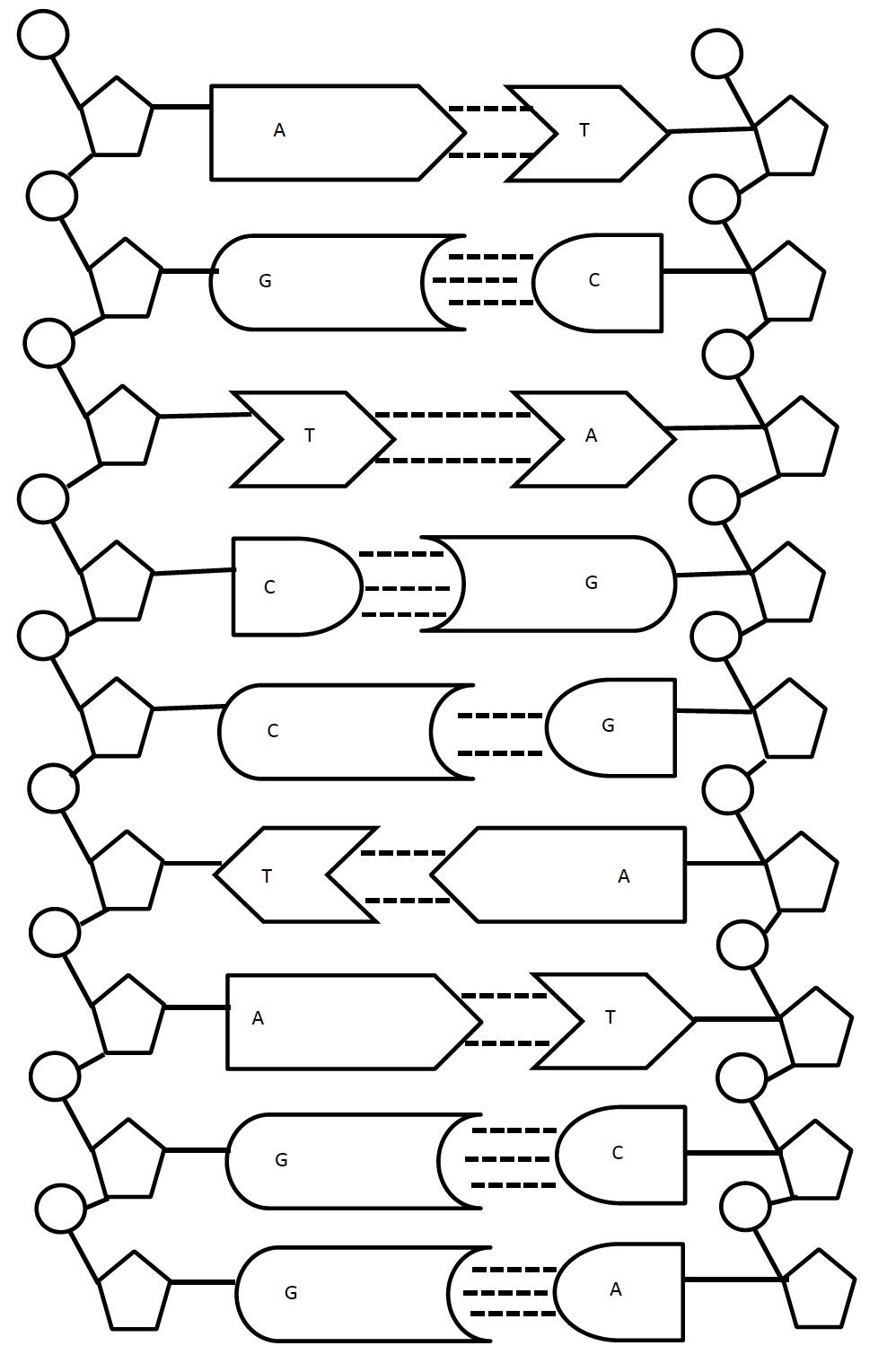
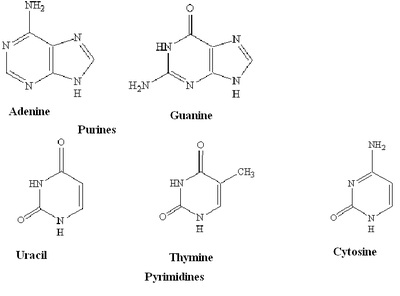
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up to form the building blocks of the DNA double helix, with adenine always pairing with thymine and cytosine always pairing with guanine.
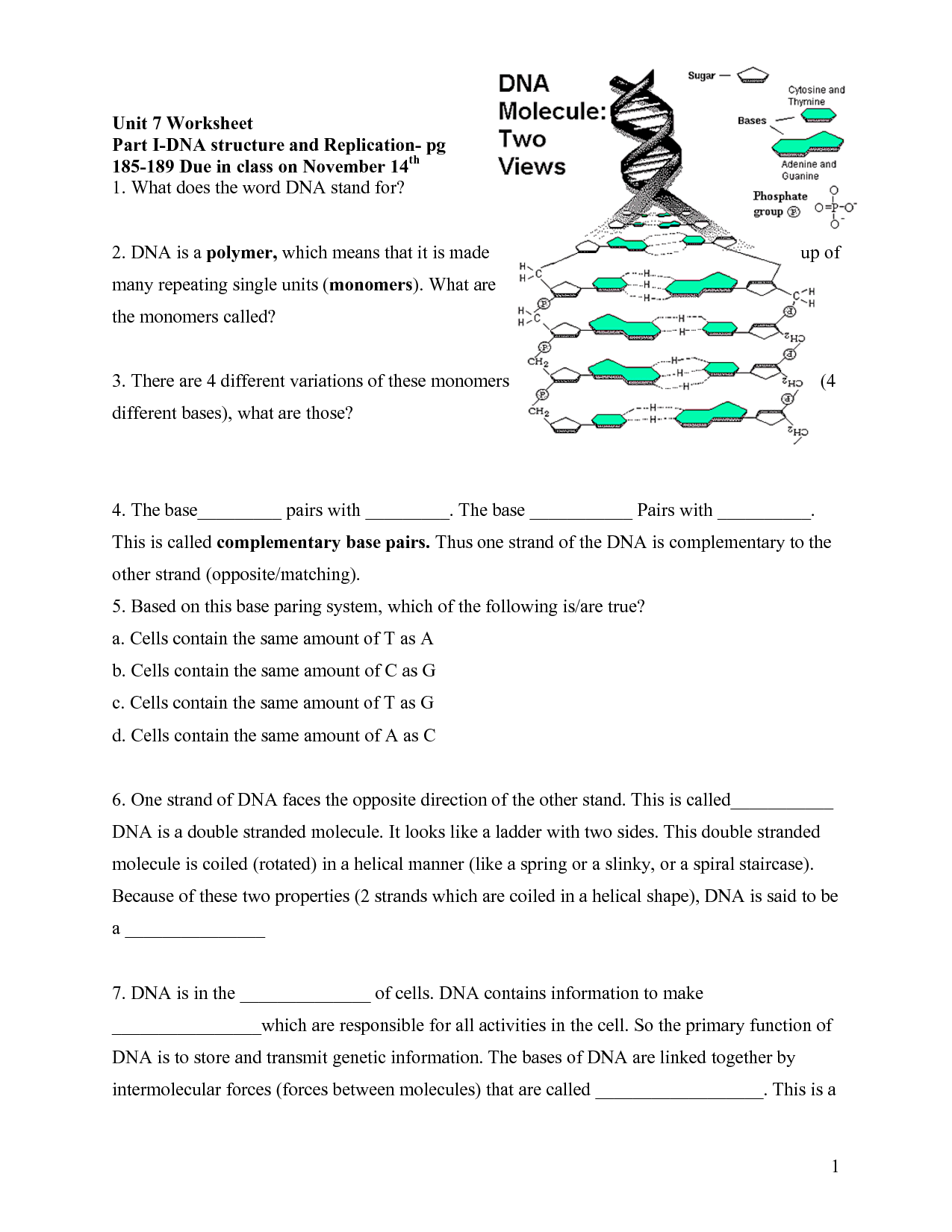
How do the nitrogenous bases pair up in DNA?
In DNA, the nitrogenous bases pair up in specific combinations known as complementary base pairs: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). This pairing is essential for the structure and function of DNA molecules, as it enables the accurate replication of genetic information during cell division.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure?
Hydrogen bonds in DNA structure play a critical role in maintaining the double helical structure of the DNA molecule. These bonds form between the nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides, specifically between adenine and thymine, and between guanine and cytosine. They help stabilize the DNA helix by holding the two strands together, allowing for the genetic information to be accurately replicated and transcribed. Without hydrogen bonds, the DNA molecule would not be able to maintain its specific shape and perform its essential functions in storing and transmitting genetic information.
What is the function of the sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA?
The sugar-phosphate backbone in DNA provides the structural framework and stability for the molecule. It helps hold the nitrogenous bases in place, ensuring that the genetic information is maintained in the correct sequence. Additionally, the negative charge of the phosphate groups along the backbone helps repel other negatively charged molecules, preventing interference with the DNA molecule.
How does DNA structure allow for replication?
The DNA molecule consists of two complementary strands that can separate from each other, allowing each strand to serve as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. During replication, enzymes unwind the double helix structure of DNA, exposing the bases on each strand. DNA polymerase then reads the template strand and adds new nucleotides to form a new complementary strand. This process enables the accurate duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA.
How is DNA compacted and organized in the nucleus of cells?
DNA in the nucleus of cells is compacted and organized through a hierarchical structure. The first level of compaction is the wrapping of DNA around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which then further coil into chromatin fibers. These fibers then loop and coil into higher-order structures, ultimately condensing into distinct chromosomes during cell division. Specific proteins, such as condensins and cohesins, play essential roles in organizing and shaping the DNA within the nucleus, allowing for proper gene regulation and cell function.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments