DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a high school biology student who wants to master the concepts of DNA structure and replication? Look no further! This blog post provides you with a comprehensive DNA structure and replication worksheet answer key. With this resource, you will be able to fully grasp the intricacies of DNA and confidently tackle any related questions or assignments.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
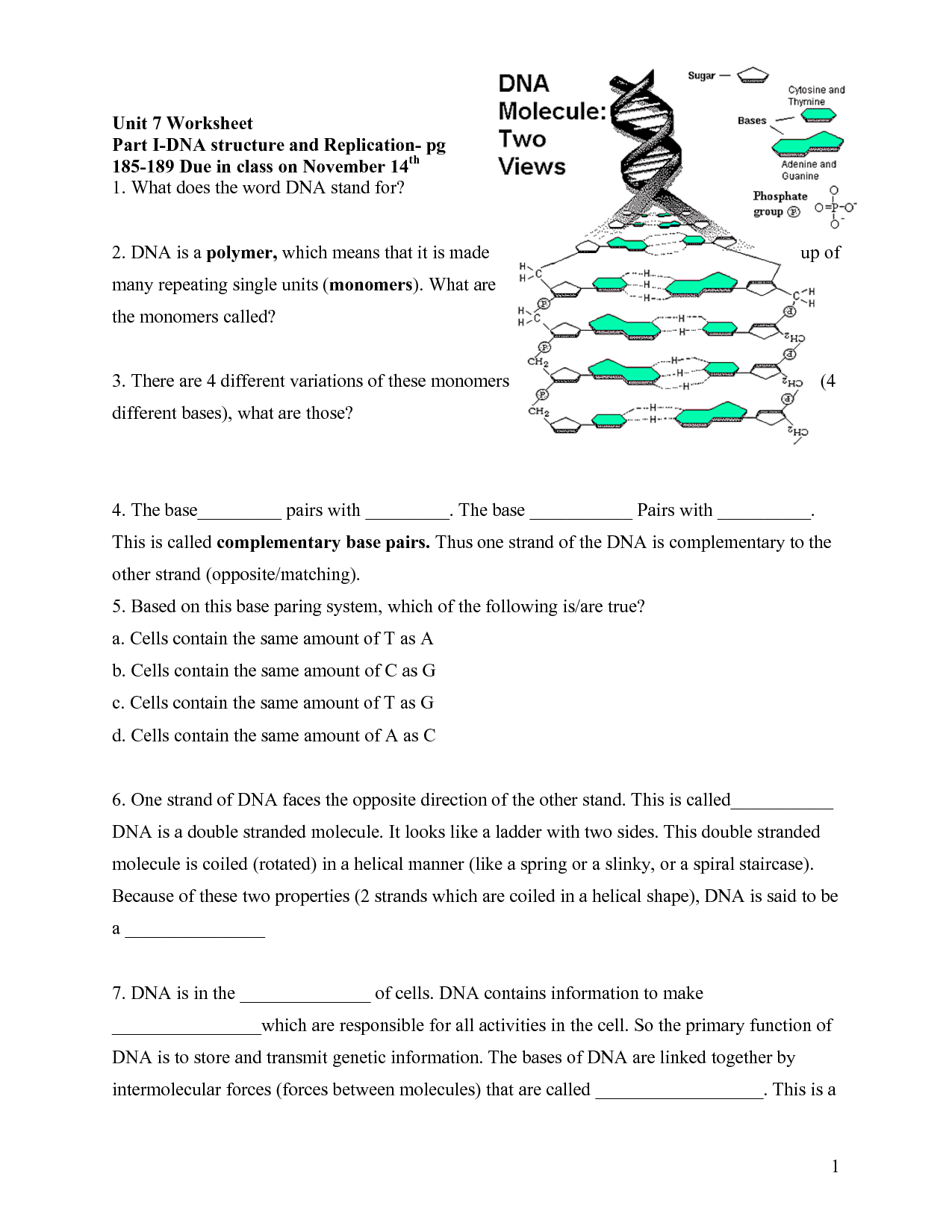
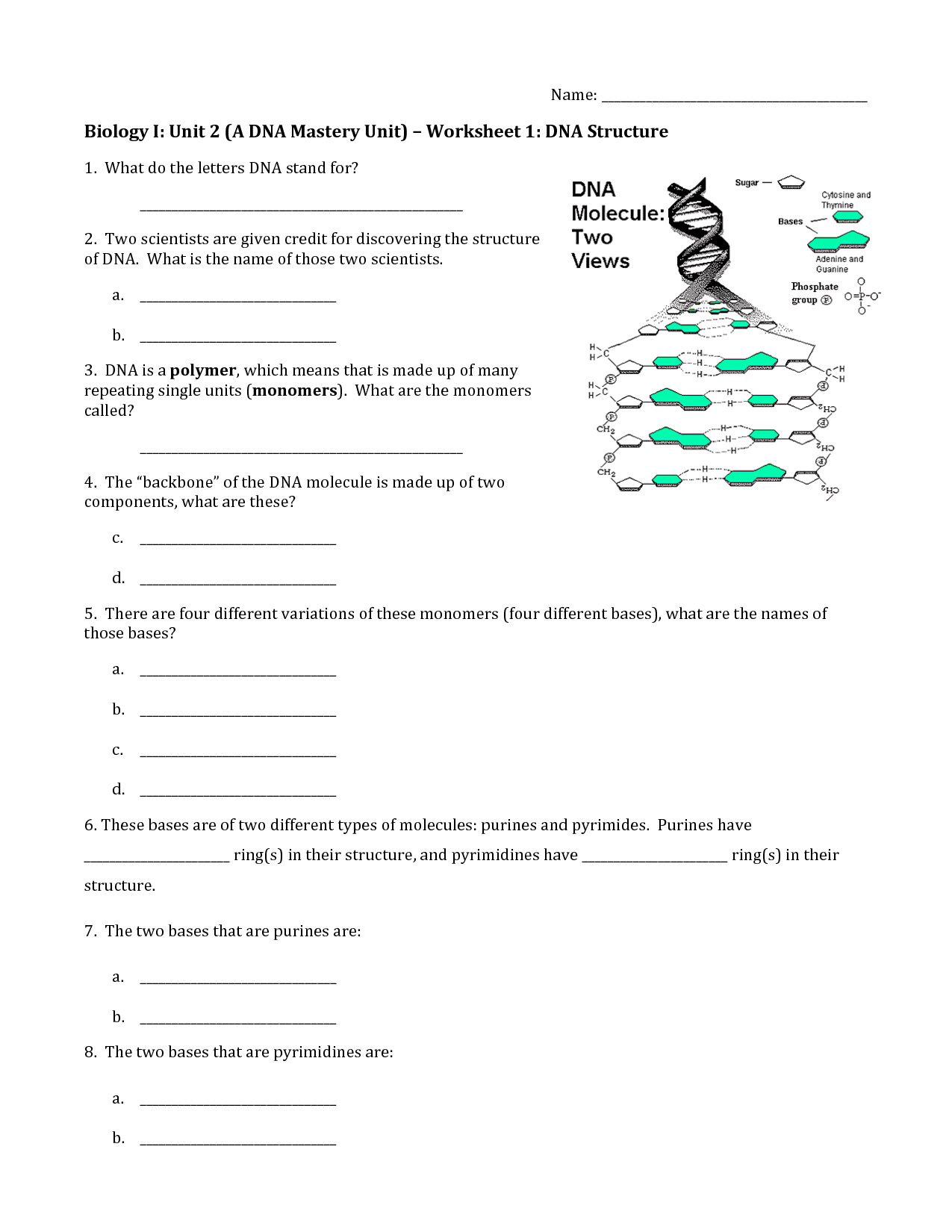
What does DNA stand for?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
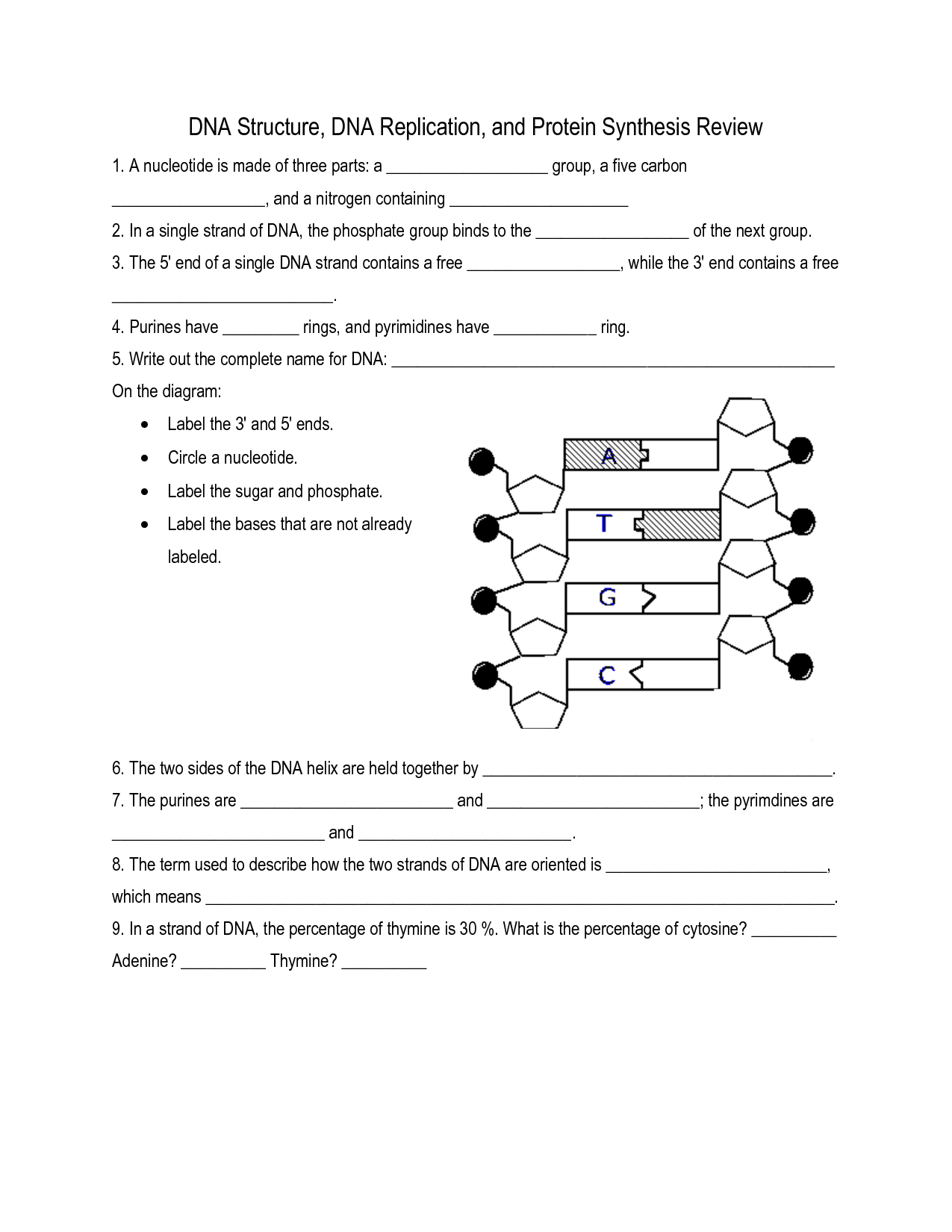
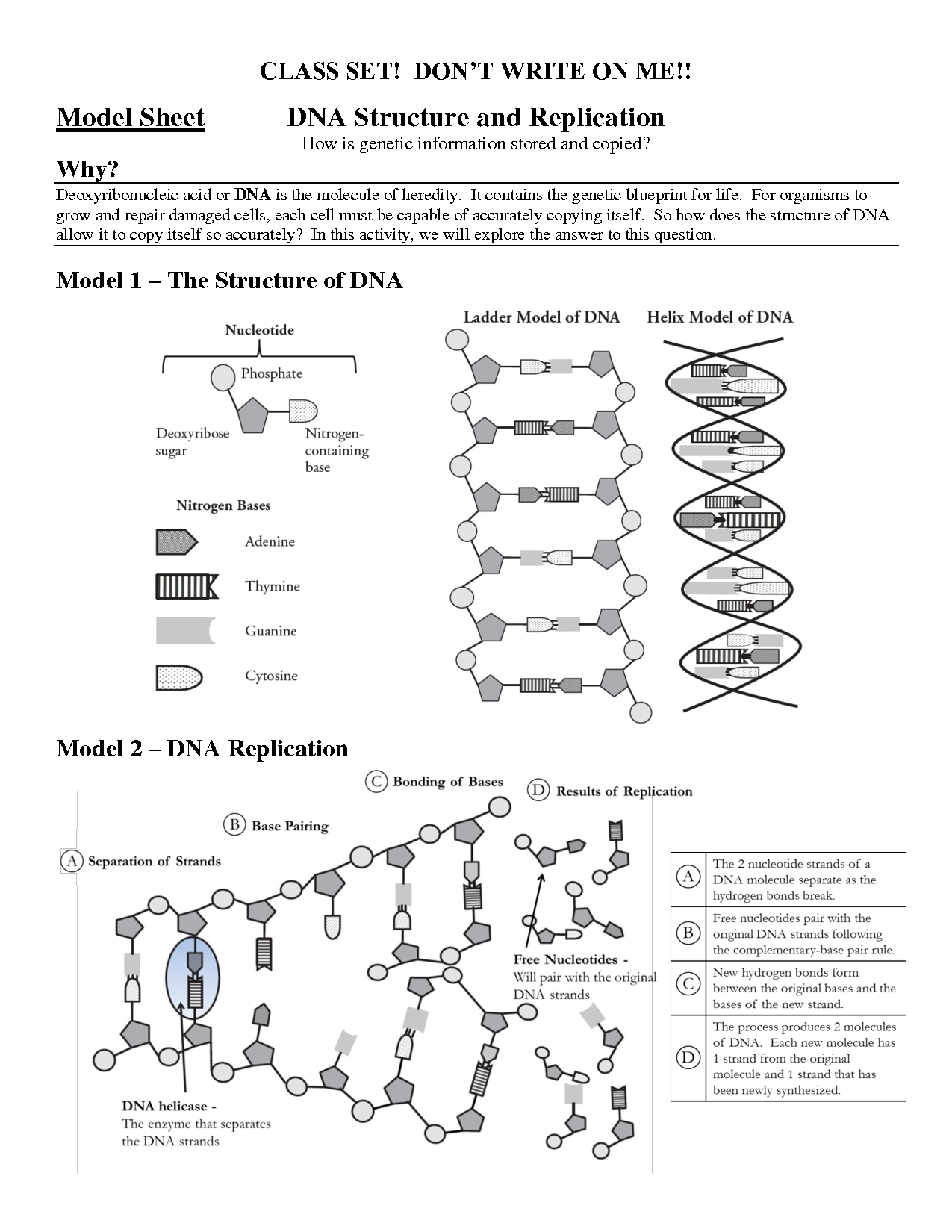
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide consists of three components: a sugar molecule (either ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (either adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine in DNA, or adenine, uracil, cytosine, or guanine in RNA).
How are nucleotides arranged in a DNA molecule?
Nucleotides are arranged in a DNA molecule as a double helix structure, where two strands of nucleotides are bound together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (adenine pairs with thymine, cytosine pairs with guanine). The nucleotide sequence in one strand determines the sequence in the other strand, creating a stable and complementary pairing that forms the basis of genetic information storage and replication in living organisms.
What are the base pairing rules in DNA?
The base pairing rules in DNA dictate that adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C), forming complementary base pairs. This principle of complementary base pairing is essential for the replication and transcription of DNA, as well as understanding genetic coding and inheritance in organisms.
Describe the structure of a DNA molecule.
A DNA molecule is a double helix structure composed of two long strands of nucleotides twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. This base pairing allows for the replication of DNA and the transfer of genetic information.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of new DNA strands during DNA replication. It does so by adding nucleotides to the growing DNA chain, following the base-pairing rules where adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). DNA polymerase also has proofreading capabilities to ensure accurate replication, making it a crucial player in maintaining the integrity and fidelity of the genetic information passed on to daughter cells.
What is the function of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication by unwinding the double-stranded DNA helix, separating the two DNA strands and creating a replication fork. This unwinding process allows the DNA polymerase enzyme to access and copy the DNA template during replication. By separating the DNA strands, helicase helps ensure accurate and efficient DNA replication.
What is the significance of the leading and lagging strands in DNA replication?
The leading and lagging strands in DNA replication are significant because they represent the two different ways in which the two DNA strands are synthesized. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, allowing for smooth and uninterrupted replication, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous fragments called Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together by DNA ligase. This process ensures accurate and efficient replication of the entire DNA molecule.
Describe the process of DNA replication.
DNA replication is a complex process that occurs in the nucleus of a cell during the S phase of the cell cycle. It begins with the unwinding of the double helix structure of the DNA molecule by helicase enzymes. The separated strands serve as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands by DNA polymerase enzymes. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments which are later joined by DNA ligase. This results in two identical daughter DNA molecules, each containing one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
How does DNA replication ensure its accuracy?
DNA replication ensures its accuracy through a series of mechanisms. The DNA polymerase enzyme checks the base pairing between the template strand and the newly synthesized strand, correcting any errors through proofreading. Additionally, mismatch repair enzymes scan the newly synthesized DNA for errors and correct them. Furthermore, the DNA replication process is highly regulated, with checkpoints and signaling pathways that monitor and control the process, ensuring that errors are detected and fixed before the cell divides. Overall, these mechanisms work together to maintain the fidelity of DNA replication and limit the accumulation of errors in the genetic material.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments