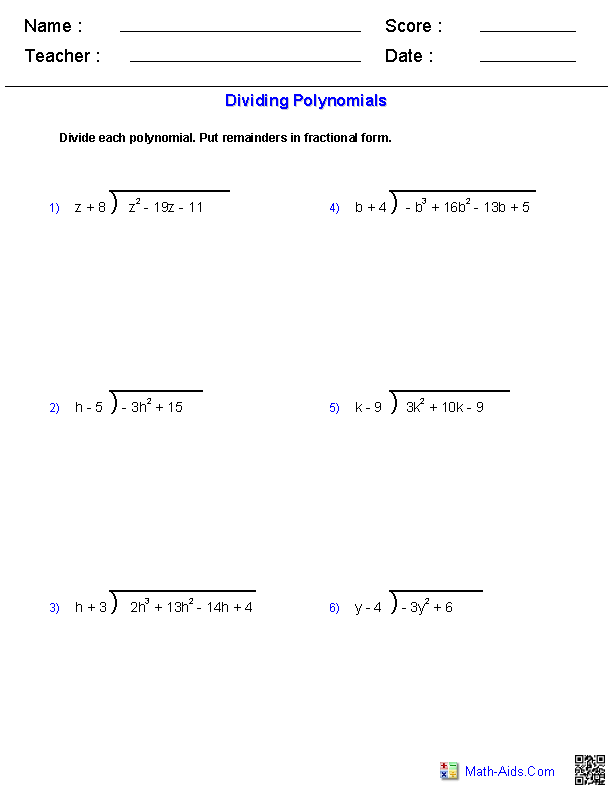
Dividing Polynomials Worksheet
Are you seeking a comprehensive study aid to improve your understanding of dividing polynomials? Look no further, as we have just the resource for you. Our Dividing Polynomials Worksheet is designed to help students grasp the concept of polynomial division and its various applications. Whether you are a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student reviewing for a math course, this worksheet will provide you with ample practice and reinforcement.
Table of Images 👆
- Adding Polynomials Worksheet
- Polynomial Long Division Worksheet
- Multiplying and Factoring Polynomials Worksheet
- Factoring Polynomials Worksheet
- Algebra Factoring Polynomials Worksheet
- 6th Grade Long Division Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Multiplying Polynomials Distributive Property
- Factoring Polynomials Worksheet with Answers
- Multiplication of Exponents and Division Worksheets
- Polynomials with Negative Exponents Worksheets
- Polynomial Practice Worksheets with Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of a polynomial?
A polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of variables, coefficients, and exponents, combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents. It is typically written in the form of a sum of terms, where each term is a constant or coefficient multiplied by one or more variables raised to a non-negative integer exponent.
How do you determine the degree of a polynomial?
The degree of a polynomial is determined by examining the highest power of the variable (usually x) that appears in the polynomial. In other words, the degree is the highest exponent of the variable in the polynomial. For example, in the polynomial 3x^2 + 5x - 1, the highest power of x is 2, so the degree of this polynomial is 2.
What is the purpose of dividing polynomials?
The purpose of dividing polynomials is to simplify complex expressions and solve equations more easily. It allows us to break down a polynomial into simpler components, making it easier to factor, find roots, or perform other operations. Dividing polynomials is an essential skill in algebra and is used in various mathematical applications, including calculus, engineering, and physics.
What is the quotient when dividing a polynomial by a monomial?
When dividing a polynomial by a monomial, the quotient is another polynomial where each term is divided by the monomial. Each term in the original polynomial is divided by the monomial, and the resulting coefficients are the coefficients of the corresponding terms in the quotient polynomial. The exponents of the variables are decreased by the degree of the monomial being divided by.
How do you divide a polynomial by a binomial?
To divide a polynomial by a binomial, you can use polynomial long division or synthetic division. Polynomial long division involves dividing each term of the polynomial by the binomial, similar to long division with numbers. Synthetic division is a faster method that works for dividing by binomials of the form x - c, where c is a constant. Remember to follow the steps carefully and perform the necessary operations to simplify the division process and obtain the quotient.
What is the role of the remainder in polynomial division?
The role of the remainder in polynomial division is to represent what is left over after the polynomial division process is completed. It allows us to determine whether one polynomial evenly divides another, and if not, the remainder helps convey the amount by which the division is incomplete. The remainder is crucial for understanding the relationship between the dividend, divisor, quotient, and their interactions in polynomial division.
How do you determine if one polynomial is a factor of another?
To determine if one polynomial is a factor of another, you can use polynomial division. Divide the polynomial you suspect is a factor (the divisor) into the polynomial you want to check (the dividend). If the division results in a remainder of zero, then the polynomial you were testing is indeed a factor of the original polynomial.
What is the procedure for dividing a polynomial by a polynomial using long division?
To divide a polynomial by another polynomial using long division, first write the dividend inside the division symbol and the divisor outside the symbol. Then, divide the first term of the dividend by the first term of the divisor to determine the first term of the quotient. Next, multiply the entire divisor by the first term of the quotient and subtract this result from the dividend. Bring down the next term of the dividend and repeat the process until all terms have been accounted for. The final result will be the quotient and any remainder left over.
What happens when the degree of the divisor polynomial is greater than the dividend polynomial?
When the degree of the divisor polynomial is greater than the degree of the dividend polynomial in polynomial division, the result is a quotient of zero and a remainder equal to the dividend polynomial. This is because the divisor polynomial is too large to divide into the dividend polynomial, so the division process cannot be completed fully, resulting in a zero quotient and the original dividend as the remainder.
How do you simplify the quotient when dividing polynomials?
To simplify the quotient when dividing polynomials, you need to perform polynomial long division or use synthetic division. Divide the highest degree term of the dividend by the highest degree term of the divisor to find the first term of the quotient. Then multiply the divisor by this term, subtract it from the dividend to find a new polynomial, and repeat the process until you have a remainder with a lower degree than the divisor. This will give you the simplified quotient of the division.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments