Chromosome Structure Worksheet
Are you struggling to understand the structure of chromosomes? Look no further! This blog post will provide you with a helpful chromosome structure worksheet that will simplify the concepts and help you grasp this fundamental topic in genetics. Designed for beginners and students studying biology, this informative worksheet breaks down the various components of chromosomes and their functions, allowing you to enhance your understanding of this crucial subject.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
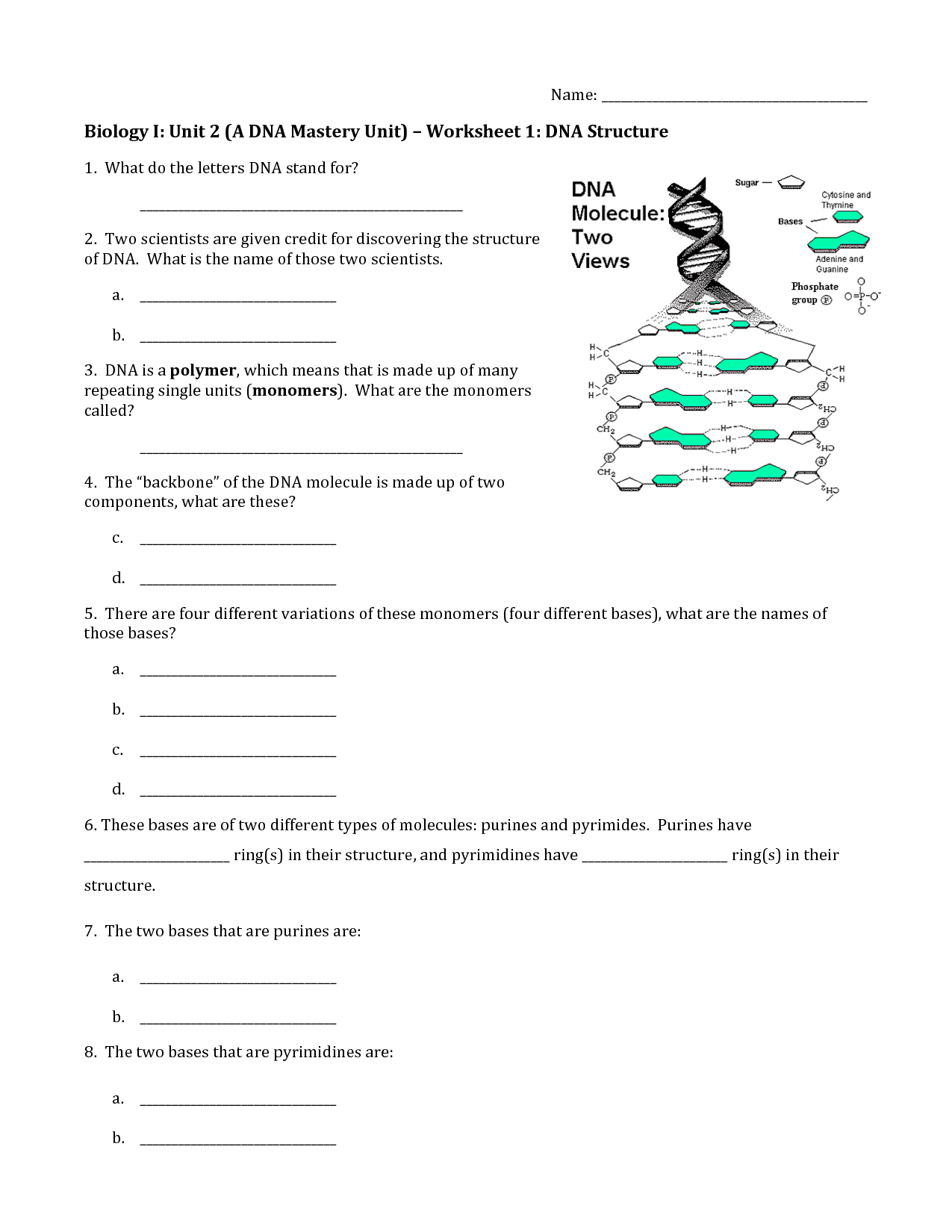
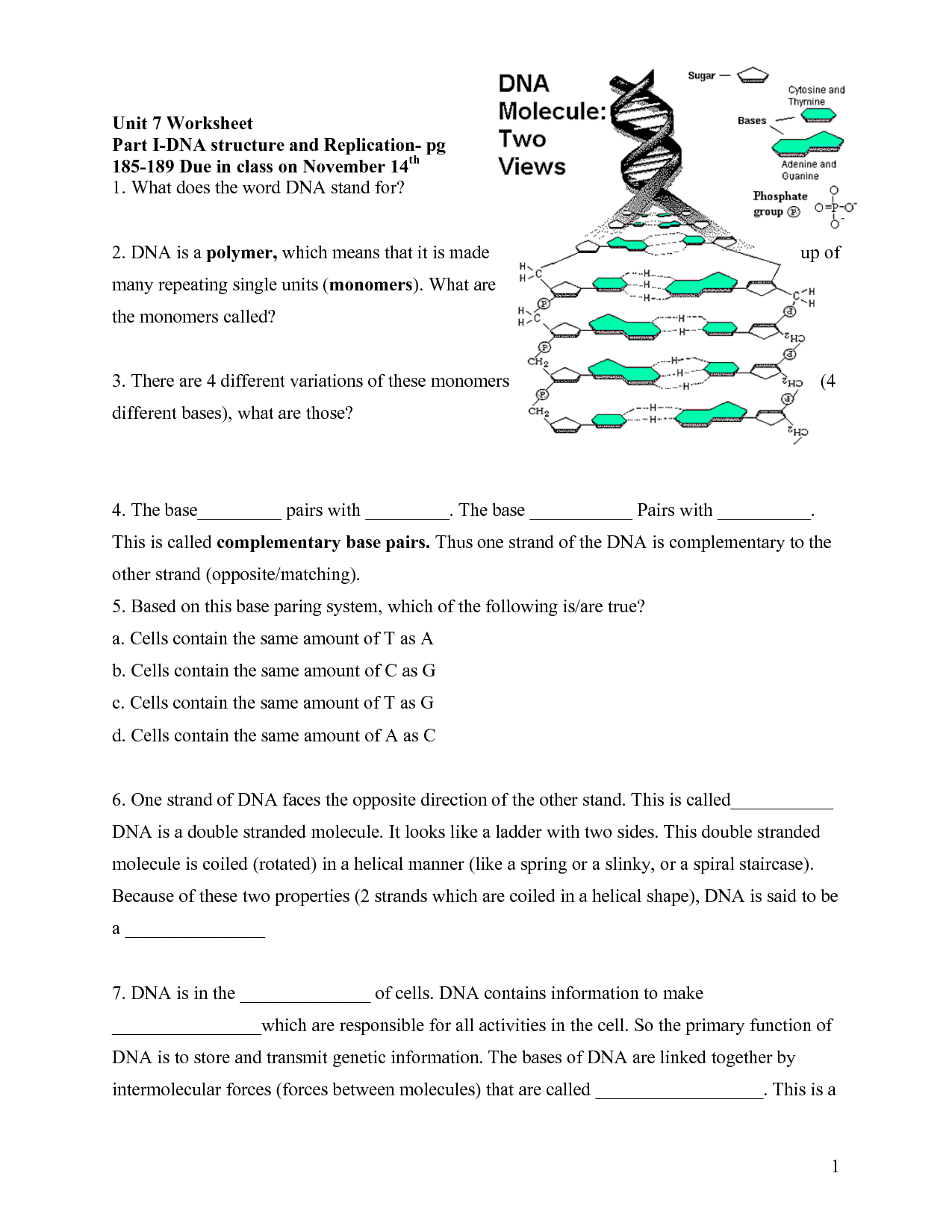
What is the primary component of a chromosome?
The primary component of a chromosome is DNA, which carries the genetic information in the form of genes that control the development and functioning of living organisms.
What are the two main types of chromatin?
The two main types of chromatin are euchromatin and heterochromatin. Euchromatin is less condensed and more transcriptionally active, allowing for gene expression. In contrast, heterochromatin is more condensed and generally transcriptionally inactive, playing a role in maintaining chromosome structure and regulating gene expression.
How is DNA packaged within a chromosome?
DNA is packaged within a chromosome by being wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. These nucleosomes, consisting of DNA and histones, then coil and fold further to create a more condensed structure known as chromatin. The chromatin further condenses to form the visible, distinct structure of the chromosome. This packaging of DNA allows for compact storage of genetic material and helps regulate gene expression.
What is the role of histones in chromosome structure?
Histones are protein molecules that play a crucial role in chromosome structure by organizing and compacting DNA into a complex called chromatin. These proteins bind to DNA and help to package it efficiently within the nucleus of a cell. Histones also regulate gene expression by controlling access to the DNA for transcription factors. Their interactions with DNA play a key role in determining how tightly or loosely packed the chromatin is, which in turn affects the accessibility of genes for transcription and ultimately influences the functioning of the cell.
What are telomeres, and what is their function?
Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences located at the ends of chromosomes that protect the genetic material from degradation and maintain the stability of the chromosome. Their main function is to prevent the loss of essential genetic information during DNA replication and cell division. Additionally, telomeres play a crucial role in determining the lifespan of cells and are implicated in aging and disease processes.
What is the purpose of centromeres in chromosome structure?
Centromeres are specialized regions of DNA found on chromosomes that play a crucial role in cell division. Their main purpose is to ensure the accurate separation of chromosomes during cell division, as they serve as attachment sites for spindle fibers that help pull apart sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. This process ensures that each new daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes, essential for maintaining genetic stability and preventing abnormalities.
How does chromosome structure differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes have a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid region of the cell, lacking a membrane-bound nucleus. In contrast, eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes enclosed within a membrane-bound nucleus. Additionally, eukaryotic chromosomes are associated with histone proteins, forming a more complex structure compared to prokaryotic chromosomes. Eukaryotic chromosomes also have telomeres at the ends to protect genetic material during cell division.
What is the significance of chromosome banding patterns?
Chromosome banding patterns are significant in cytogenetics because they allow for the visualization and identification of individual chromosomes, thus aiding in the detection of chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions, duplications, and translocations. These patterns provide a unique signature for each chromosome, allowing for precise karyotyping and analysis of genetic disorders and diseases. Additionally, chromosome banding patterns help in understanding evolutionary relationships among species and can be used in prenatal genetic testing and cancer research.
What are the different types of chromosomal mutations that can occur?
The different types of chromosomal mutations that can occur include deletions (loss of a segment of a chromosome), duplications (extra copies of a segment of a chromosome), inversions (reversal of a segment within a chromosome), translocations (movement of a segment from one chromosome to another), and chromosomal fusions (joining of two chromosomes). These mutations can lead to genetic disorders or changes in the structure and function of an organism's genetic material.
How does chromatin remodeling affect gene expression?
Chromatin remodeling plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression by altering the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins. It involves the modification of the structure of chromatin, mainly through the loosening or tightening of DNA-histone interactions. When chromatin is in a more open conformation, gene expression is typically activated, allowing transcriptional machinery to access the DNA and transcribe the gene. Conversely, a more closed conformation suppresses gene expression by restricting access to the DNA. Therefore, chromatin remodeling mechanisms impact gene expression by modulating the accessibility of genes to transcriptional machinery, ultimately influencing the levels of mRNA and protein production.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments