DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
If you're a biology student or a science enthusiast looking to reinforce your understanding of DNA mutations, this DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key is here to assist you! This comprehensive answer key provides detailed explanations for each question, ensuring you grasp the concepts of DNA mutations and their effects on organisms.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer
- Worksheet Mutations Practice Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a DNA mutation?
A DNA mutation is a permanent change in the sequence of nucleotides within DNA molecules, which can occur spontaneously or be induced by external factors such as radiation or chemicals. Mutations can alter the structure or function of proteins, leading to a variety of outcomes ranging from harmless to harmful, including genetic disorders, diseases, or even beneficial adaptations in evolution.
What causes DNA mutations?
DNA mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to mutagenic agents such as radiation, chemicals, and certain viruses. Additionally, errors that occur during DNA replication or repair processes can lead to mutations. Factors such as UV radiation from the sun, smoking, and aging can also contribute to the accumulation of mutations in DNA.
How do DNA mutations affect genetic information?
DNA mutations can alter the genetic information by changing the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. This can lead to different proteins being produced or affect gene regulation, ultimately influencing the organism's traits and health. Mutations can be neutral, beneficial, or harmful, with harmful mutations potentially causing genetic disorders or diseases. The impact of DNA mutations on genetic information underscores the essential role they play in evolution and the diversity of life on Earth.
What are the different types of DNA mutations?
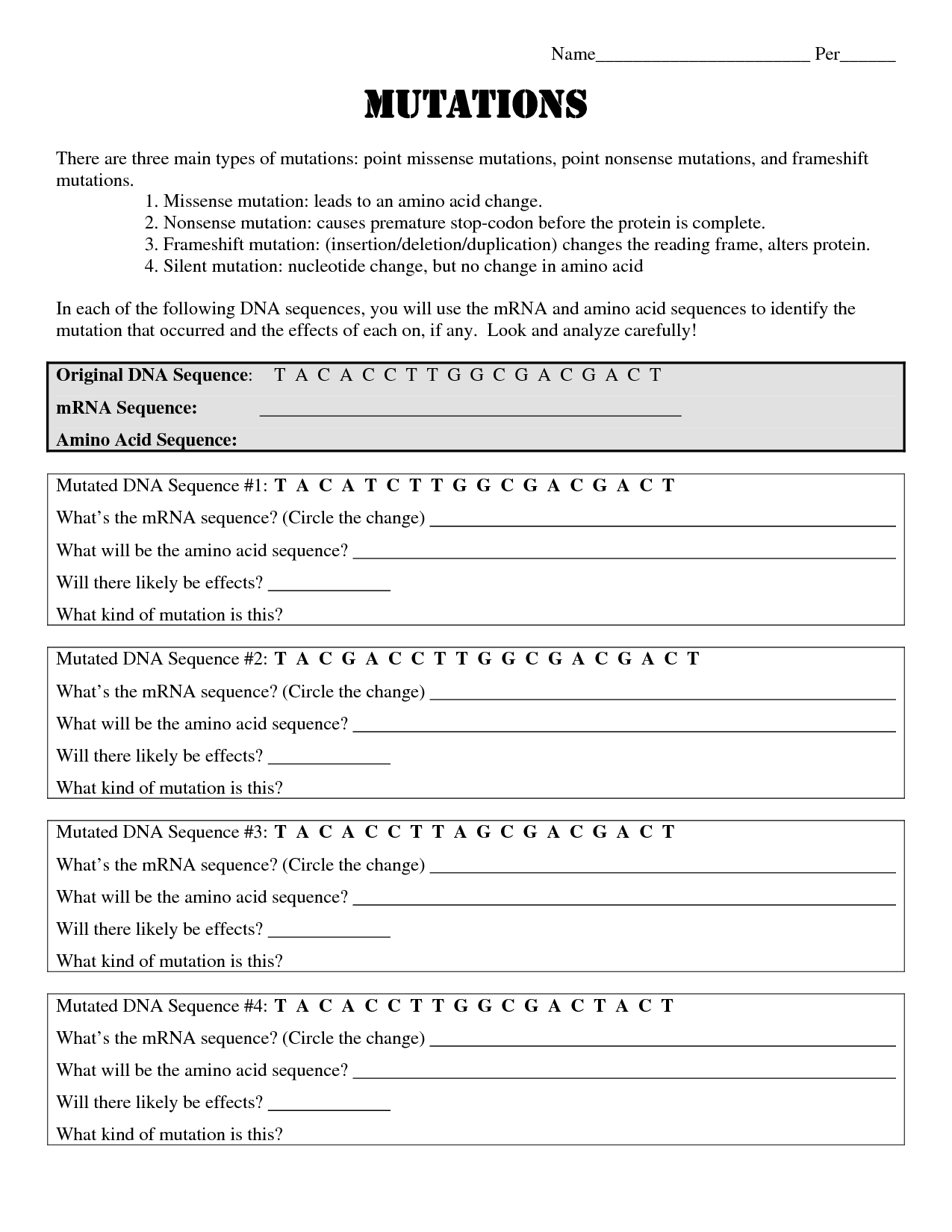
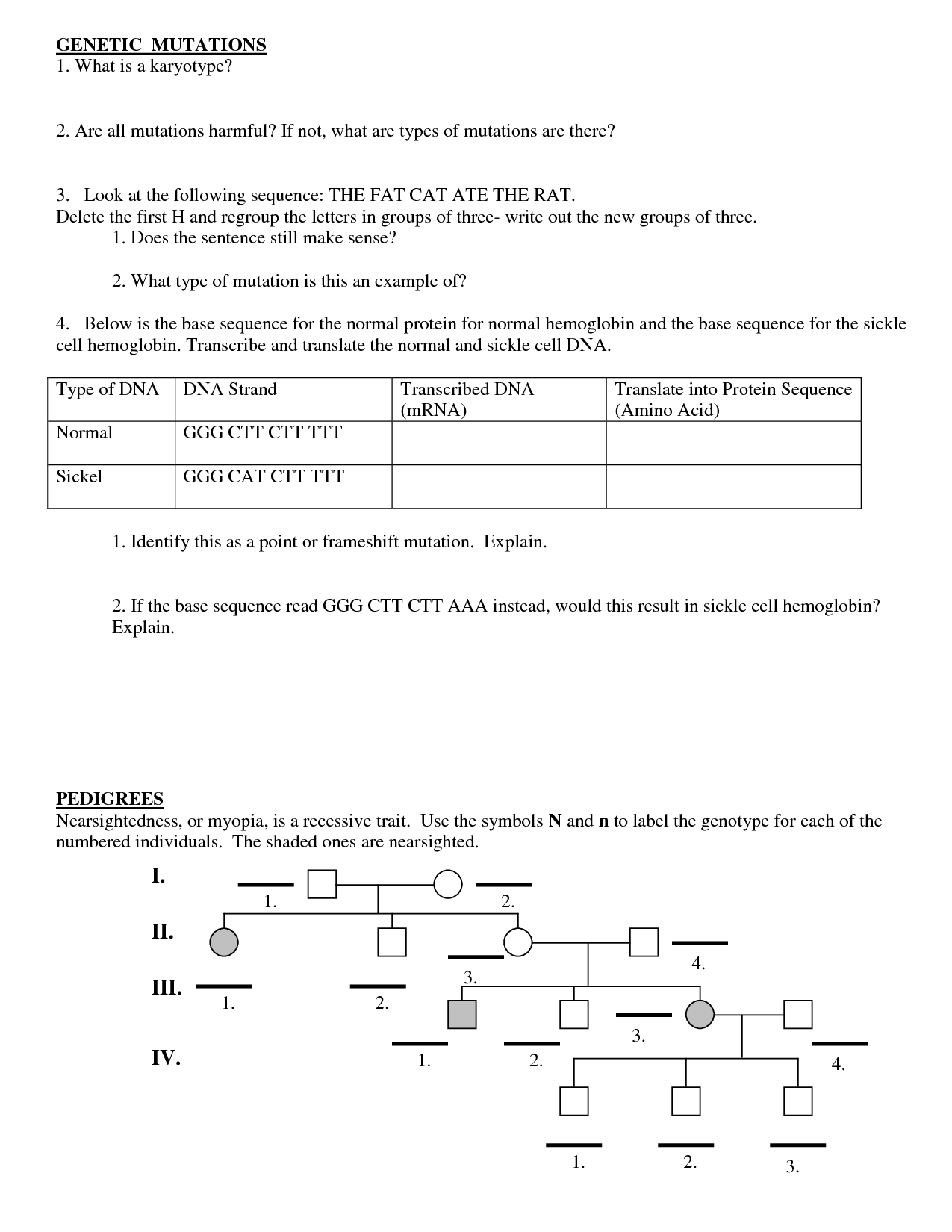
There are several types of DNA mutations, including point mutations (substitution of a single base pair), frameshift mutations (insertion or deletion of a number of base pairs not divisible by three, which shifts the reading frame), and chromosomal mutations (involving changes in the structure or number of entire chromosomes). Other types include silent mutations (do not result in a change in amino acid sequence), missense mutations (result in a different amino acid being coded for), nonsense mutations (create a premature stop codon), and splice site mutations (affecting the splicing of introns and exons during mRNA processing). These mutations can impact protein function and can lead to genetic disorders or diseases.
What is the difference between a gene mutation and a chromosomal mutation?
A gene mutation is a change in the sequence of nucleotides in a specific gene, while a chromosomal mutation involves changes in the structure or number of whole chromosomes. Gene mutations affect individual genes and can result in changes to specific traits, while chromosomal mutations can impact multiple genes or entire chromosome sets and can have a more widespread effect on an organism's development and function.
How do point mutations occur?
Point mutations occur as a result of changes in a single nucleotide base of the DNA sequence. This can happen due to a variety of factors such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic substances like radiation or certain chemicals, or spontaneous changes in the DNA structure. Point mutations can result in different outcomes, from no observable change to significant effects on the functioning of the gene or protein encoded by the affected DNA sequence.
What are the consequences of a frameshift mutation?
Frameshift mutations can have severe consequences as they shift the reading frame of the genetic code, resulting in the alteration of all amino acids downstream of the mutation site. This can lead to the production of completely non-functional, shortened, or abnormal proteins which may disrupt normal cellular functions, potentially causing genetic disorders or diseases. The impact of frameshift mutations depends on the specific gene affected and the resulting changes in protein structure and function.
What is a silent mutation?
A silent mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that does not result in a change in the corresponding amino acid within a protein. This means that the mutation can occur without any noticeable effect on the organism because the altered codon still codes for the same amino acid. Silent mutations are often considered neutral or benign as they do not lead to changes in protein structure or function.
How can DNA mutations lead to genetic disorders?
DNA mutations can lead to genetic disorders by altering the genetic code, resulting in changes to proteins or gene functions needed for normal cellular processes. These changes can disrupt normal development and function of the body, leading to various health conditions or diseases. Mutations can affect crucial biological processes such as cell division, DNA repair, and protein function, ultimately leading to the manifestation of genetic disorders in individuals.
Can DNA mutations be beneficial?
Yes, DNA mutations can be beneficial in certain circumstances. Beneficial mutations can lead to new traits or characteristics that provide an advantage to an organism, such as increased resistance to diseases or improved ability to survive in specific environments. These mutations can drive evolution by allowing organisms to adapt and thrive in changing conditions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments