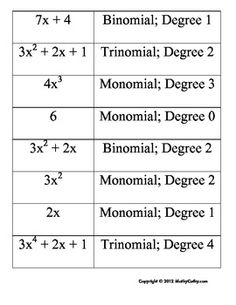
Dividing Polynomials by Binomials Worksheet
Are you a high school student or a math enthusiast seeking a comprehensive worksheet that covers the topic of dividing polynomials by binomials? Look no further! In this blog post, we will introduce you to a worksheet that will provide ample practice in dividing polynomials by binomials, helping you master this important concept in algebra.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the first step in dividing a polynomial by a binomial?
The first step in dividing a polynomial by a binomial is to ensure that the polynomial is written in descending order of exponents, with any missing terms represented by placeholders of zero coefficients.
How do you check if the binomial is a factor of the polynomial?
To check if a binomial is a factor of a polynomial, you can use the Remainder Theorem. Divide the polynomial by the binomial using long division or synthetic division. If the remainder is zero, then the binomial is a factor of the polynomial. If there is a non-zero remainder, then the binomial is not a factor.
How do you determine the quotient in polynomial division?
To determine the quotient in polynomial division, divide the leading term of the dividend by the leading term of the divisor to get the first term of the quotient. Multiply the divisor by this term, subtract the result from the dividend, and repeat the process with the new leading term until the degree of the dividend is less than the degree of the divisor, obtaining the final quotient.
What is the remainder in polynomial division?
The remainder in polynomial division is the polynomial that is left over after dividing the dividend by the divisor, such that it cannot be divided any further. It is important to note that the degree of the remainder will always be less than the degree of the divisor.
How do you write the division of a polynomial by a binomial in long division form?
To write the division of a polynomial by a binomial in long division form, set up the division by dividing the first term of the polynomial by the first term of the binomial. Multiply the binomial by the quotient obtained, then subtract the result from the polynomial. Bring down the next term of the polynomial and repeat the process until all terms have been divided. The final result will be the quotient and possibly a remainder if the degree of the dividend is less than the divisor.
What is the purpose of synthetic division in dividing polynomials by binomials?
The purpose of synthetic division in dividing polynomials by binomials is to simplify and expedite the process of polynomial division. It provides a quicker and more straightforward method compared to long division, allowing for a more efficient way to determine the quotient and remainder when dividing a polynomial by a linear binomial. Synthetic division is particularly useful when working with polynomials of higher degrees or when there are multiple divisions to be done.
What happens when the degree of the binomial is greater than the degree of the polynomial?
When the degree of the binomial is greater than the degree of the polynomial, the binomial will dominate the polynomial in terms of growth rate as the values of x get larger. The behavior of the polynomial will be largely determined by the largest exponent in the binomial, making the polynomial essentially act like the dominant term in the binomial.
How do you know if a polynomial is completely divisible by a binomial?
You can determine if a polynomial is completely divisible by a binomial by using the factor theorem. If the binomial is a factor of the polynomial, then the remainder obtained by dividing the polynomial by the binomial is zero. This implies that when you substitute the root of the binomial into the polynomial, the result will be zero.
What is the relation between the roots of the polynomial and the binomial divisor?
The relation between the roots of a polynomial and the binomial divisor can be understood through the Factor Theorem. If a polynomial has a root that is equal to the divisor, then the binomial divisor is a factor of the polynomial, meaning it divides the polynomial evenly without a remainder. Therefore, the roots of the polynomial are related to the binomial divisor in terms of factorization and division.
Can a polynomial have multiple binomial divisors?
Yes, a polynomial can have multiple binomial divisors. In fact, a polynomial can have any number of binomial divisors depending on its factors. A binomial divisor is a polynomial that can be factored into two terms, such as (x + a), and divides the original polynomial evenly without a remainder.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




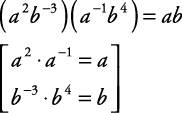
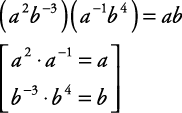
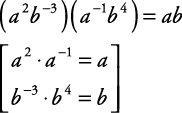

















Comments