Dihybrid Cross Problems Worksheet
A dihybrid cross problems worksheet is a useful tool for students learning about genetic inheritance. This worksheet provides practice problems involving the crossing of two different traits or genes in organisms. By using a dihybrid cross worksheet, students can better understand how different genes are passed on from parents to offspring and gain a deeper insight into the concept of genetic variation.
Table of Images 👆
- Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
- Monohybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
- Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answers
- Dihybrid Punnett Square Practice Problems Answers
- Dihybrid Cross Practice Worksheet
- Dihybrid Crosses Practice Problems
- Dihybrid Punnett Square Practice Worksheets
- Dihybrid Cross Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Dihybrid Cross Worksheet with Answer Key
- Dihybrid Crosses Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
- Dihybrid Crosses Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a dihybrid cross?
A dihybrid cross is a breeding experiment or genetic cross involving two organisms that differ in two traits, typically represented by two genes on different chromosomes. The purpose of a dihybrid cross is to examine the inheritance patterns of these two traits and determine how they are passed on to offspring, taking into account the principles of Mendelian genetics such as independent assortment and segregation.
What are the genotypes of the parental generation in a dihybrid cross?
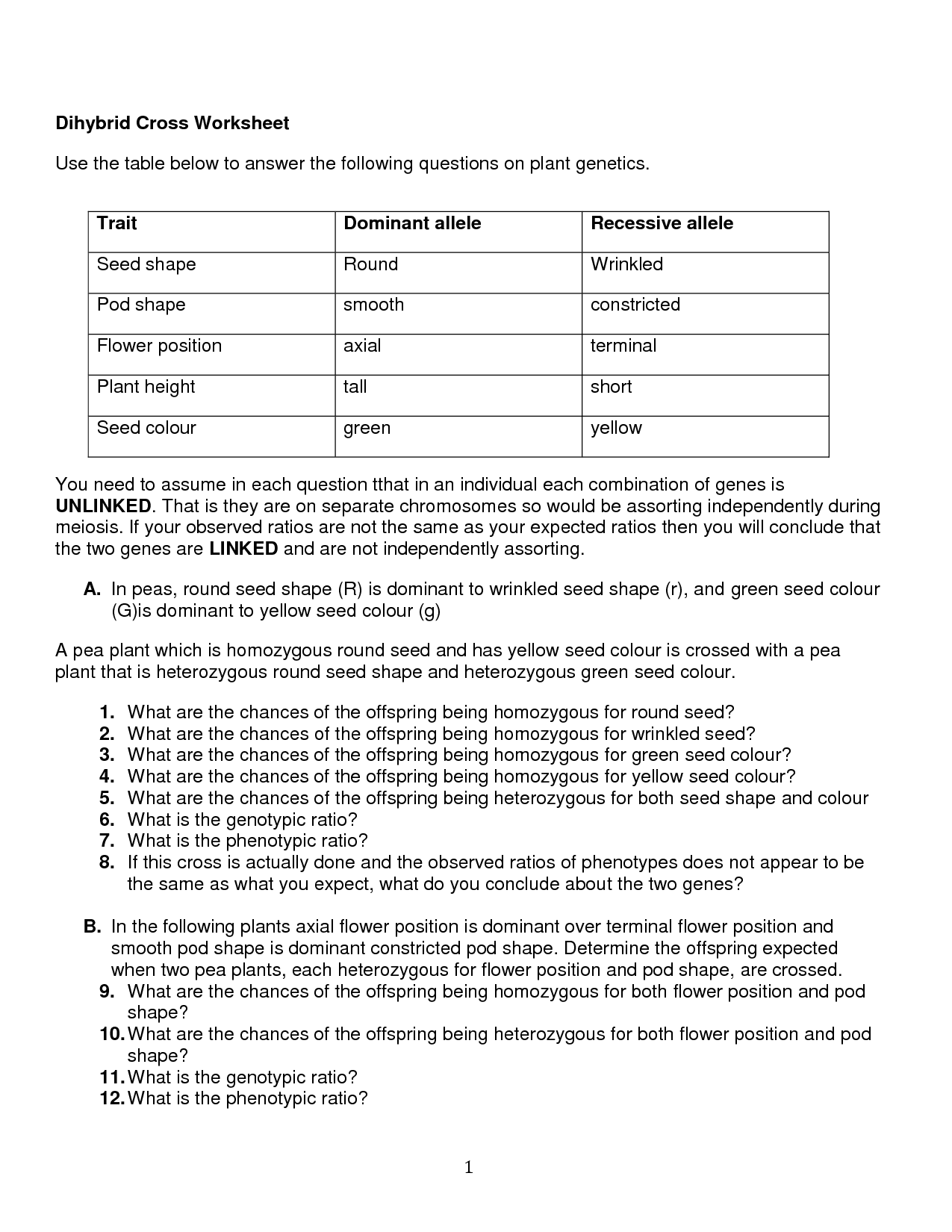
In a dihybrid cross, the genotypes of the parental generation usually involve two alleles for each of the two different genes being studied, such as one dominant and one recessive allele for each gene. For example, if studying seed shape (R - round, r - wrinkled) and seed color (Y - yellow, y - green) in pea plants, the parental generation could have genotypes like RRYY and rryy, where one allele represents one gene and the other allele represents the other gene.
How many possible genotypes are there in the F1 generation of a dihybrid cross?
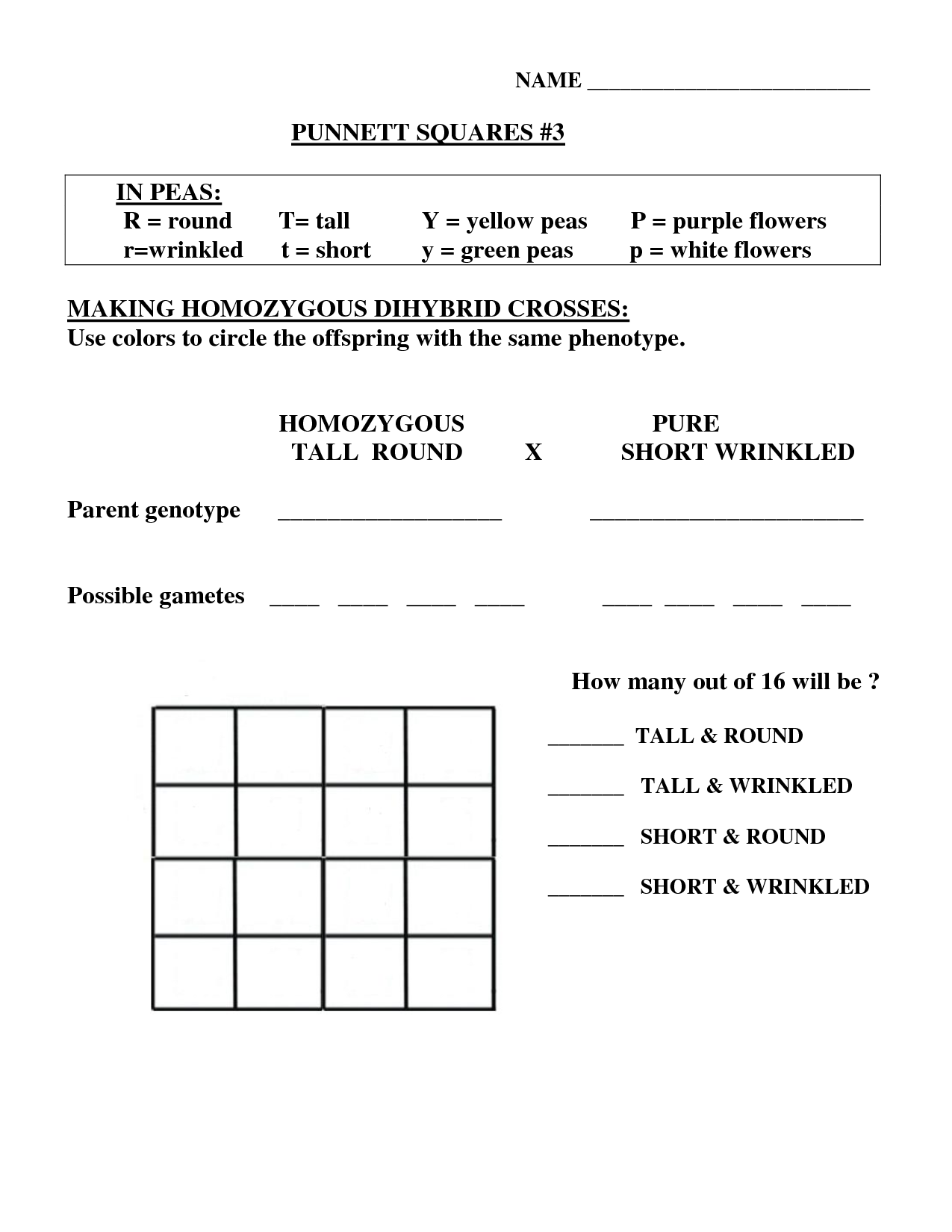
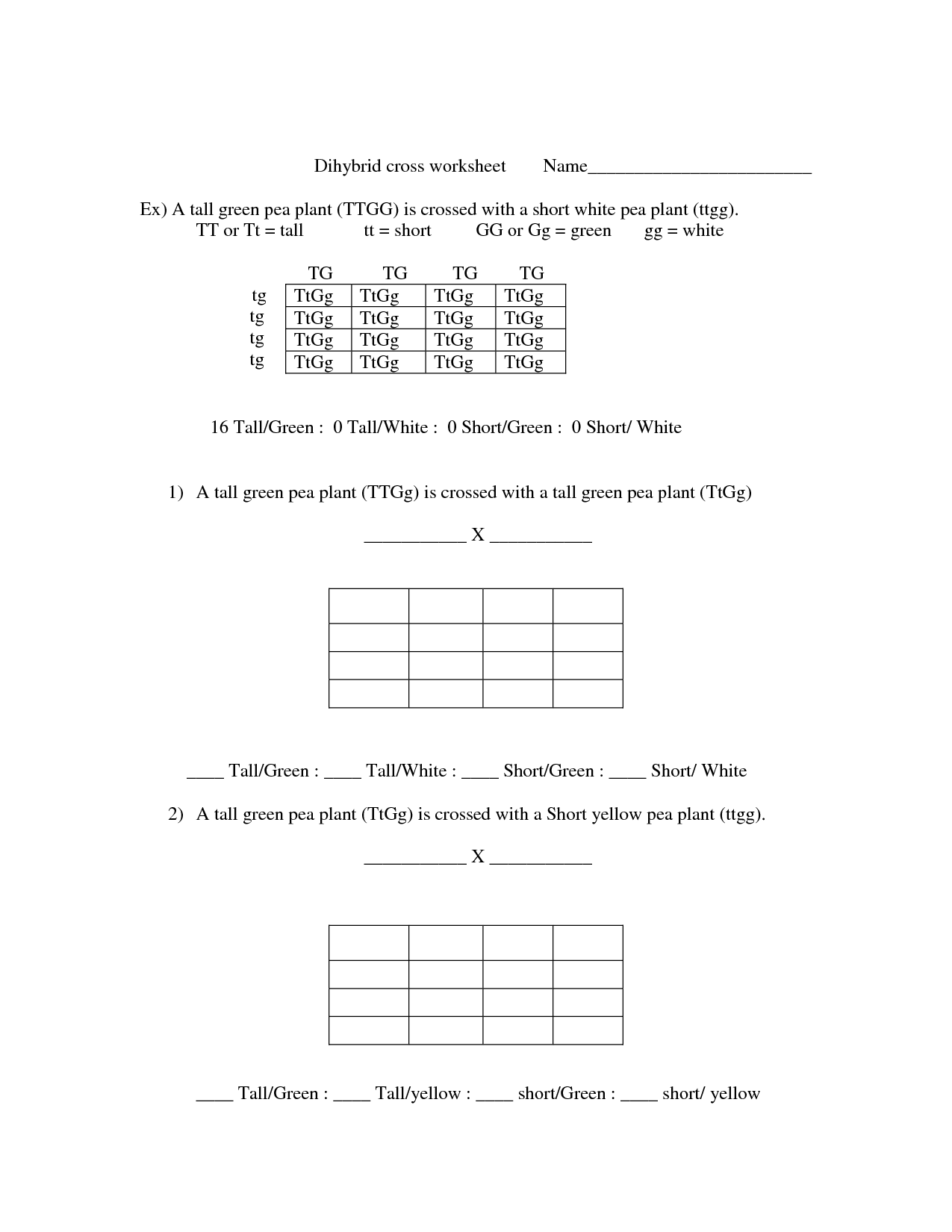
There are 16 possible genotypes in the F1 generation of a dihybrid cross, resulting from the combination of two heterozygous individuals with two different traits. This is because there are 2^(number of traits) possible genotypes, which equals 2^2 = 16 in a dihybrid cross.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square in a dihybrid cross?
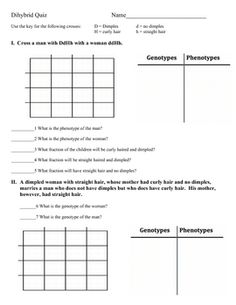
The purpose of a Punnett square in a dihybrid cross is to predict the possible outcomes of offspring with regard to two different traits inherited from the parental generation. By utilizing the Punnett square, it is possible to determine the different combinations of alleles that can be passed down from the parents to their offspring, helping to understand the genetic probabilities and potential phenotypic ratios of the offspring resulting from the cross.
What is the principle of independent assortment in a dihybrid cross?
The principle of independent assortment in a dihybrid cross states that during gamete formation, the alleles of one gene segregate independently of the alleles of another gene. This means that the inheritance of alleles for one trait does not influence the inheritance of alleles for another trait, allowing for a greater genetic diversity in offspring. This principle was proposed by Gregor Mendel based on his experiments with pea plants and is a fundamental concept in genetics.
How do you calculate the probability of a specific genotype in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross?
To calculate the probability of a specific genotype in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross, you can use the Punnett square method. Start by creating a 4x4 Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring. Then calculate the probability of each genotype by counting the number of squares that represent that genotype and dividing it by the total number of squares in the Punnett square. This will give you the probability of each specific genotype in the F2 generation of the dihybrid cross.
What is the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross involving two heterozygous parents?
In a dihybrid cross involving two heterozygous parents, the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation is 9:3:3:1. This ratio arises from the inheritance of two different traits, each controlled by different genes on separate chromosomes, resulting in a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio of the offspring exhibiting the different combinations of the two traits.
How is the law of segregation applied in a dihybrid cross?
In a dihybrid cross, the law of segregation is applied by considering two different genes that assort independently, meaning they segregate independently during gamete formation. This results in each parent passing on only one allele for each gene to their offspring. This leads to the expression of different gene combinations in the offspring, demonstrating how traits are inherited independently from one another.
How are dihybrid crosses different from monohybrid crosses?
Dihybrid crosses differ from monohybrid crosses in that dihybrid crosses involve the study of two different traits in the offspring, each controlled by two different genes located on different chromosome pairs, while monohybrid crosses focus on the study of only one trait governed by one gene pair. This means that dihybrid crosses consider the inheritance of two different traits simultaneously and result in phenotypic ratios that are more complex compared to the simpler ratios seen in monohybrid crosses.
Can a dihybrid cross result in offspring with different phenotypes than the parental generation?
Yes, a dihybrid cross can result in offspring with different phenotypes than the parental generation due to the independent assortment of alleles during gamete formation. This can lead to new combinations of traits in the offspring that were not present in the parental generation, resulting in different phenotypes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments