Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Key
Worksheets are a valuable tool for educators and students alike, providing a structured way to practice and reinforce essential concepts. If you're searching for a comprehensive worksheet on diffusion and osmosis, you've come to the right place. This diffusion and osmosis worksheet key is designed to help students master these important biological processes by providing clear and concise explanations, along with relevant practice questions. Whether you're a teacher looking for a resource to enhance your lesson plans or a student seeking to improve your understanding, this worksheet is an essential companion for studying diffusion and osmosis.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
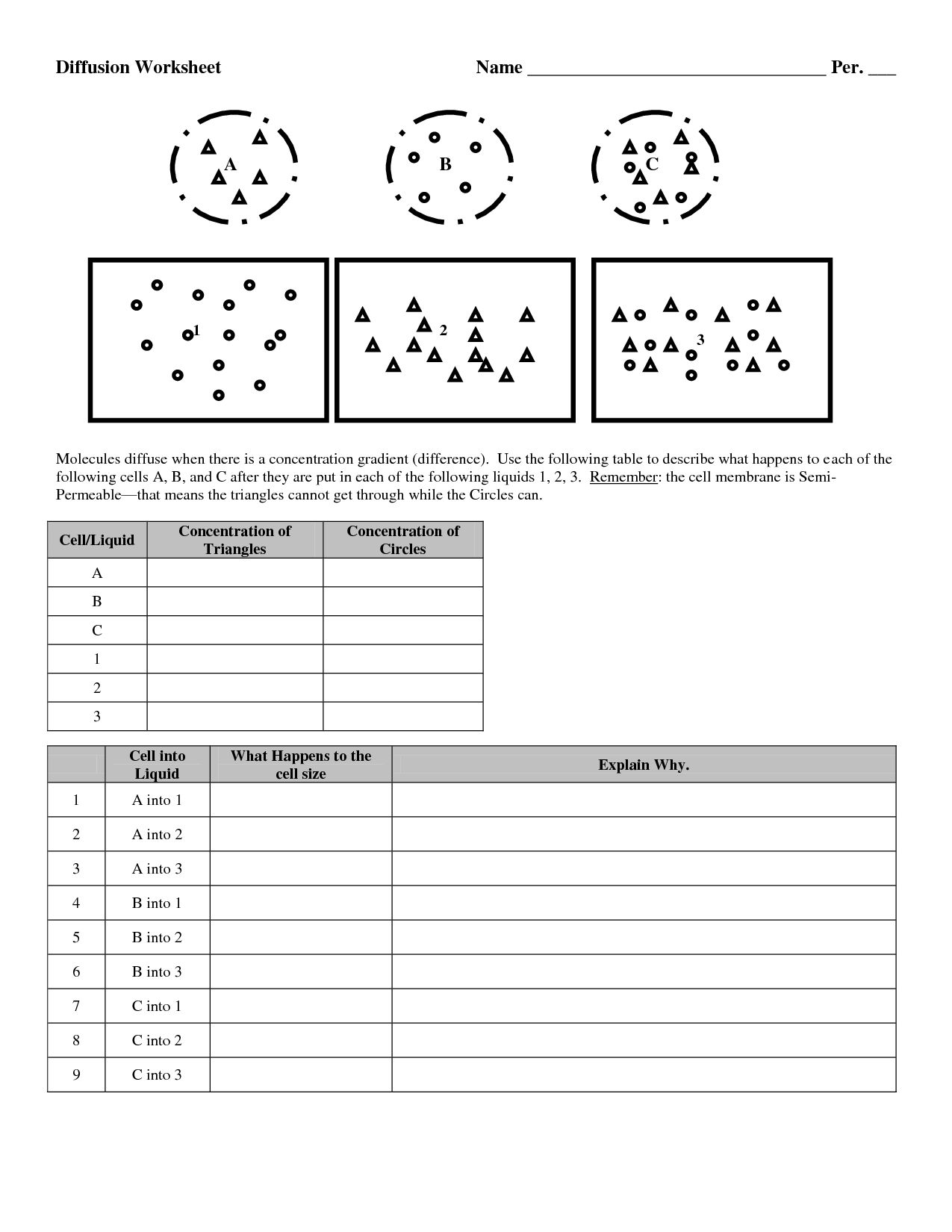
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules or particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, resulting in their even distribution. This process occurs due to the random movement of particles and is vital for various biological and physical processes, such as the exchange of gases in our lungs or the absorption of nutrients by cells.
How does diffusion occur?
Diffusion is a passive process in which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, driven by random thermal motion. This movement continues until the molecules are evenly distributed throughout the space. The rate of diffusion is influenced by factors such as temperature, molecular size, and the concentration gradient.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Several factors affect the rate of diffusion, including the concentration gradient (the greater the difference in concentration between two areas, the faster the diffusion), temperature (higher temperatures generally increase the rate of diffusion), surface area (larger surface areas allow for more molecules to diffuse), molecular size (smaller molecules diffuse more quickly), and the medium in which diffusion occurs (diffusion is typically faster in liquids and gases compared to solids).
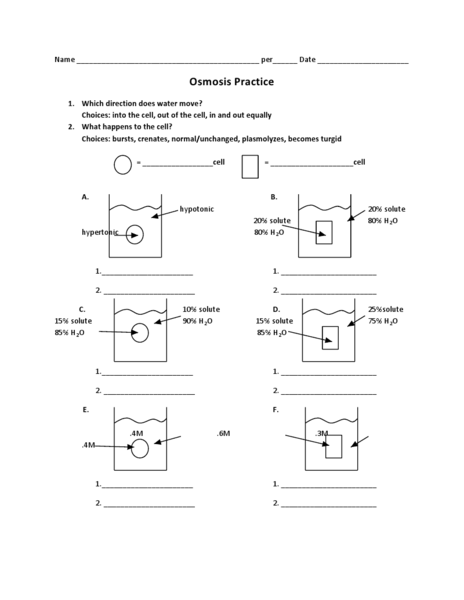
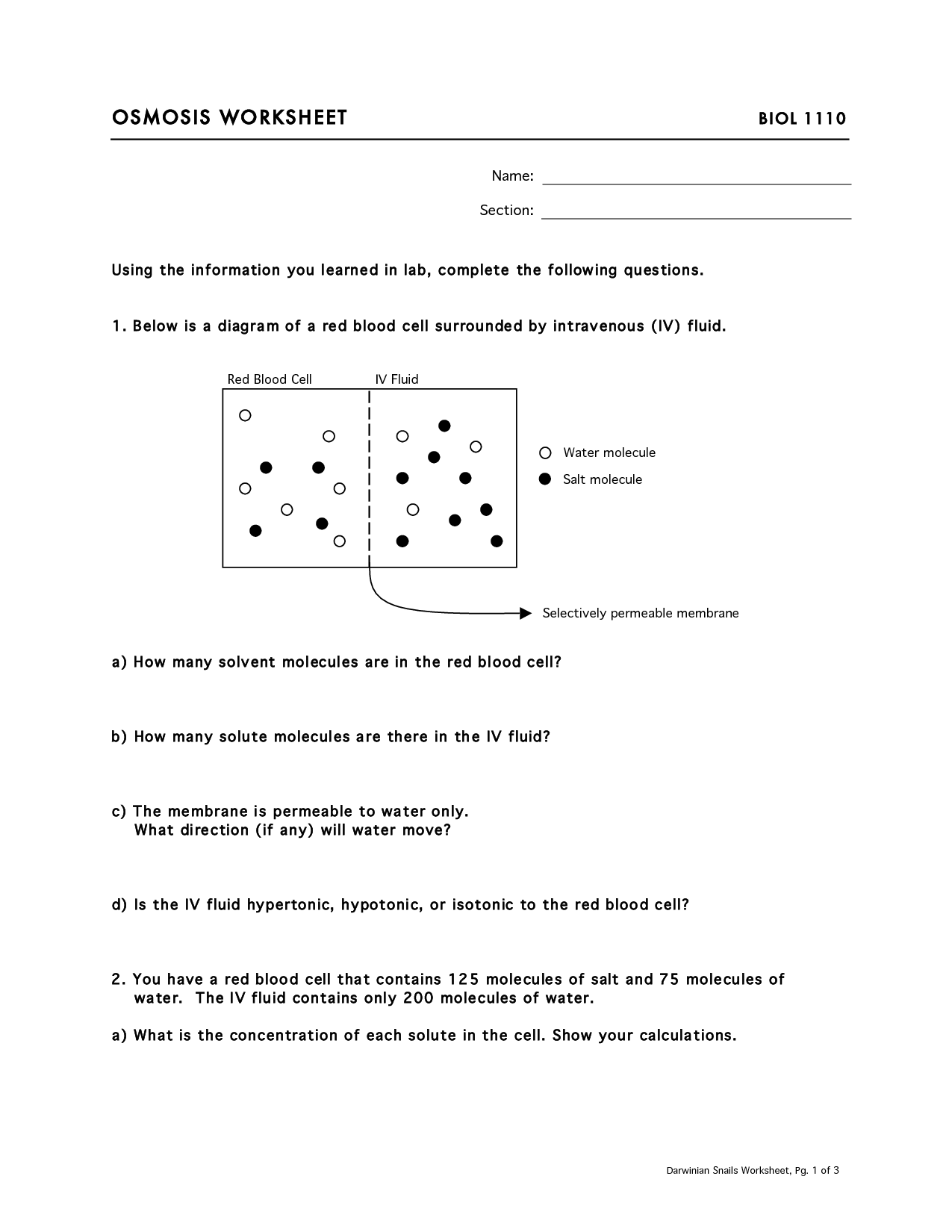
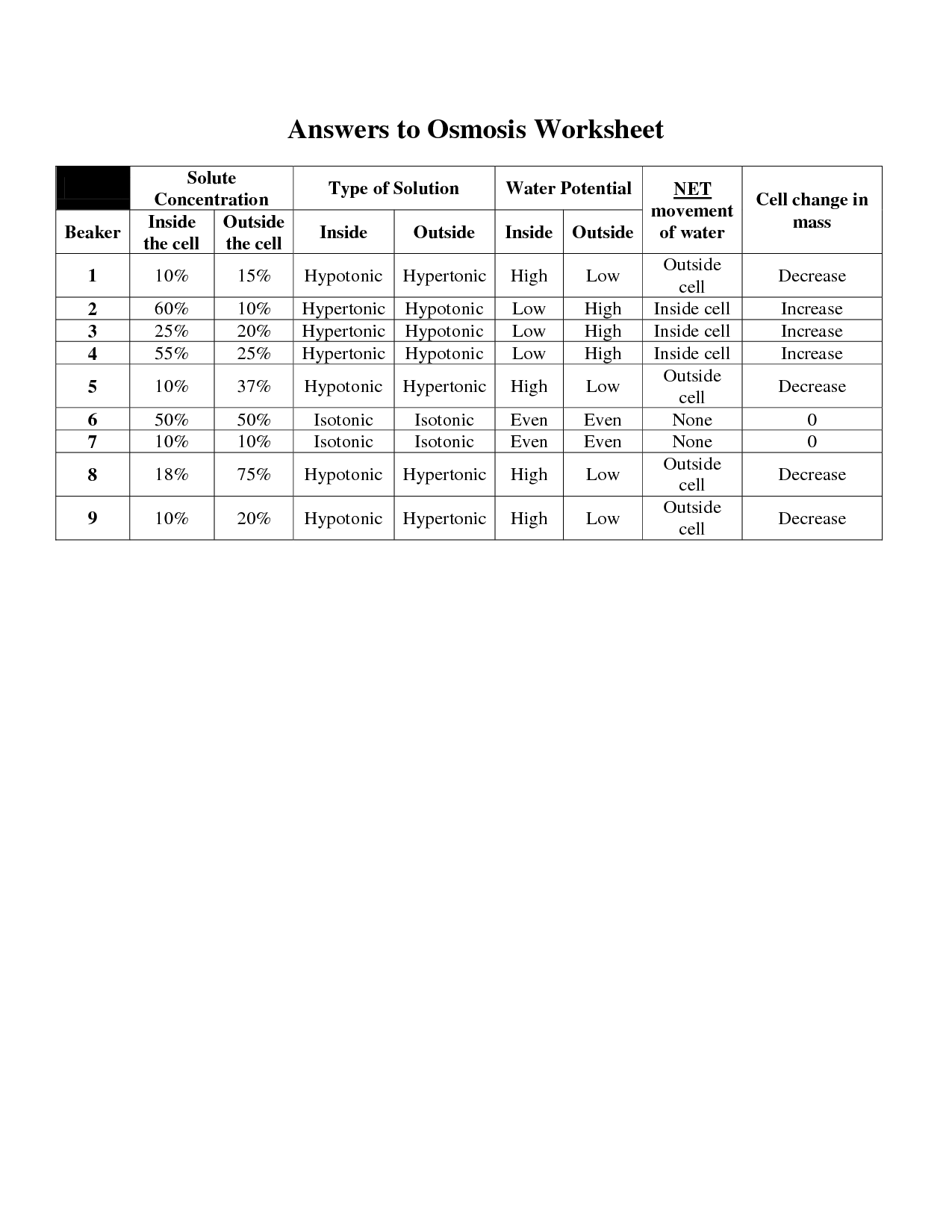
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the process by which molecules of a solvent move through a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration, in order to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane. This movement of solvent molecules occurs until equilibrium is reached, creating a pressure known as osmotic pressure.
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
Osmosis and diffusion are both processes of passive transport, where molecules move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. The key difference is that osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane, while diffusion refers to the movement of any type of molecule (not just water) from high to low concentration, without the need for a membrane necessarily.
What is the purpose of a selectively permeable membrane in osmosis?
The purpose of a selectively permeable membrane in osmosis is to allow certain molecules or ions to pass through while restricting the movement of others. This selective permeability helps to regulate the flow of water and solutes between the two sides of the membrane, ensuring that the concentration gradient is maintained and allowing for proper cell function and osmotic balance.
How does osmosis maintain cell homeostasis?
Osmosis maintains cell homeostasis by regulating the movement of water across the cell membrane. The process ensures that the concentration of water inside and outside the cell remains balanced, preventing excessive water gain or loss that could disrupt the cell's internal environment. Cells use osmosis to maintain proper hydration levels and to transport nutrients and waste products effectively, contributing to overall cell function and stability.
What happens to an animal cell in a hypertonic solution?
When an animal cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (a solution with a higher concentration of solutes than the cell's cytoplasm), water will move out of the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to shrink or shrivel up in a process called crenation. This is because the external solution has a higher solute concentration, creating a gradient that draws water out of the cell, leading to a decrease in the cell's volume.
What happens to a plant cell in a hypotonic solution?
When a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will move into the cell due to osmosis, causing the cell to swell and potentially burst. The cell wall helps prevent bursting by exerting pressure on the cell membrane, a state known as turgor pressure. This increased pressure in the cell can lead to the cell becoming turgid, which is important for maintaining the structural integrity of the plant.
How does the process of osmosis impact living organisms?
Osmosis is a crucial process for living organisms as it allows for the movement of water and dissolved substances across cell membranes to maintain proper hydration and control internal concentrations of solutes. It helps in regulating the balance of fluids inside and outside cells and is essential for processes like nutrient uptake, waste removal, and maintaining cell turgidity. However, imbalances in osmosis can have adverse effects, such as causing cells to swell or shrink, leading to cellular damage or dysfunction. Overall, osmosis plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning and survival of living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments