Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are an invaluable resource for students of all ages and levels of education. Whether you're a teacher looking for new ways to reinforce concepts or a student seeking additional practice, worksheets provide a structured and organized platform for learning. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of worksheets, specifically focusing on diffusion and osmosis, topics that are commonly studied in biology and chemistry classes.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
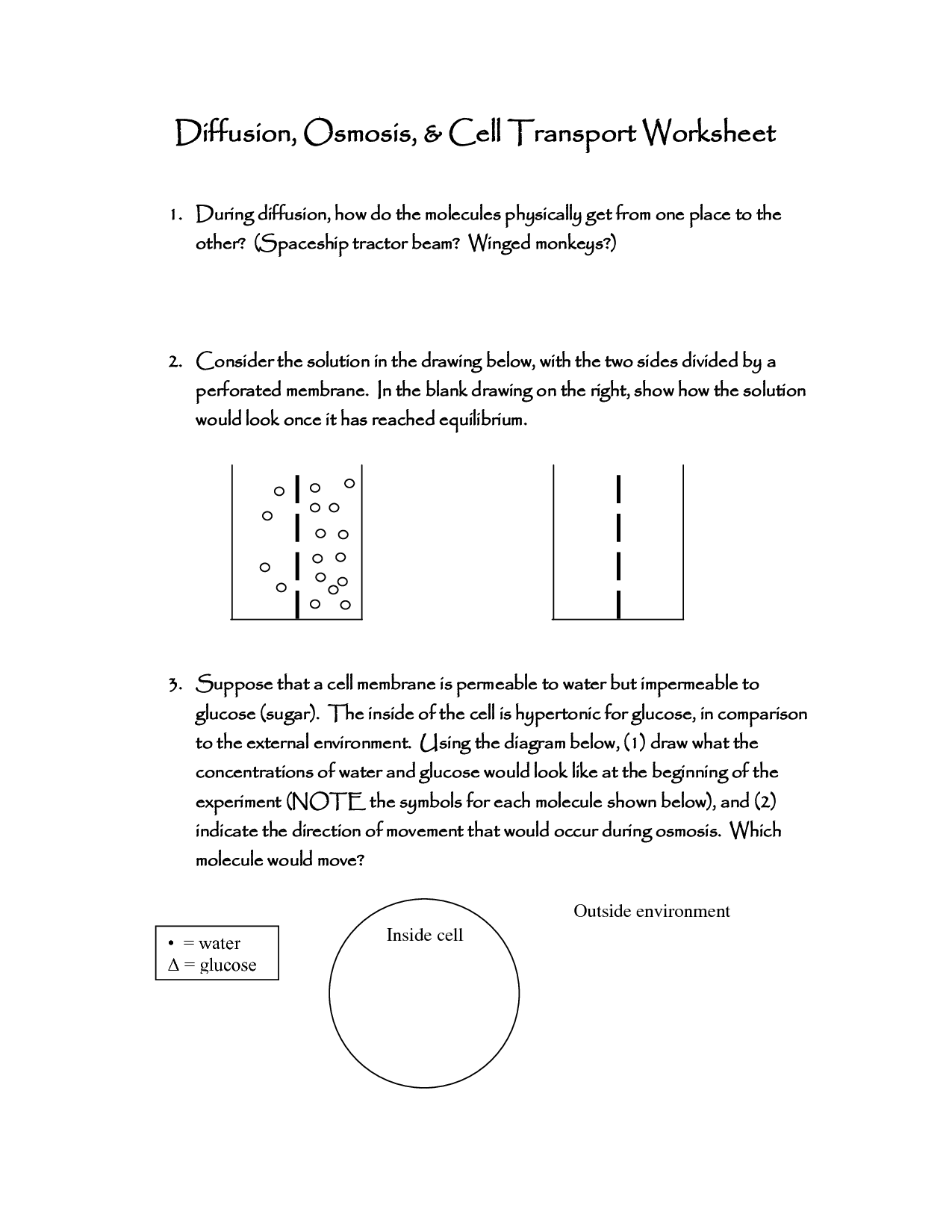
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the process by which particles or molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, due to random thermal motion. This movement leads to the equalization of concentration throughout a medium, until reaching a state of equilibrium.
How does diffusion occur?
Diffusion is the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the natural tendency of particles to spread out and achieve a state of equilibrium. This movement occurs due to random kinetic energy, with particles colliding and bouncing off each other, eventually leading to an even distribution of particles throughout the space.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Several factors can affect the rate of diffusion, including the size of the molecules or ions diffusing, the temperature of the system (higher temperatures generally increase the rate of diffusion), the concentration gradient (the greater the difference in concentration, the faster the diffusion), the medium through which diffusion occurs (diffusion tends to occur more quickly in gases than in liquids or solids), and the surface area available for diffusion (larger surface areas facilitate faster diffusion). Additionally, the presence of barriers or obstacles in the medium can also affect the rate of diffusion.
How does temperature impact the rate of diffusion?
Temperature directly impacts the rate of diffusion by affecting the kinetic energy of molecules. As temperature increases, molecules move faster and have greater kinetic energy, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions. This results in a higher rate of diffusion because the molecules can more easily overcome barriers and mix with other substances in the surrounding environment. Conversely, at lower temperatures, molecules move slower and have less energy, which slows down the diffusion process.
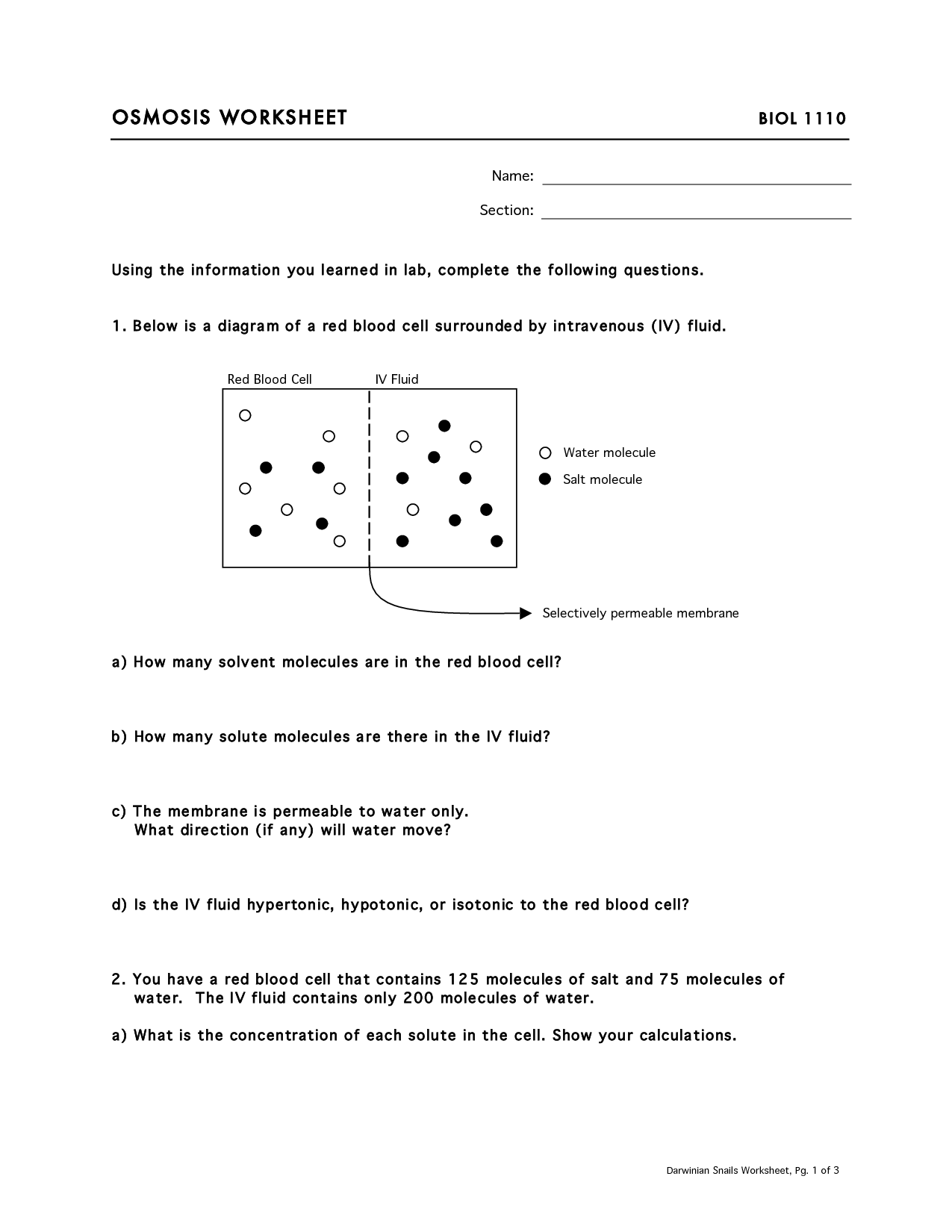
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles (usually water) through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This process helps equalize the concentration of solute on both sides of the membrane until equilibrium is reached.
What is the role of a selectively permeable membrane in osmosis?
A selectively permeable membrane in osmosis acts as a barrier that allows only certain molecules or ions to pass through while restricting the movement of others. This membrane controls the flow of water and solutes to maintain balance between the concentrations of solutes on either side of the membrane. In osmosis, water moves across the selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration in order to equalize the concentration on both sides, resulting in the movement of water molecules.
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
Osmosis and diffusion are both passive transport processes that involve the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. However, osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane, while diffusion is the movement of any type of molecule (not just water) across a membrane or through a solution. Additionally, osmosis involves the movement of water only, while diffusion can involve the movement of various types of molecules.
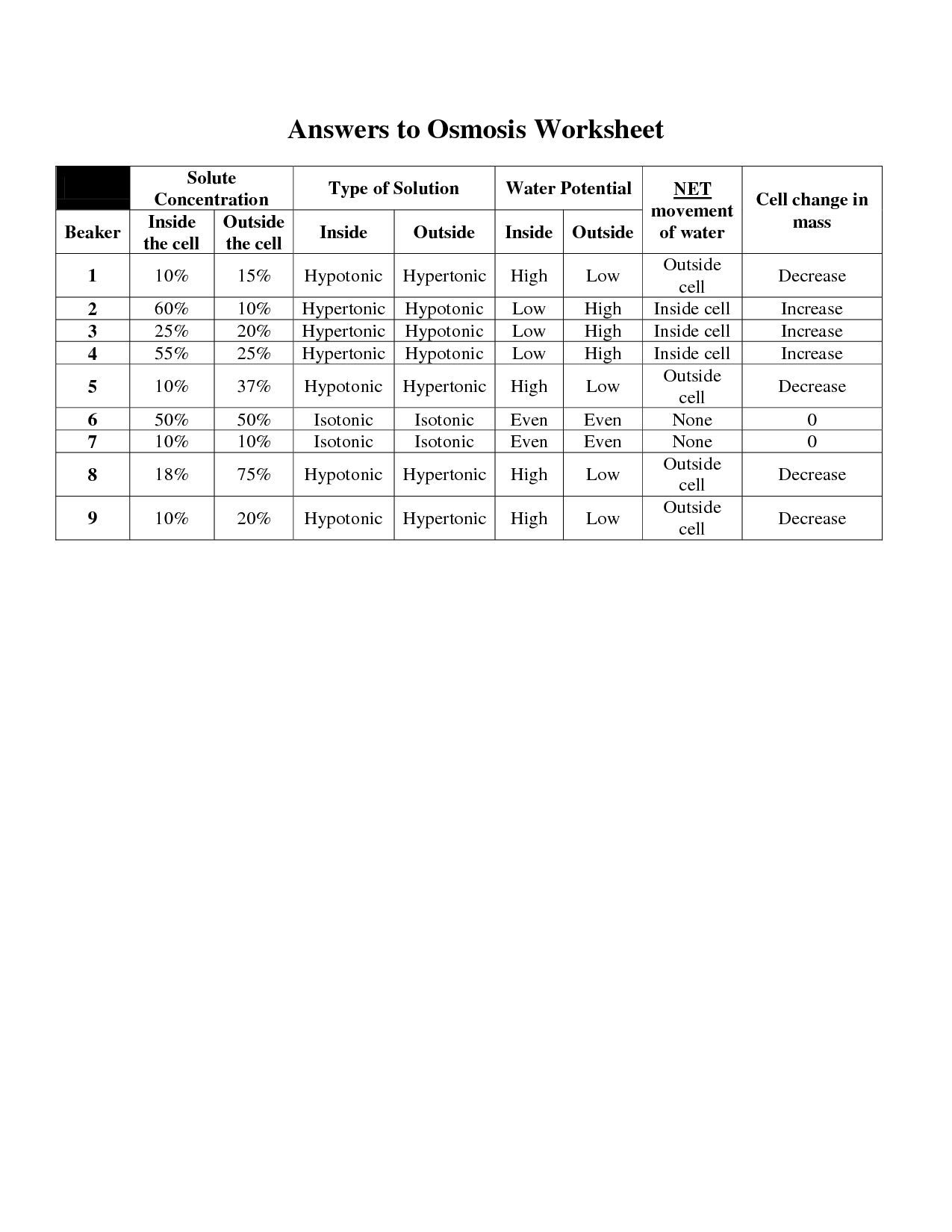
What are the differences between isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions?
Isotonic solutions have the same concentration of solutes as the cells in the body, leading to no net movement of water. Hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes than the cells, causing water to leave the cells and shrink. Hypotonic solutions have a lower concentration of solutes than the cells, resulting in water entering the cells and potentially causing them to burst.
How do cells regulate osmotic pressure?
Cells regulate osmotic pressure through a process called osmoregulation. This is achieved by controlling the movement of water and solutes across the cell membrane. Specialized membrane proteins, such as aquaporins, facilitate the movement of water. Additionally, cells can actively transport ions and solutes to adjust their internal osmolarity in response to changes in their external environment. This allows cells to maintain their structural integrity and function properly despite fluctuating external osmotic conditions.
How do osmosis and diffusion contribute to the functioning of living organisms?
Osmosis and diffusion are fundamental processes in living organisms that are essential for maintaining homeostasis. Diffusion allows molecules to move from areas of high concentration to low concentration, helping to transport nutrients, waste products, and signaling molecules within cells and between cells. Osmosis, a specific type of diffusion, involves the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane to balance the concentration of solutes on either side. This process is crucial for regulating the internal environment of cells and ensuring proper cellular function, as well as for processes like nutrient uptake in plants and maintaining blood pressure in animals. Overall, osmosis and diffusion play key roles in various physiological processes that support the functioning of living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments