DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet
Understanding the structure of DNA and RNA is a fundamental aspect of biology education. Whether you are a student preparing for an exam or a teacher looking for engaging learning materials, worksheets can provide a valuable resource to enhance your understanding of this important topic.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
- DNA and RNA Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Structure Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Function Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
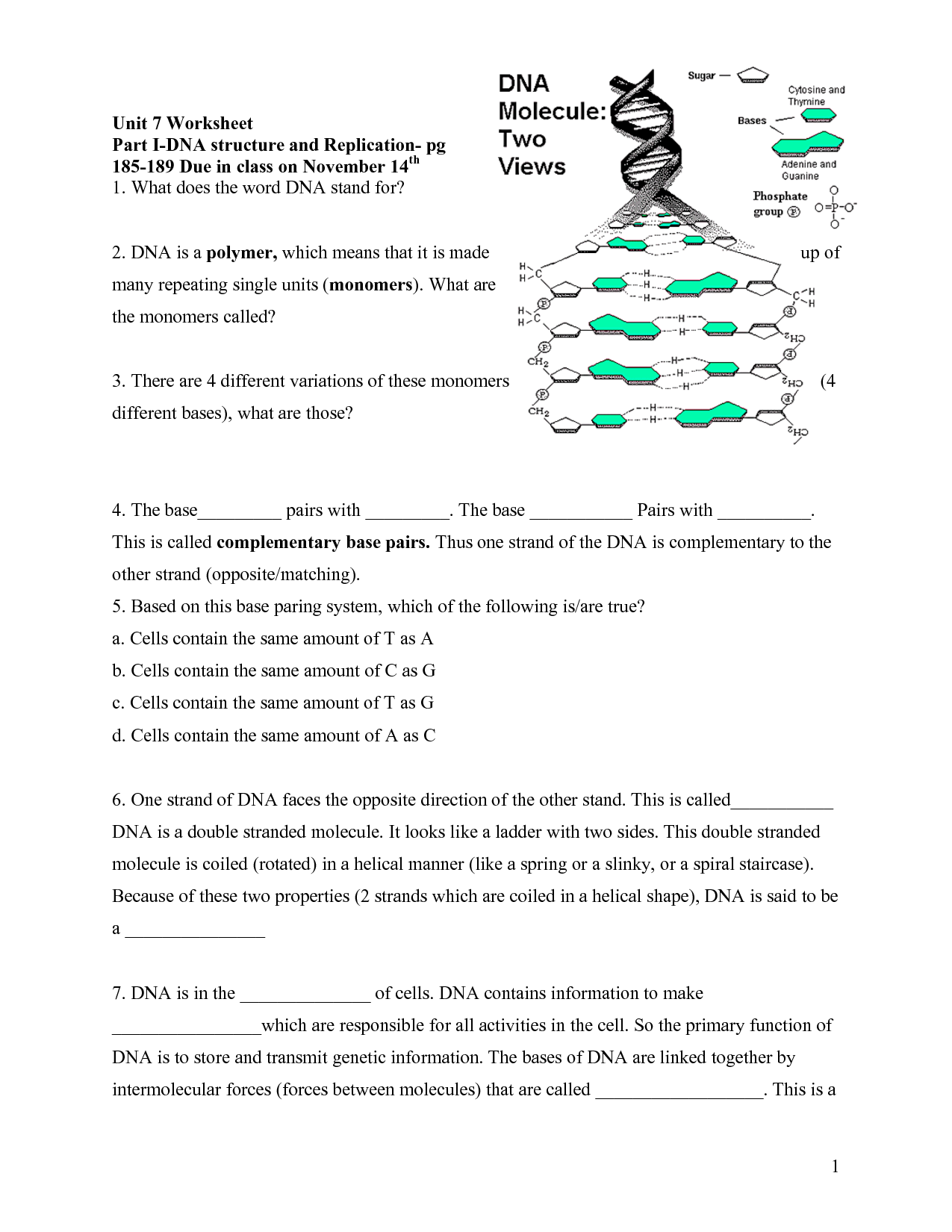
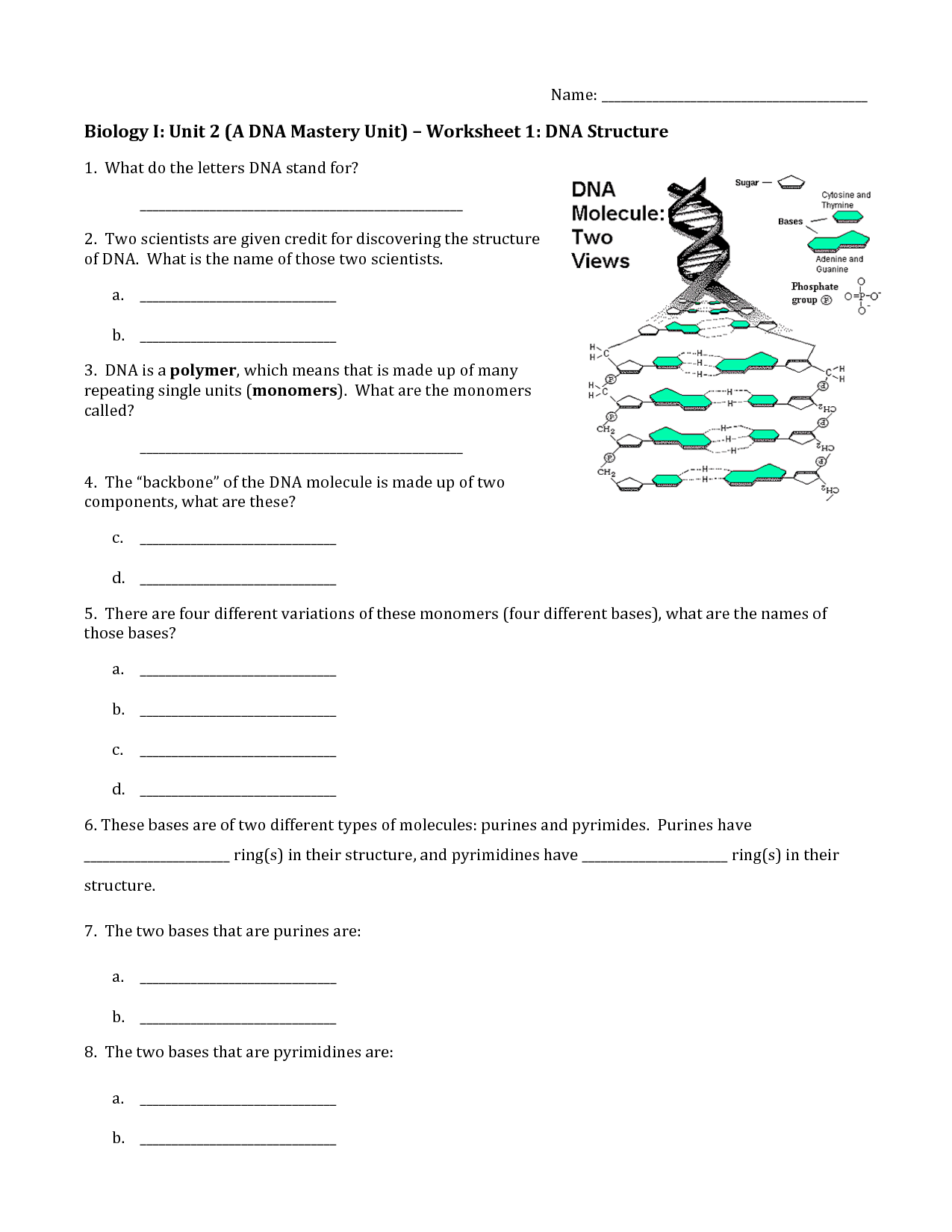
Describe the structure of DNA.
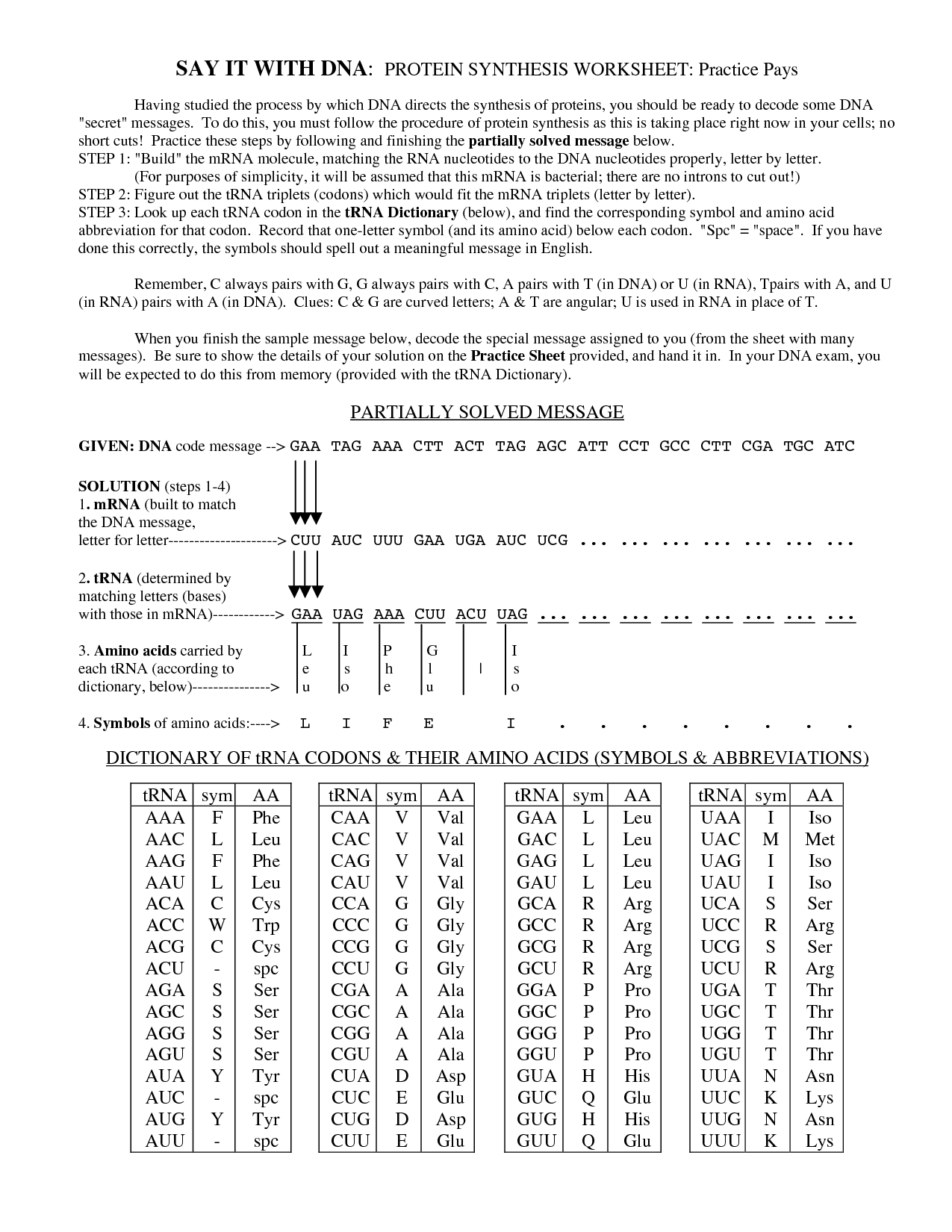
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double helix structure composed of two complementary strands of nucleotides twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The nitrogenous bases on opposite strands pair up through hydrogen bonds – adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine – to form base pairs. This base pairing allows DNA replication and provides the genetic code that determines the traits and functions of an organism.
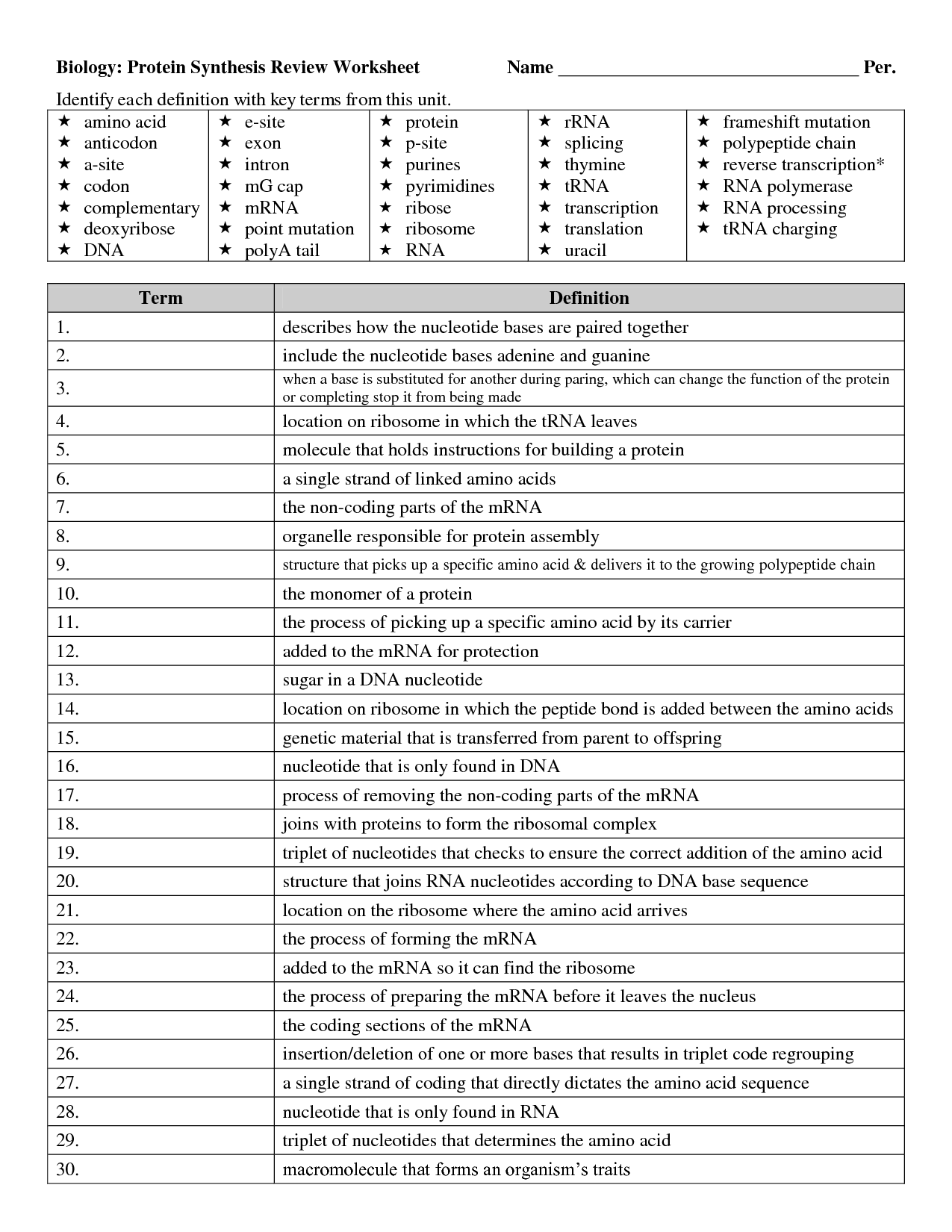
Explain the structure of RNA.
RNA is a single-stranded molecule composed of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil), a ribose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases pair up in a complementary manner: adenine pairs with uracil, and guanine pairs with cytosine. RNA can fold into various secondary structures, such as hairpin loops and stem-loop structures, due to hydrogen bonding between complementary bases. This flexibility allows RNA to carry out a variety of functions in the cell, including serving as a template for protein synthesis and catalyzing biochemical reactions.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). These nucleotides are arranged in a complementary manner to form the double helix structure of DNA, which encodes the genetic information in all living organisms.
What are the building blocks of RNA?
The building blocks of RNA are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar (ribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil). The sequence of these nucleotides in RNA molecules determines the genetic information and functional properties of the RNA.
How do DNA and RNA differ in terms of sugar composition?
DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, while RNA contains ribose sugar. The key difference between these sugars is that deoxyribose lacks one oxygen atom compared to ribose. This difference in sugar composition contributes to the distinct functions and structures of DNA and RNA in biological processes.
Compare the base pairing in DNA and RNA.
In both DNA and RNA, base pairing involves adenine (A) pairing with thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) in RNA, and guanine (G) pairing with cytosine (C). However, unlike DNA which contains deoxyribose sugar, RNA contains ribose sugar. This difference means that RNA contains uracil instead of thymine and can form stable secondary structures due to its single-stranded nature, unlike the double-stranded structure of DNA.
Describe the directionality of DNA and RNA strands.
Both DNA and RNA strands have directionality dictated by the orientation of their sugar-phosphate backbones. DNA strands run in an antiparallel direction, with one strand running in a 5' to 3' direction and the complementary strand running in a 3' to 5' direction. RNA also has a 5' to 3' directionality, with nucleotides added to the 3' end during synthesis. This directionality is essential during processes like replication and transcription when nucleotides are added in a specific order.
Explain the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA and RNA structure.
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the secondary structure of DNA and RNA. In DNA, hydrogen bonds form between complementary base pairs (adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine), holding the double helix structure together. In RNA, hydrogen bonds are involved in base pairing between adenine-uracil and guanine-cytosine, contributing to the formation of secondary structures like hairpins and loops. Overall, hydrogen bonds are essential for maintaining the integrity and functionality of DNA and RNA molecules.
How does the double helix structure contribute to DNA's function?
The double helix structure of DNA plays a critical role in its function by providing stability and enabling efficient storage of genetic information. The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nucleotide bases, allowing for precise replication during cell division and accurate transmission of genetic material. Additionally, the helix structure offers protection to the genetic code stored within the molecule, shielding it from damage and ensuring its integrity is maintained.
What are some common differences between DNA and RNA molecules?
Some common differences between DNA and RNA molecules include: DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is typically single-stranded; DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose; DNA contains the nitrogenous base thymine, while RNA contains uracil instead of thymine; DNA is mainly found in the cell nucleus, while RNA is found both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm; DNA serves as the genetic blueprint for an organism, while RNA plays various roles in gene expression and protein synthesis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments