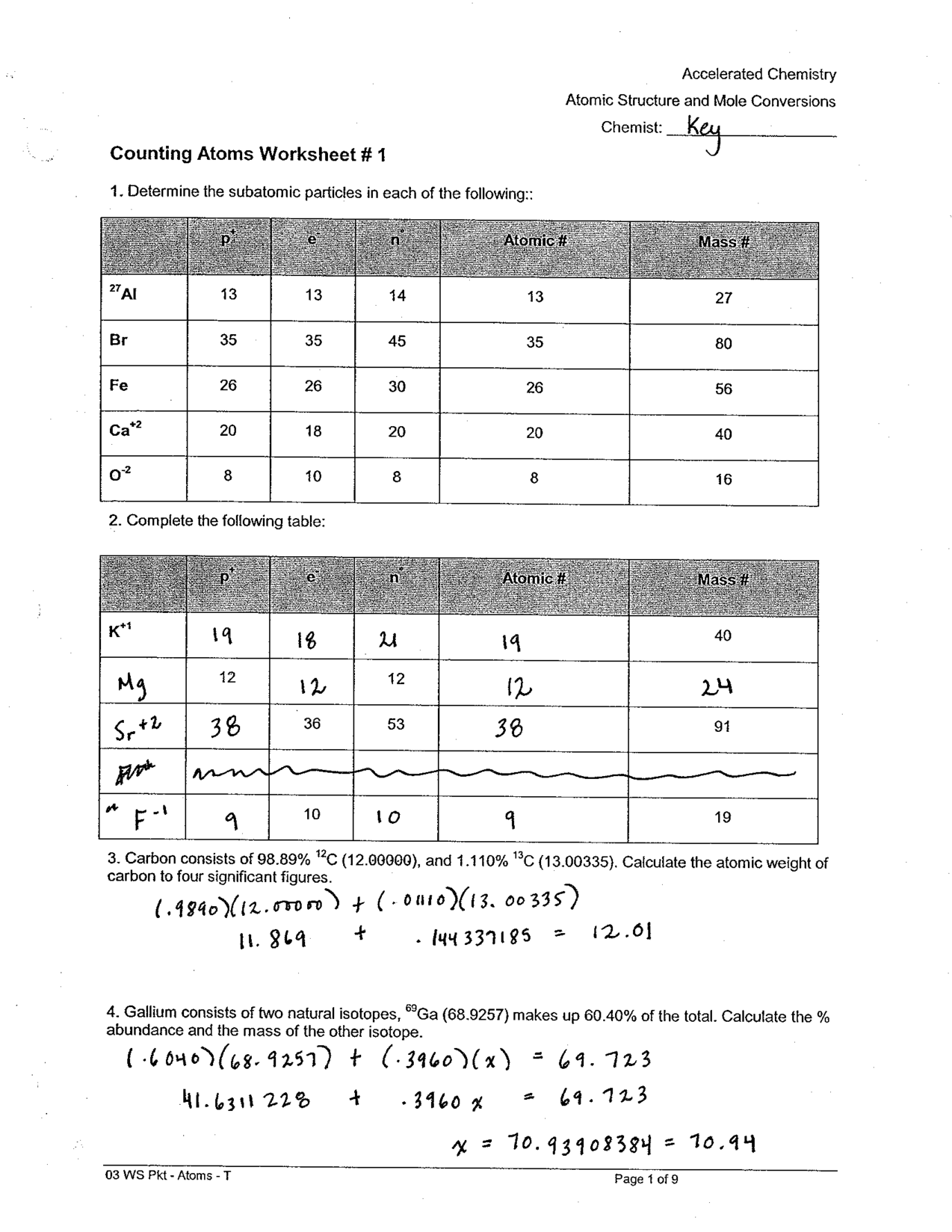
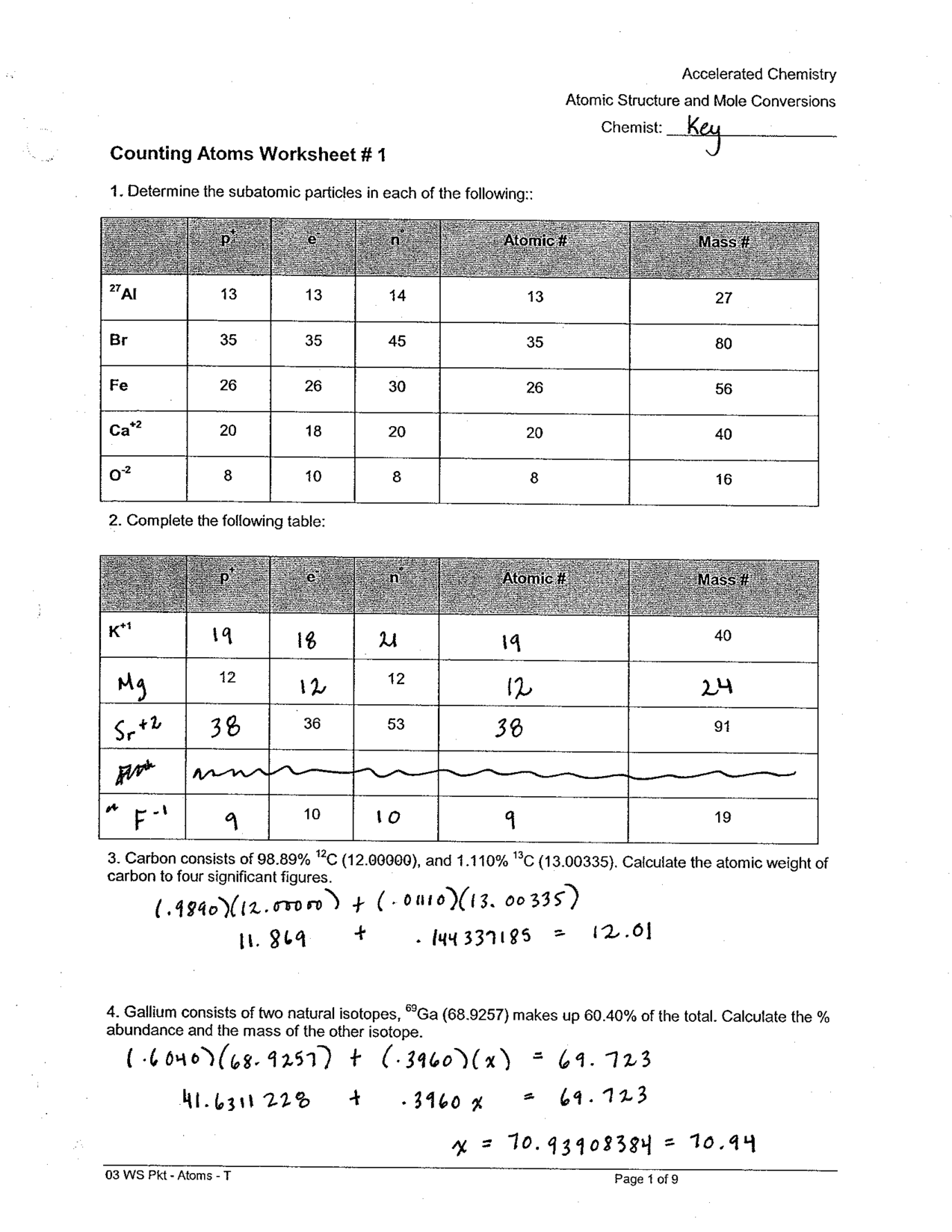
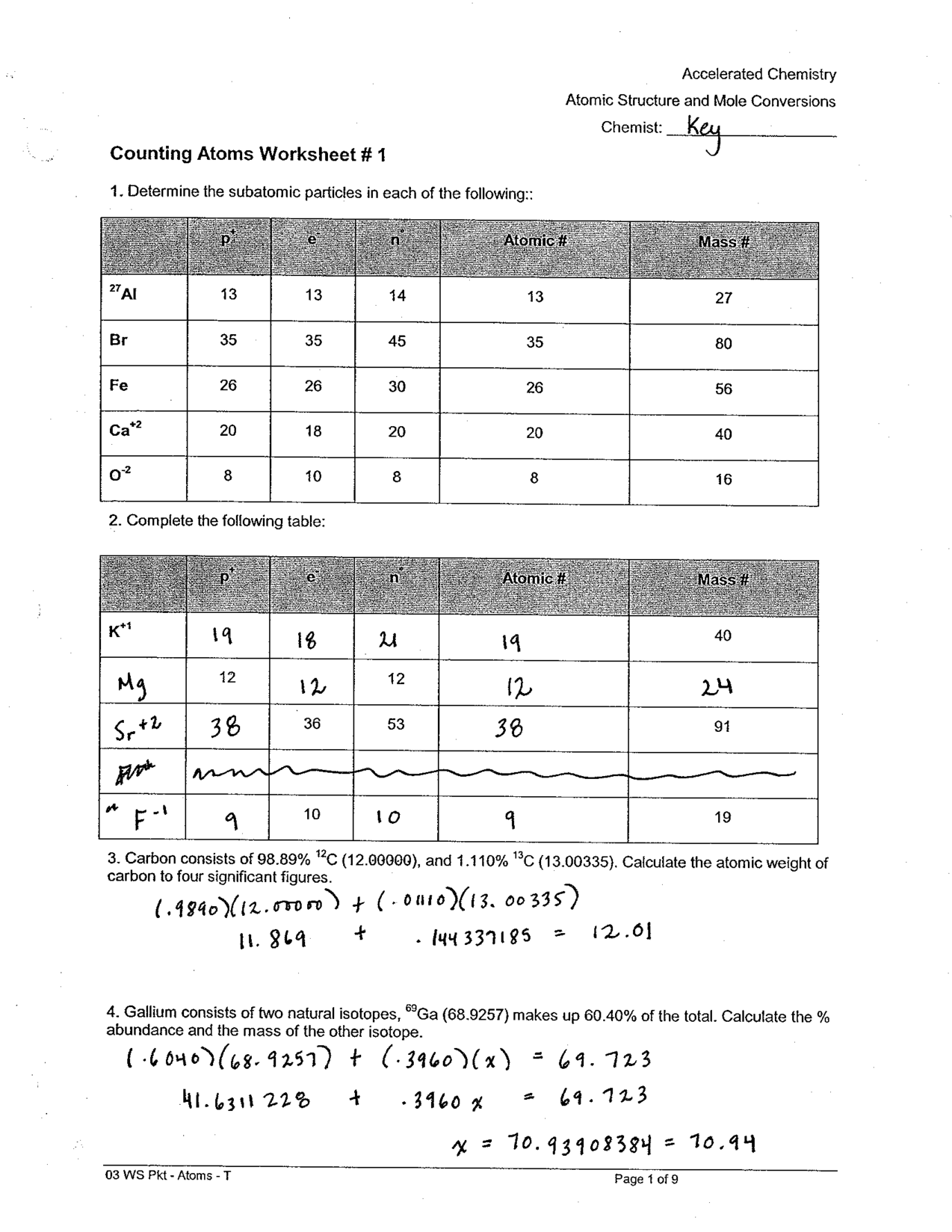
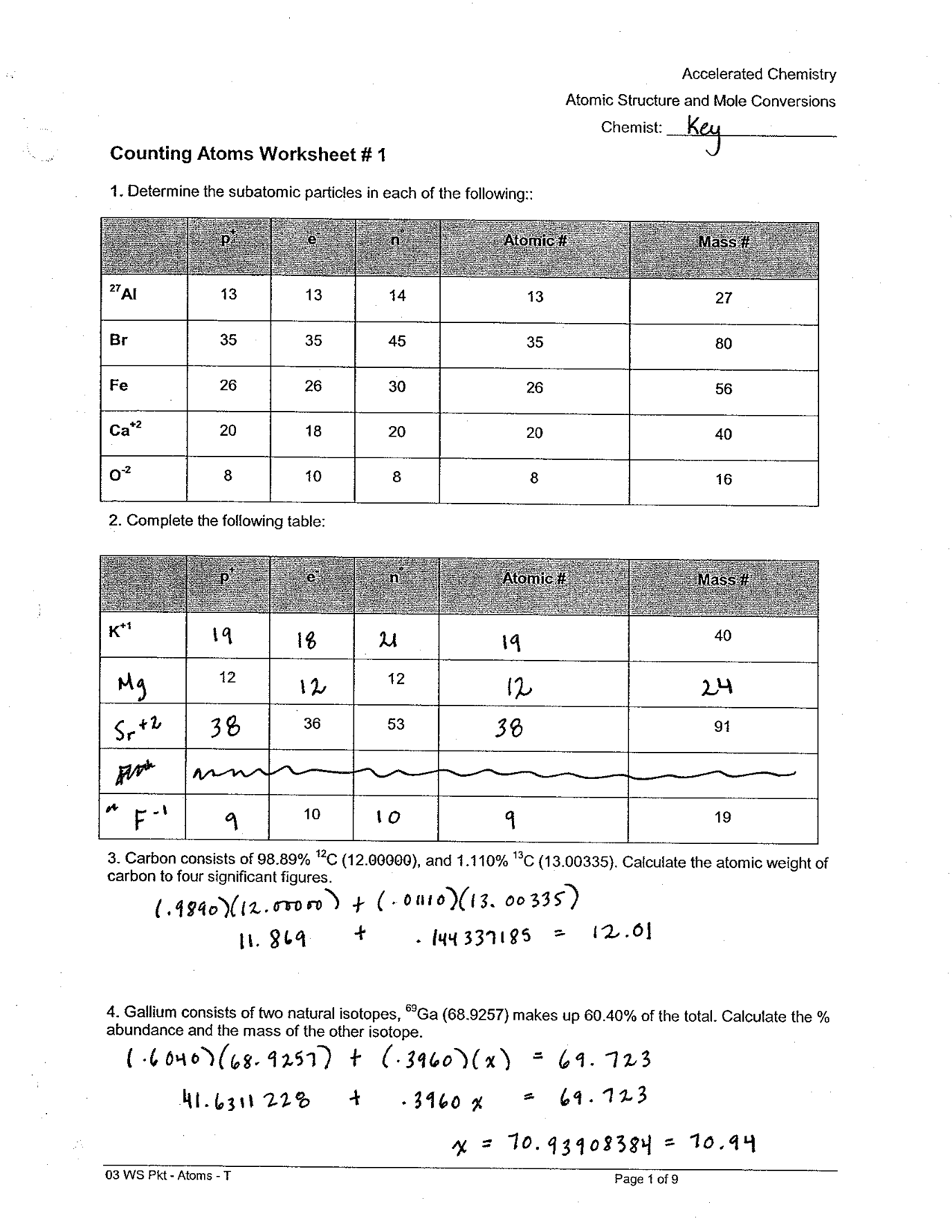
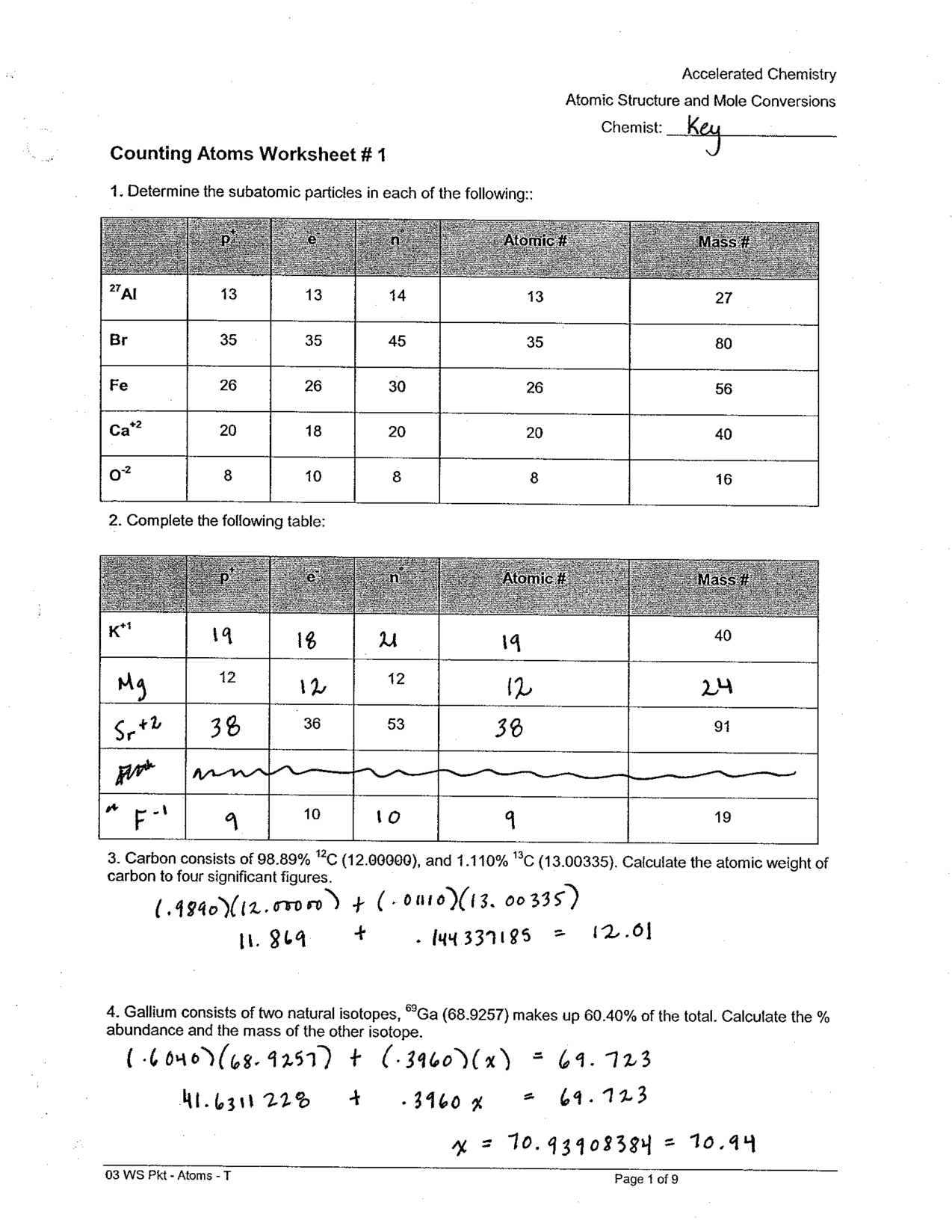
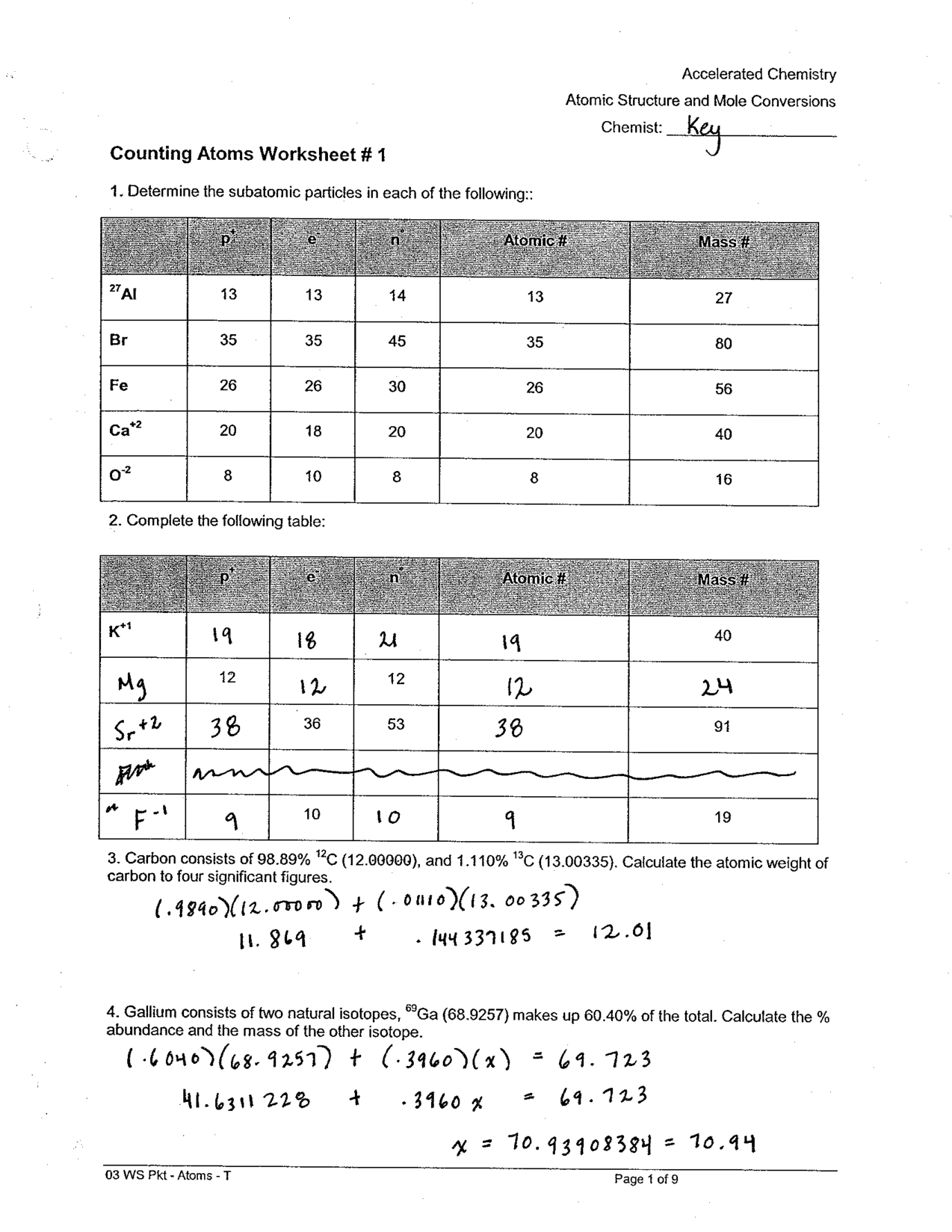
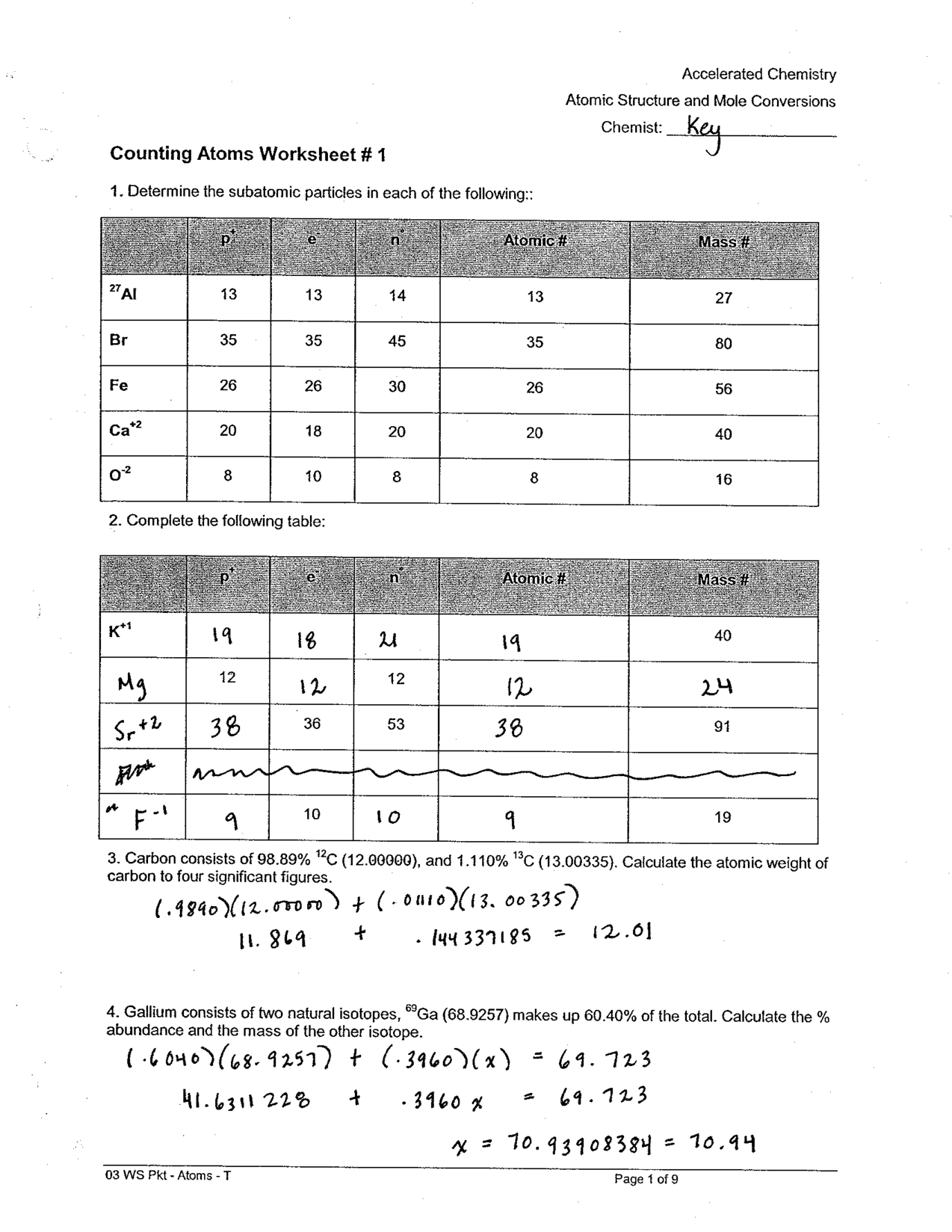
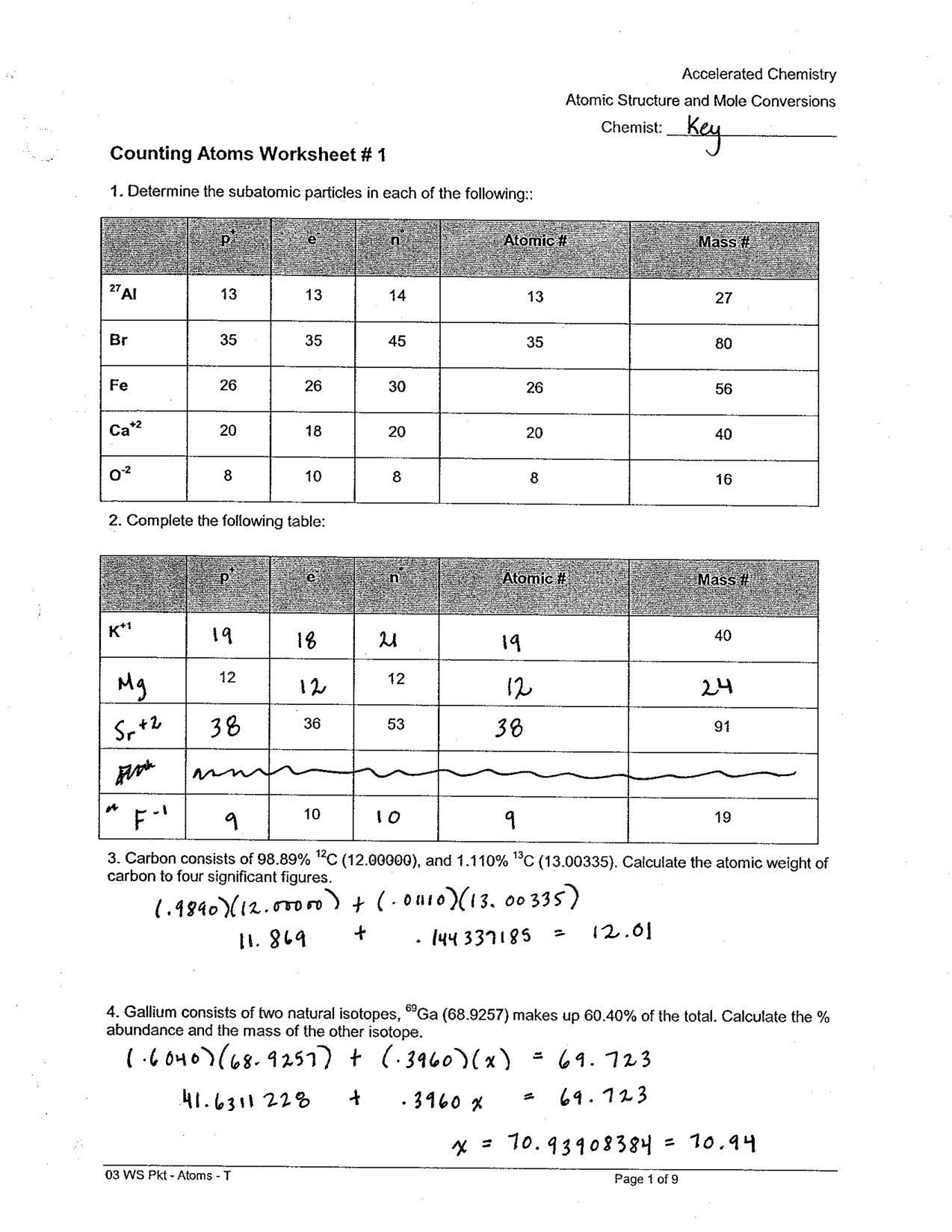
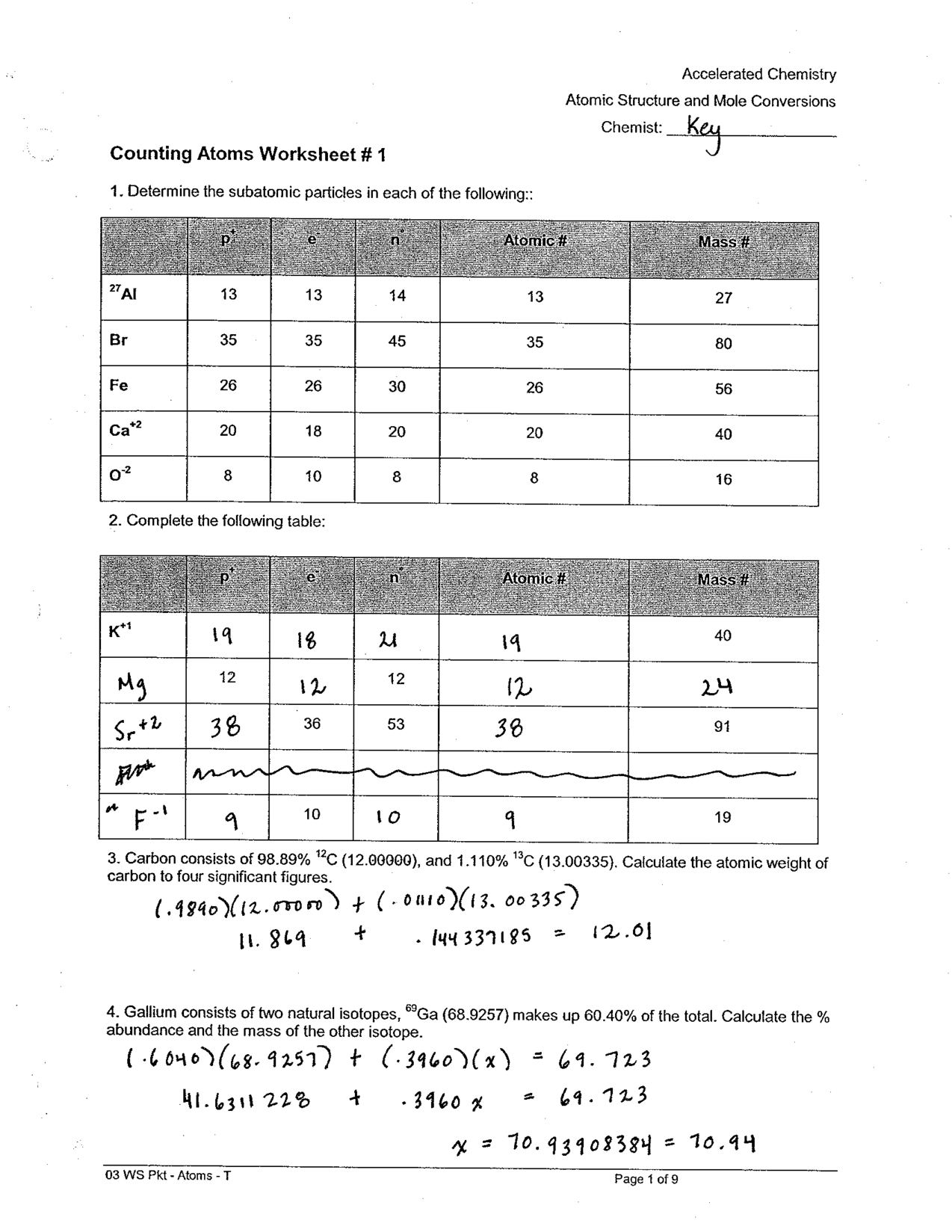
Compound Probability Worksheets Dependent
If you're a math teacher or a parent looking for worksheets on compound probability that focus specifically on dependent events, you've come to the right place. These worksheets are designed to provide practice and reinforcement on the concept of compound probability with dependent events for students in middle and high school.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the probability of drawing a red card from a deck of cards after a black card has already been drawn?
The probability of drawing a red card from a deck of cards after a black card has already been drawn is 26 out of 51, or approximately 0.51. This is because there are initially 26 red cards and 26 black cards in a deck of 52 cards, but after a black card is drawn, there are only 26 red cards left out of the remaining 51 cards.
A bag contains 5 red marbles and 3 blue marbles. What is the probability of drawing two red marbles in a row without replacement?
The probability of drawing a red marble on the first draw is 5/8. Since the first red marble is not replaced, the probability of drawing a second red marble is 4/7 (as there are now 4 red marbles and 7 total marbles remaining in the bag). Therefore, the probability of drawing two red marbles in a row without replacement is (5/8) * (4/7) = 20/56 or 5/14.
In a pack of 52 cards, what is the probability of drawing two hearts in a row without replacement?
The probability of drawing a heart on the first draw is 13/52, as there are 13 hearts in a deck of 52 cards. After drawing a heart, there are now 51 cards left in the deck, with 12 hearts remaining. Therefore, the probability of drawing another heart on the second draw is 12/51. Multiplying these probabilities together gives (13/52) * (12/51) = 3/52, which is the probability of drawing two hearts in a row without replacement from a deck of 52 cards.
A jar contains 4 green candies and 6 red candies. If two candies are drawn, what is the probability of drawing a green candy first and then a red candy without replacement?
To calculate the probability of drawing a green candy first and then a red candy without replacement, we multiply the probabilities. The probability of drawing a green candy first is 4/10 (since there are a total of 10 candies), and after drawing one green candy, there will be 9 candies left (3 green and 6 red). Therefore, the probability of drawing a red candy next is 6/9. Multiplying these two probabilities, we get (4/10) * (6/9) = 24/90 = 4/15. Therefore, the probability of drawing a green candy first and then a red candy without replacement is 4/15.
In a box, there are 8 black balls and 4 white balls. If three balls are drawn without replacement, what is the probability of getting two black balls and one white ball in any order?
The probability of getting two black balls and one white ball in any order can be calculated by considering all the possible ways this combination can occur. There are ${8 \choose 2} \times {4 \choose 1} = 28 \times 4 = 112$ ways to choose 2 black balls out of 8 and 1 white ball out of 4. The total number of ways to choose 3 balls out of 12 is ${12 \choose 3} = 220$. Therefore, the probability is 112/220 = 28/55.
From a bag with 10 marbles (6 blue and 4 yellow), two marbles are drawn without replacement. What is the probability of drawing a blue marble first and then a yellow marble?
First, calculate the probability of drawing a blue marble first. There are 6 blue marbles out of a total of 10 marbles, so the probability of drawing a blue marble first is 6/10. Next, after drawing a blue marble, there will be 5 blue and 4 yellow marbles left in the bag, making a total of 9 marbles. The probability of drawing a yellow marble next is 4/9. To find the probability of both events happening, multiply the probabilities together: (6/10) x (4/9) = 24/90, which simplifies to 4/15. Therefore, the probability of drawing a blue marble first and then a yellow marble is 4/15.
A box contains 7 green balls and 5 red balls. If two balls are drawn without replacement, what is the probability of drawing a red ball first and then a green ball?
To find the probability of drawing a red ball first and then a green ball, we need to first calculate the probability of drawing a red ball followed by a green ball. The probability of drawing a red ball first is 5/12, as there are 5 red balls out of a total of 12 balls. After drawing a red ball, there will be 6 green balls and 11 total balls left in the box. Therefore, the probability of drawing a green ball second is 6/11. To find the overall probability, we multiply the two probabilities: (5/12) * (6/11) = 30/132 = 5/22. So, the probability of drawing a red ball first and then a green ball is 5/22.
In a jar, there are 3 black candies and 2 white candies. If two candies are drawn without replacement, what is the probability of drawing a white candy first and then a black candy?
The probability of drawing a white candy first is 2/5, and after that, there will be 2 black candies left among 4 total candies. Therefore, the probability of drawing a black candy second is 2/4. Multiplying these probabilities together, the overall probability of drawing a white candy first and then a black candy is (2/5) * (2/4) = 1/5 or 0.2.
A deck of cards contains 26 red cards and 26 black cards. If two cards are drawn without replacement, what is the probability of drawing a red card first and then a black card?
The probability of drawing a red card first and then a black card can be calculated as the product of the probabilities of each event happening sequentially. The probability of drawing a red card first is 26/52 (as there are 26 red cards out of 52 total cards), and after drawing a red card, there are 25 red cards left and 26 black cards out of a total of 51 cards. So, the probability of drawing a black card next is 26/51. Therefore, the total probability is (26/52) * (26/51) = 1/2 * 26/51 = 26/102, which simplifies to 13/51. So, the probability of drawing a red card first and then a black card is 13/51.
In a bag, there are 9 green marbles and 7 blue marbles. What is the probability of drawing a blue marble from the bag after a green marble has already been drawn without replacement?
After drawing a green marble from the bag, there are now 8 green marbles and 7 blue marbles left. Therefore, the probability of drawing a blue marble after a green marble has been drawn without replacement is 7/15.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments