Chloroplast and Photosynthesis Worksheet
Are you a science teacher searching for an engaging activity to help your students understand the concepts of chloroplasts and photosynthesis? Look no further! We have developed a comprehensive and informative worksheet that will challenge your students to dive deep into the fascinating world of these vital cellular structures and the essential process they facilitate. With clear instructions and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet is designed to stimulate critical thinking and enhance understanding of this complex subject. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of chloroplasts and photosynthesis!
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is chloroplast?
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and some protists that are responsible for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures sunlight for the photosynthetic process. Chloroplasts have a double membrane structure with their own DNA, allowing them to carry out their specialized functions independently within the cell.
Where are chloroplasts found within plant cells?
Chloroplasts are found within the cytoplasm of plant cells, specifically in the mesophyll cells of the leaves. They are also present in other green parts of the plant such as stems and green fruits.
What is the main function of chloroplasts?
The main function of chloroplasts is to perform photosynthesis, a process that enables plants and other photosynthetic organisms to convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen, which is essential for the survival of plants and many other organisms in the food chain.
What pigment gives chloroplasts their green color?
Chlorophyll is the pigment that gives chloroplasts their green color.
What is the process in which chloroplasts convert sunlight into chemical energy?
The process in which chloroplasts convert sunlight into chemical energy is known as photosynthesis. This process involves capturing light energy with pigments such as chlorophyll, which is found in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. Light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil into glucose and oxygen. This chemical energy, in the form of glucose, is then used by the plant for growth and other metabolic processes.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
The two main stages of photosynthesis are the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). In the light-dependent reactions, light energy is captured by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. These energy carriers are then used in the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into sugars with the help of ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions.
Which stage of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts?
The light-dependent reactions, which are the first stage of photosynthesis, occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. During this stage, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which are used in the subsequent light-independent reactions to produce glucose.
What is the primary product of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis?
The primary product of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis is adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH).
What is the purpose of the Calvin cycle or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis?
The purpose of the Calvin cycle, or the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis, is to use the energy and products generated during the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. This process involves a series of chemical reactions that result in the production of sugars that can be used by plants for energy, growth, and maintenance.
How does the structure of a chloroplast relate to its function in photosynthesis?
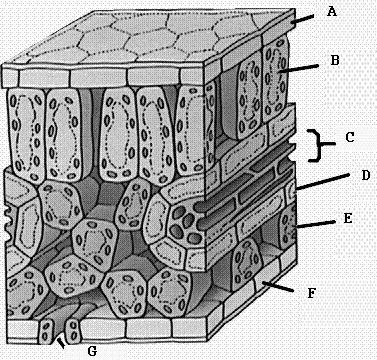
The structure of a chloroplast is highly specialized for its function in photosynthesis. The double membrane surrounds the organelle, providing a protective barrier, while the stroma, thylakoids, and grana inside contain chlorophyll and other pigments essential for capturing light energy. These structures facilitate the process of converting light energy into chemical energy by enabling the sequential steps of photosynthesis, such as light absorption, electron transport, and ATP production. Additionally, the presence of enzymes and other molecules within the chloroplast allows for the synthesis of organic compounds, like glucose, through the Calvin cycle. Ultimately, the unique structure of a chloroplast is crucial for its role in photosynthesis, as it enables the organelle to efficiently carry out the complex biochemical reactions required for the production of food and oxygen.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments