DNA Coloring Worksheet Key
Worksheets are a valuable educational resource that can enhance learning for students of all ages. Whether you are an educator seeking to reinforce concepts, a parent looking for supplementary materials, or a student seeking additional practice, worksheets can provide a structured and engaging way to grasp new information. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of worksheets as an effective tool for learning about the intricate world of DNA and genetics.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Replication Coloring Sheet
- The Double Helix DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of coloring a DNA molecule?
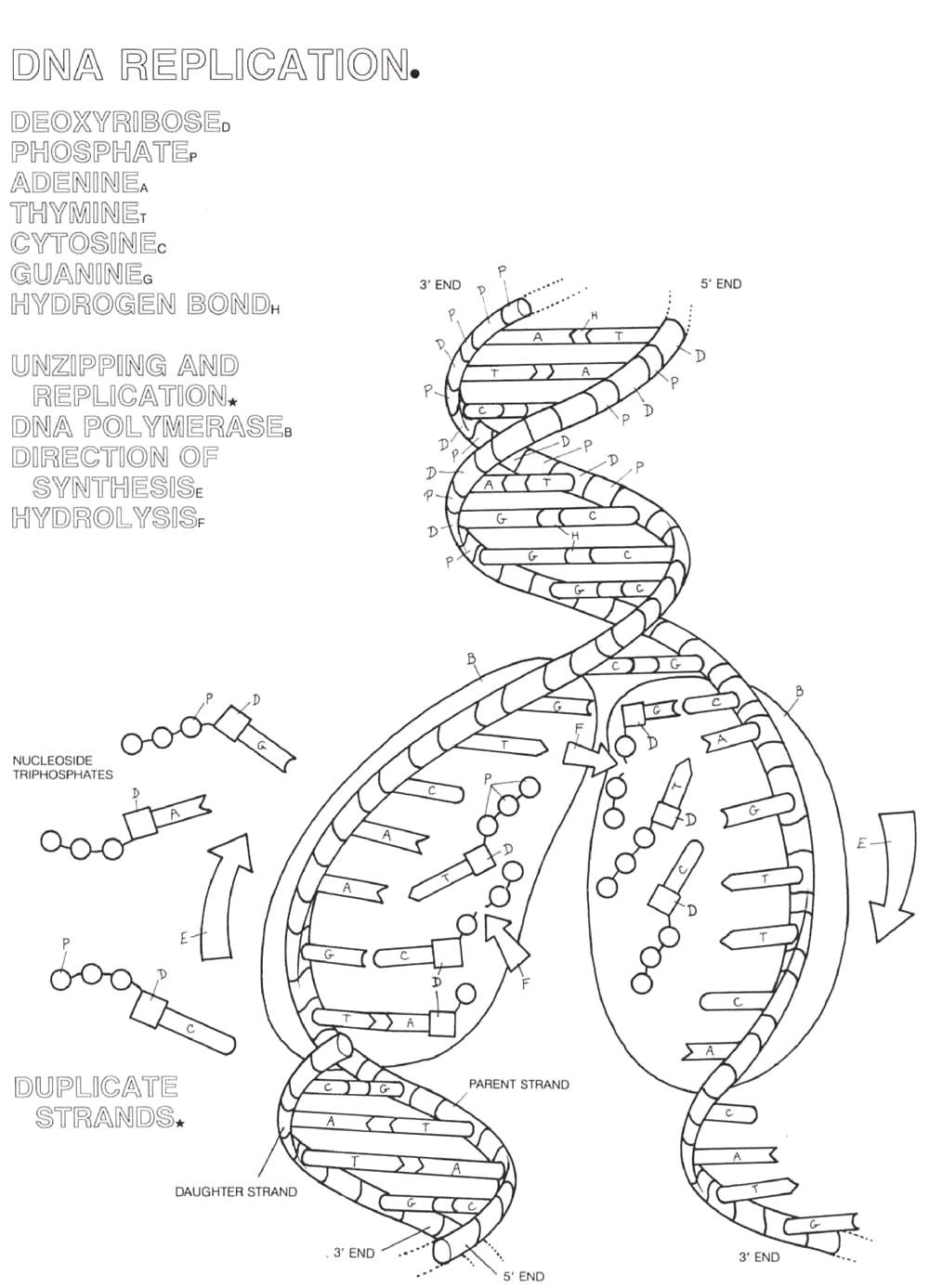
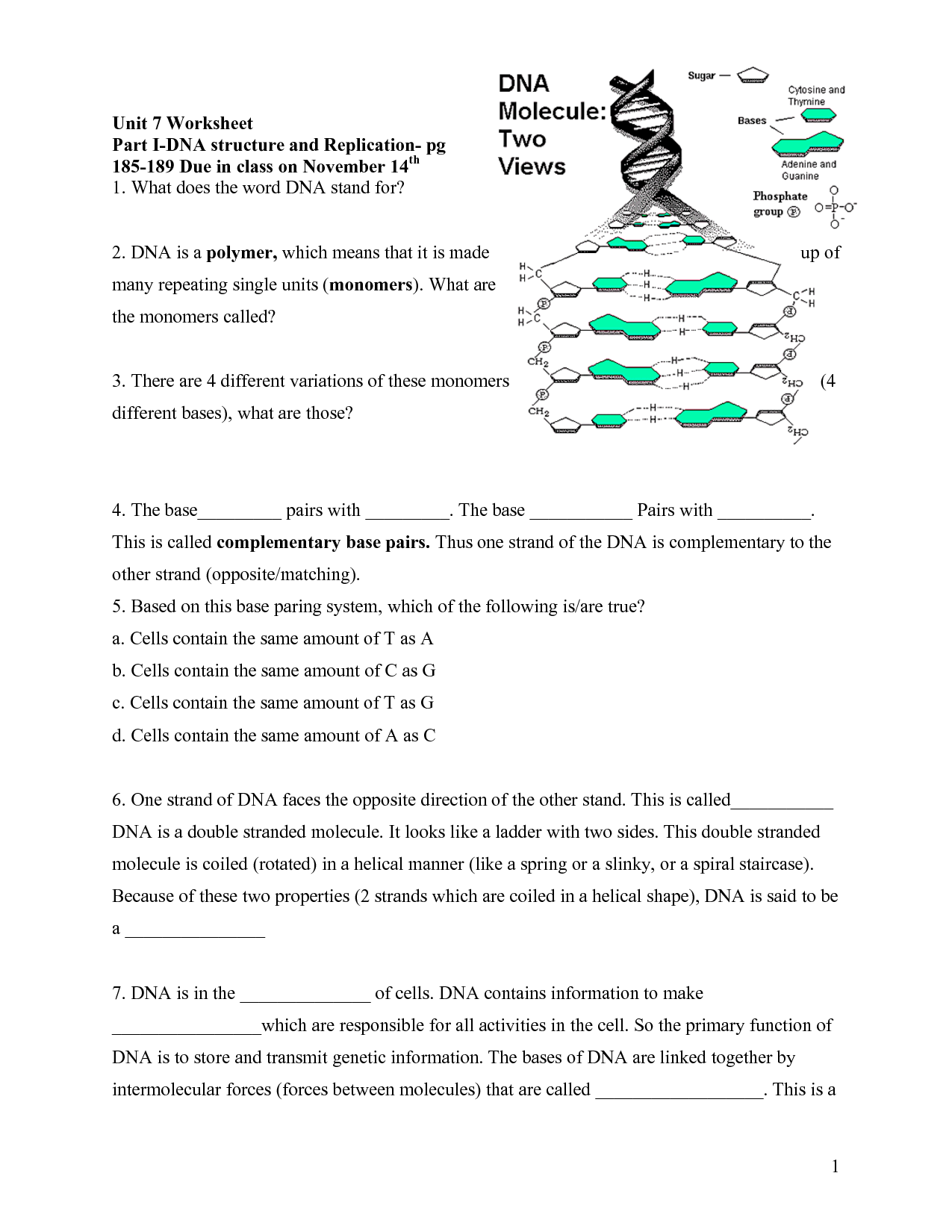
The purpose of coloring a DNA molecule is to visually distinguish between the different nucleotide bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) that make up the genetic code. By coloring each base with a different color, scientists can easily identify and analyze specific sequences of DNA, enabling them to study genes, mutations, and genetic variations with greater precision and clarity.
What is the specific function of the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
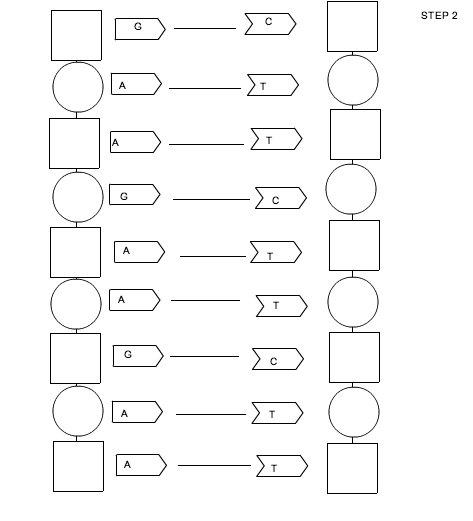
The specific function of the nitrogenous bases in DNA is to carry genetic information by forming base pairs that make up the double helix structure of DNA. There are four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), and their specific pairing (A with T and C with G) allows for the precise and complementary base pairing crucial for DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Why are complementary base pairs always paired together in DNA?
Complementary base pairs are always paired together in DNA because of the specific hydrogen bonding patterns that allow them to form stable bonds. Adenine always pairs with thymine and guanine with cytosine, forming two hydrogen bonds and three hydrogen bonds, respectively. This base pairing is vital for maintaining the double helix structure of DNA, ensuring accurate replication and transmission of genetic information during cell division and protein synthesis processes.
Which nitrogenous base pairs with adenine in DNA?
Thymine pairs with adenine in DNA through hydrogen bonding.
What is the structure of a DNA molecule?
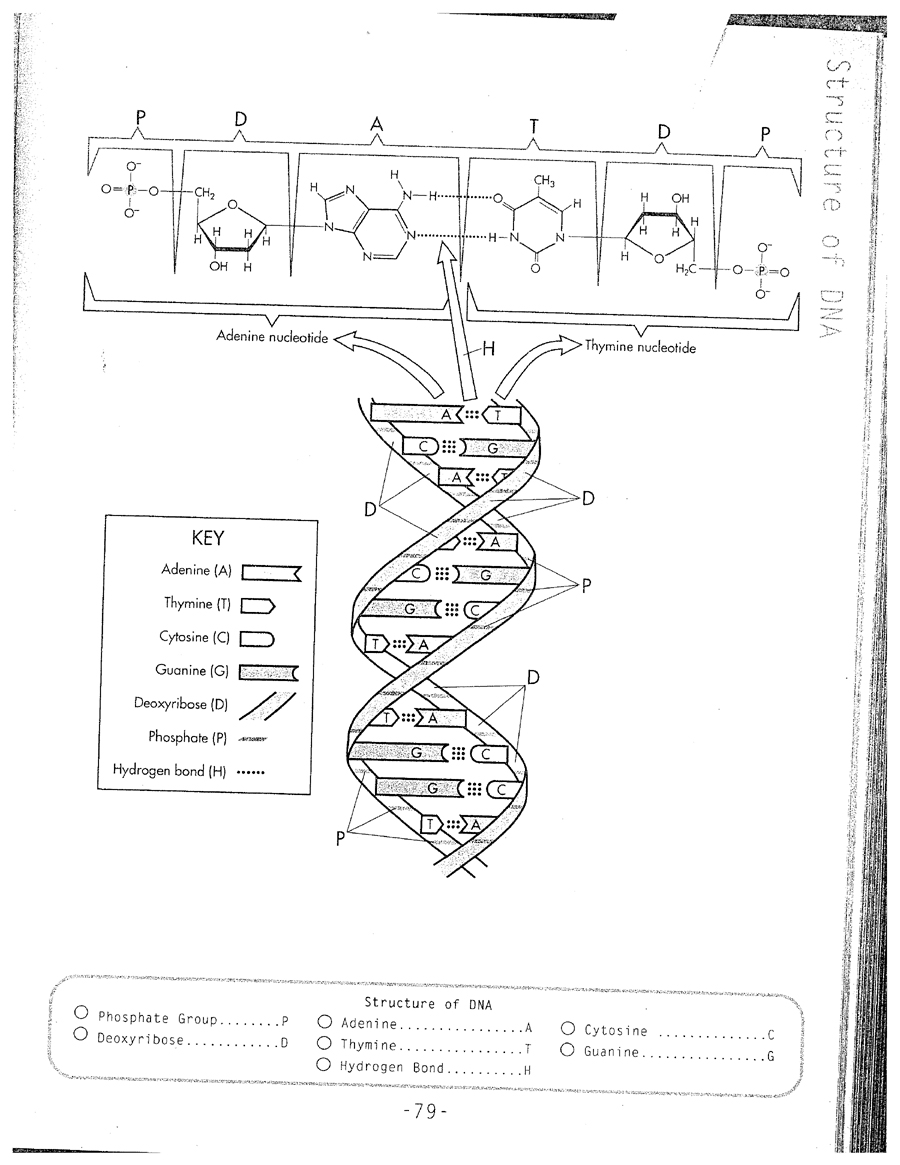
A DNA molecule is a double helix structure composed of two strands that are connected by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases. The backbone of the DNA molecule is made up of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups, while the nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) are stacked in the interior of the double helix. The bases pair in a specific way - adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine - forming base pairs that provide the genetic information encoded in the DNA molecule.
What are the two main components of a nucleotide in DNA?
The two main components of a nucleotide in DNA are a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base, which can be adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The phosphate group is attached to the 5' carbon of the sugar molecule, deoxyribose, forming the backbone of the DNA strand, while the nitrogenous base is attached to the 1' carbon of the sugar and pairs with another nitrogenous base in the complementary DNA strand, forming the double helix structure of DNA.
How many hydrogen bonds form between cytosine and guanine in a DNA molecule?
Three hydrogen bonds form between cytosine and guanine in a DNA molecule.
How does DNA encoding and transmitting genetic information?
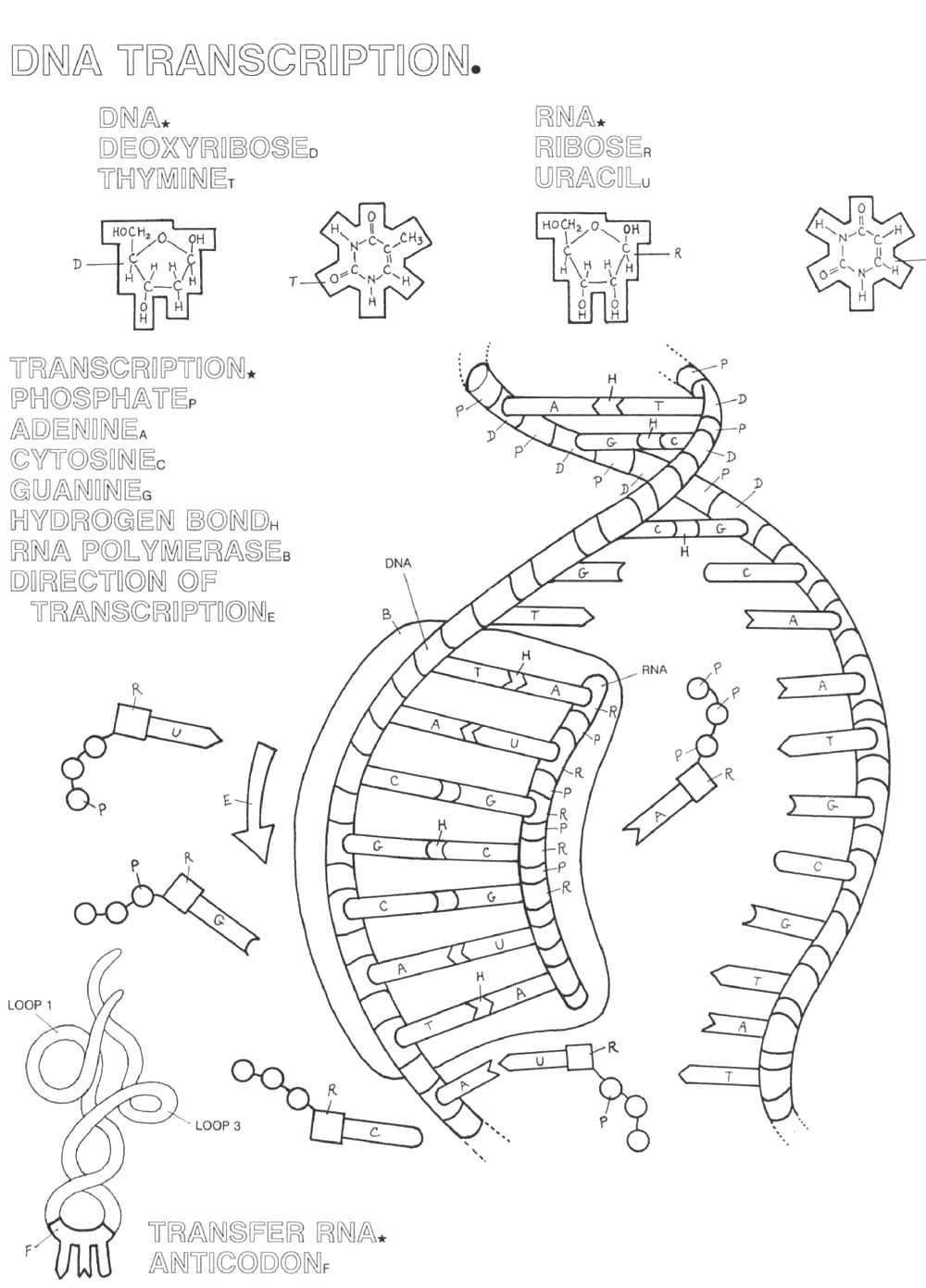
DNA serves as a molecule that encodes genetic information by storing the instructions needed for the growth, development, and functioning of living organisms. This information is transmitted through processes such as DNA replication, where a cell copies its DNA before dividing in mitosis or meiosis, and DNA transcription, where the information in DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA for protein synthesis. Ultimately, DNA encodes genetic information through its sequence of nucleotide bases, which code for specific amino acids and proteins, playing a crucial role in determining an organism's traits and characteristics.
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA serves as the template for the synthesis of proteins through a process called transcription and translation. During transcription, the DNA sequence is used to create a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that carries the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. This mRNA is then read by ribosomes during translation to assemble amino acids in the specific order dictated by the mRNA sequence, ultimately leading to the production of a protein. Therefore, DNA provides the instructions for protein synthesis by encoding the sequence of amino acids that make up each protein.
How does the unique sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA determine an organism's traits?
The unique sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA serves as the genetic code that carries information to make proteins, which are essential for determining an organism's traits. The specific sequence of bases determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein, which ultimately influences the structure and function of the protein. Different combinations of nitrogenous bases lead to the production of different proteins, ultimately shaping an organism's traits such as physical appearance, behavior, and overall function.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments