Constitutional Compromises Worksheet
The Constitutional Compromises Worksheet is designed for middle and high school students who are studying American history or government. This comprehensive worksheet serves as an essential resource to help students understand and analyze the various compromises made during the drafting and ratification of the United States Constitution. With a clear focus on the individuals and the subject matter, this worksheet offers a thorough examination of the important decisions and concessions that shaped our nation's founding document.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
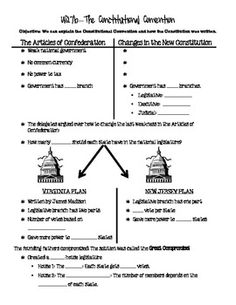
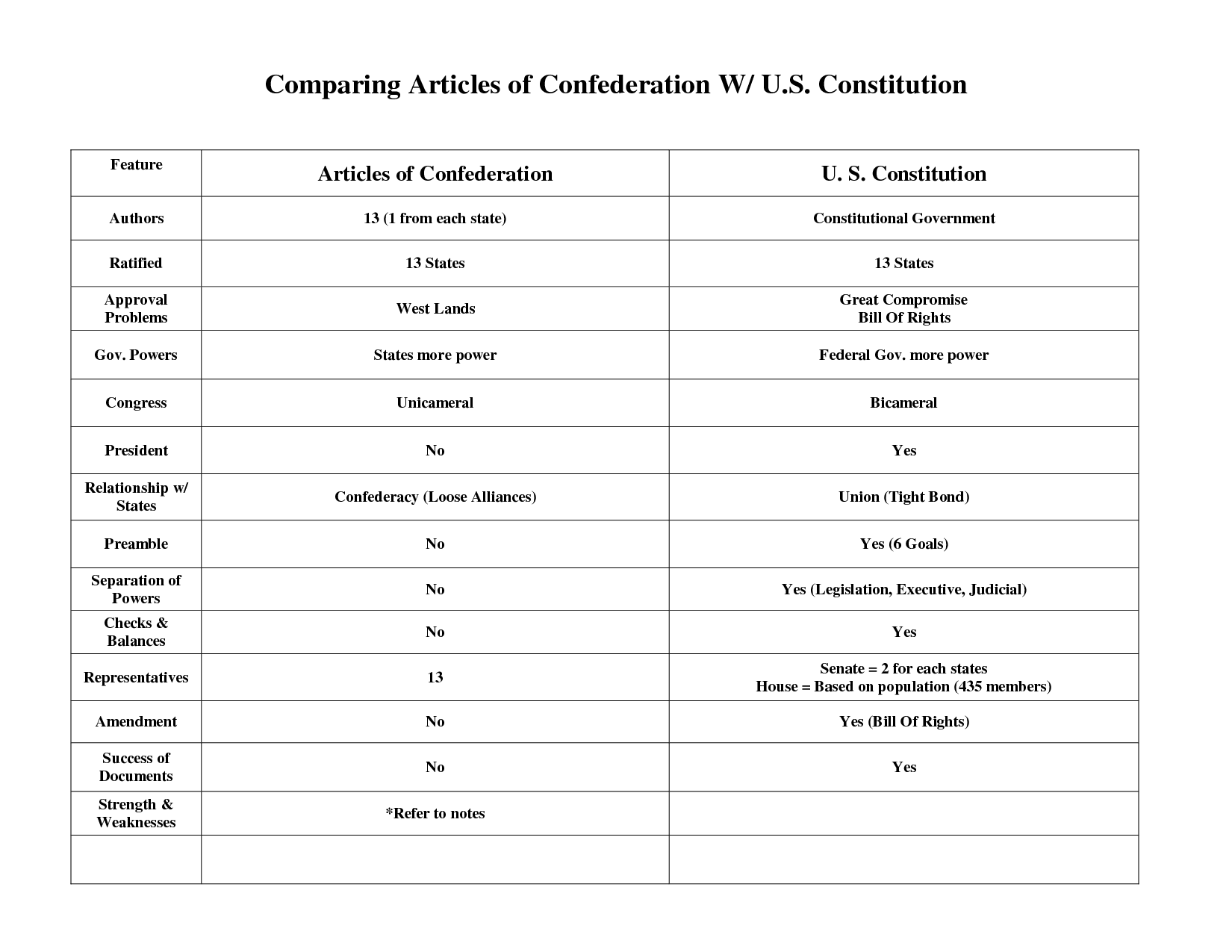
What were the Constitutional Compromises of 1787?
The Constitutional Compromises of 1787 were the Great Compromise, which established a bicameral legislature with representation based on population in the House of Representatives and equal representation per state in the Senate; the Three-Fifths Compromise, which counted enslaved individuals as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of determining representation in Congress and taxation; and the Commerce Compromise, which allowed Congress to regulate interstate and foreign commerce but prohibited export taxes and favored northern states in regulating commerce.
What was the purpose of the Great Compromise?
The purpose of the Great Compromise, also known as the Connecticut Compromise, was to resolve the heated debate over representation in the newly formed United States Congress. It proposed a bicameral legislature, with one house based on population size (House of Representatives) and the other providing equal representation for each state (Senate), striking a balance between the interests of large and small states at the Constitutional Convention in 1787.
What issue did the Three-Fifths Compromise address?
The Three-Fifths Compromise addressed the issue of how enslaved individuals would be counted for the purposes of representation in Congress and taxation during the Constitutional Convention in 1787. This compromise determined that each enslaved person would be counted as three-fifths of a person when apportioning representation and taxes among the states.
How did the Commerce Compromise settle disputes related to trade?
The Commerce Compromise, also known as the Commerce Clause, settled disputes related to trade by granting Congress the power to regulate interstate and foreign commerce. This compromise allowed the federal government to control trade and prevent conflicting regulations between states, ensuring a unified and consistent approach to commerce throughout the country.
What was the Fugitive Slave Clause and why was it significant?
The Fugitive Slave Clause, found in Article IV, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution, mandated the return of runaway slaves to their owners. It was significant because it institutionalized and legalized the practice of capturing and returning escaped slaves, reinforcing the institution of slavery and denying freedom to those seeking to escape its oppressive conditions. It also fueled tensions between free and slave states, ultimately contributing to the growing divide that led to the Civil War.
How did the Electoral College compromise address concerns of both small and large states?
The Electoral College compromise addressed concerns of both small and large states by establishing a system where each state is allocated a number of electors based on its total number of representatives in Congress. This ensured that small states still had a proportional voice in selecting the president, as each state, regardless of size, has a minimum of three electors. At the same time, the system also gave larger states a weighted influence in the election process due to their higher population and representation in Congress. Overall, the Electoral College compromise sought to balance the interests of both small and large states in choosing the president.
What was the purpose of the Slave Trade Compromise?
The purpose of the Slave Trade Compromise was to resolve the issue of how enslaved persons would be counted for the purpose of taxation and representation in the United States. The compromise stated that enslaved individuals would be counted as three-fifths of a person for both taxation and representation in Congress, appeasing both slaveholding and non-slaveholding states during the drafting of the U.S. Constitution in 1787.
What were the main disagreements between the Northern and Southern states regarding representation?
The main disagreements between the Northern and Southern states regarding representation centered around how slaves should be counted for determining representation in Congress. The Southern states wanted slaves to be counted as full persons for representation purposes to increase their political power, while the Northern states objected, arguing that slaves should not be counted as they were not considered citizens and did not have the rights of free individuals. This led to the Three-Fifths Compromise, which determined that slaves would be counted as three-fifths of a person for representation and taxation purposes.
How did the Compromise on the Importation of Slaves affect the future of slavery in the United States?
The Compromise on the Importation of Slaves, which took effect in 1808, prohibited the importation of slaves into the United States. This led to a decline in the number of new slaves entering the country and shifted the focus of the institution of slavery towards the domestic trading and breeding of slaves within the country. It contributed to the growth of the domestic slave trade and the expansion of slavery in the southern states, further entrenching the institution and perpetuating its existence in the United States until the Civil War.
What long-term impact did the Constitutional Compromises have on the stability and unity of the United States?
The Constitutional Compromises, such as the Three-Fifths Compromise and the Great Compromise, played a significant role in fostering stability and unity in the United States in the long term. By addressing contentious issues like representation and slavery, these compromises helped to create a framework for governance that balanced the interests of different states and regions. This foundation laid the groundwork for the functioning of the federal government and the peaceful resolution of conflicts, ultimately contributing to the stability and cohesion of the nation.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments