Chromosomal Mutations Worksheet
Entity students studying genetics and chromosomal mutations. Subject This blog post will provide a comprehensive overview of the Chromosomal Mutations Worksheet, designed to enhance students' understanding of genetics and the impact of mutations on an organism's chromosomal structure.
Table of Images 👆
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene and Chromosome Mutation Worksheet Answer
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Sickle Cell Anemia Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Schizophrenia Karyotype
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
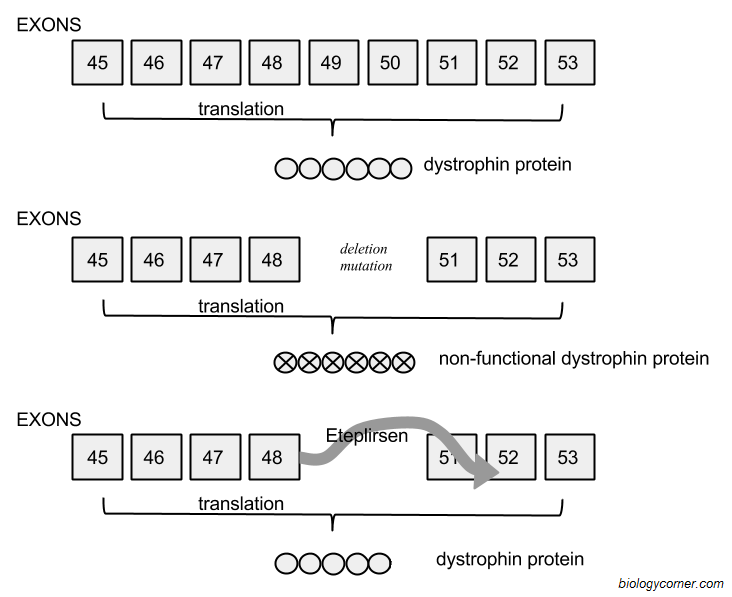
What are chromosomal mutations?
Chromosomal mutations are changes in the structure or number of chromosomes in a cell. These mutations can result from errors during cell division or exposure to certain chemicals or radiation. Examples of chromosomal mutations include deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations, which can lead to genetic disorders or abnormalities in an organism.
What is the difference between a chromosomal mutation and a gene mutation?
A chromosomal mutation involves changes in the overall structure or number of chromosomes in an organism, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, or translocations. On the other hand, a gene mutation refers to alterations in the nucleotide sequence of a gene, which can include substitutions, insertions, or deletions of nucleotides. While chromosomal mutations can involve multiple genes and have larger effects on an organism, gene mutations typically affect a single gene and can lead to changes in the function of that gene and its corresponding protein.
What are the different types of chromosomal mutations?
The different types of chromosomal mutations include deletion (loss of a segment of a chromosome), duplication (extra copies of a segment of a chromosome), inversion (reversal of a segment of a chromosome), translocation (movement of a segment of a chromosome to another chromosome), and non-disjunction (failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division). These mutations can lead to genetic disorders or abnormalities in offspring.
How do chromosomal mutations occur?
Chromosomal mutations can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including errors during DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic agents like radiation or certain chemicals, or through the recombination of genetic material during processes like crossing over in meiosis. These mutations can result in changes to the structure or number of chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders or abnormalities.
What are the consequences of chromosomal mutations?
Chromosomal mutations can lead to a variety of consequences, including genetic disorders, developmental disabilities, birth defects, and an increased risk of certain diseases such as cancer. These mutations can disrupt normal gene function, alter protein production, and affect overall cellular processes, leading to a range of health issues that can impact an individual's physical and mental well-being.
How do chromosomal mutations affect an organism's phenotype?
Chromosomal mutations can have a variety of effects on an organism's phenotype, depending on the specific nature of the mutation. Some chromosomal mutations, such as deletions or duplications of genes, can result in changes to the structure or function of proteins, leading to altered traits or characteristics. Other mutations, such as inversions or translocations, can disrupt the regulation of gene expression, potentially affecting the timing or level of protein production. Overall, chromosomal mutations have the potential to cause a range of phenotypic changes, from subtle alterations to more significant impacts on an organism's traits and behaviors.
Can chromosomal mutations be inherited?
Yes, chromosomal mutations can be inherited. They are alterations in the structure or number of chromosomes that can be passed down from one generation to another through reproductive cells. These mutations can lead to genetic disorders or variations in offspring, depending on the nature of the mutation and how it affects the genetic material.
What are some examples of chromosomal diseases caused by mutations?
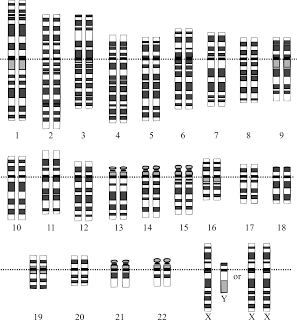
Some examples of chromosomal diseases caused by mutations include Down syndrome (trisomy 21), Turner syndrome (monosomy X), Klinefelter syndrome (XXY), Cri-du-chat syndrome (deletion of chromosome 5), and Prader-Willi syndrome (deletion of chromosome 15). These conditions result from abnormalities in the number or structure of chromosomes, leading to various physical and developmental differences in affected individuals.
How can chromosomal mutations be diagnosed?
Chromosomal mutations can be diagnosed through various techniques such as karyotyping, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) and next-generation sequencing (NGS). These methods enable the visualization and analysis of chromosomal structure, copy number variations, and sequence alterations, allowing for the identification of genetic abnormalities that may be indicative of chromosomal mutations.
Can chromosomal mutations be corrected or treated?
Chromosomal mutations, which involve changes in the structure or number of chromosomes, can often not be corrected or treated. These mutations are typically permanent and can have significant effects on an individual's health and development. However, certain genetic disorders resulting from chromosomal mutations may be managed or treated symptomatically through medical interventions and therapies. Additionally, genetic counseling and testing can help individuals understand and navigate the implications of chromosomal mutations in their families.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments