Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet
Are you a chemistry student eager to deepen your understanding of atomic structure? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore the benefits of using worksheets as a valuable learning tool for mastering this complex subject. With carefully curated content and well-designed exercises, worksheets provide an organized and structured approach to help you grasp the fundamentals of atomic structure in a clear and concise manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
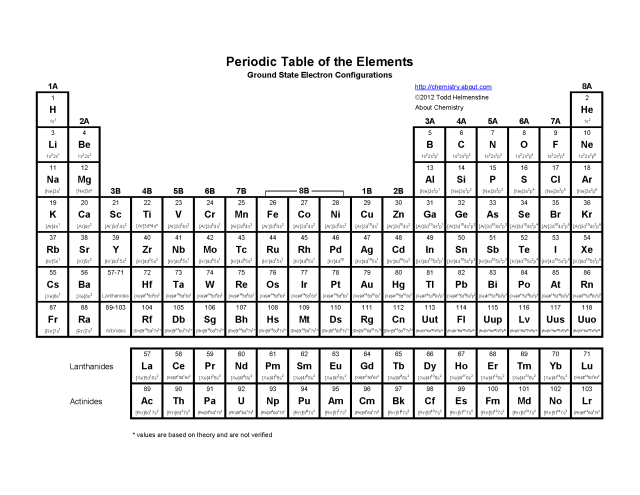
- Atomic Structure Worksheet and Periodic Table
- Atomic Structure and Theory Magic Square
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Combined Gas Law Worksheet 1 Answer Key
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Chemical Reaction Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Elements and Atoms Games
- Evolution Review Worksheet Answer Key
- Black and White Printable Periodic Table
More Chemistry Worksheets
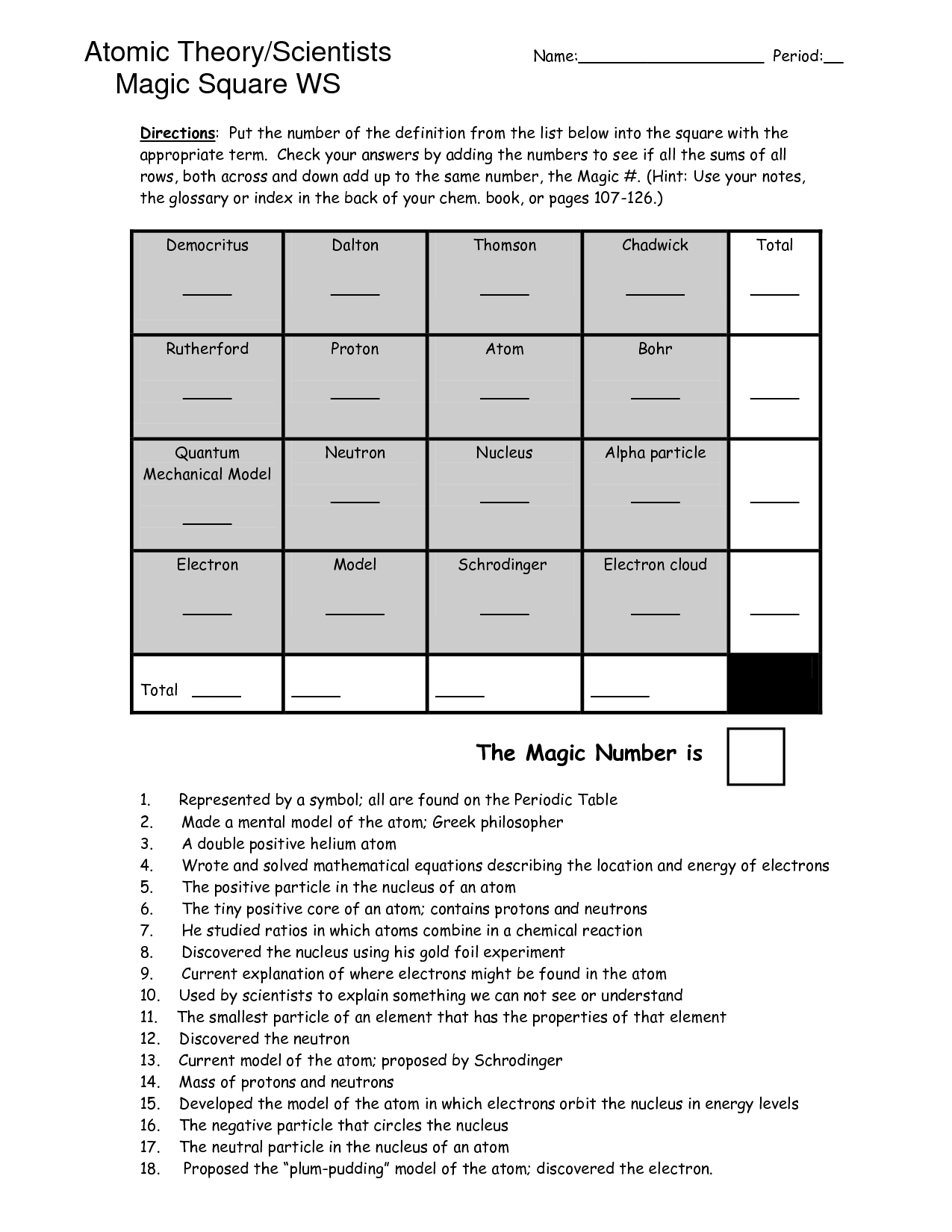
What is an atom?
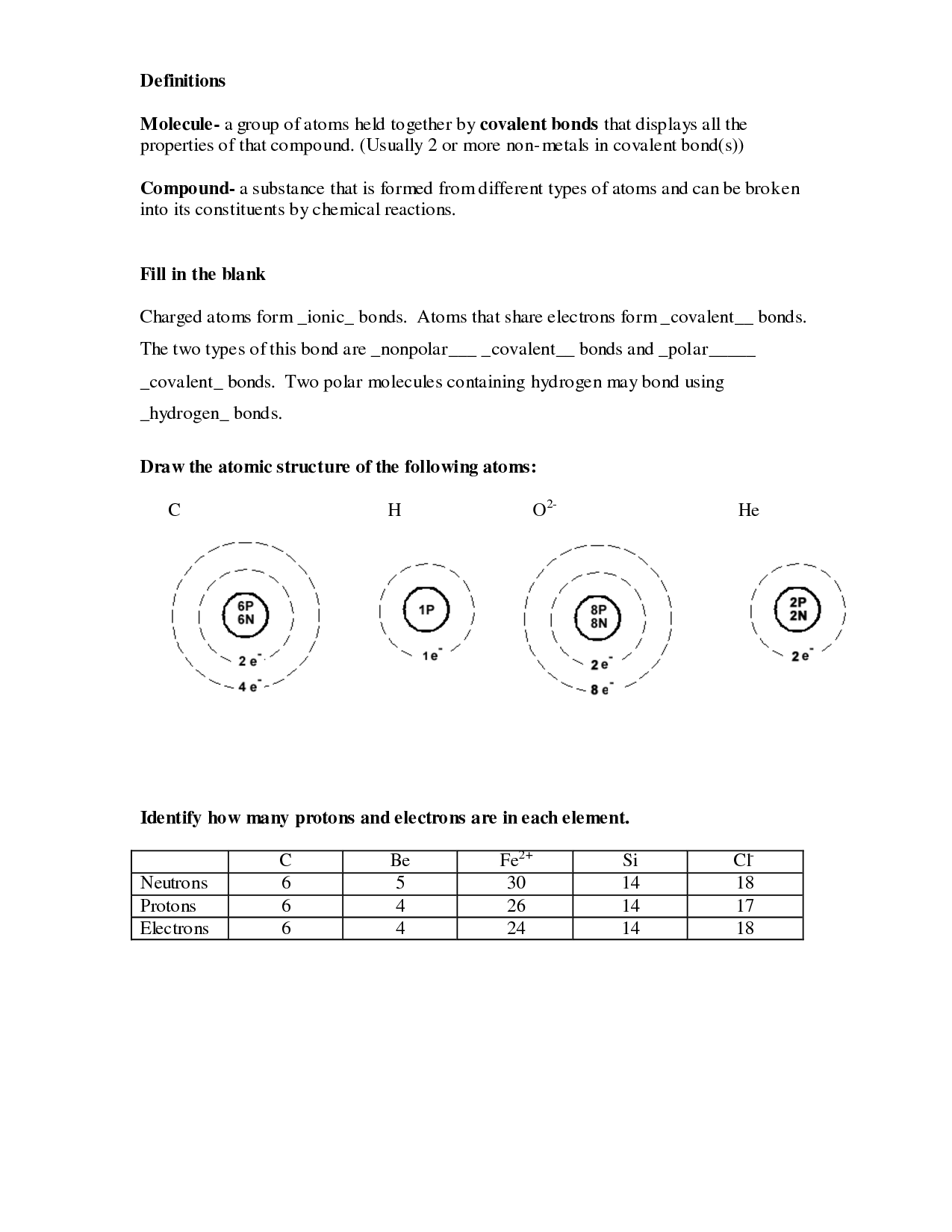
An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. It consists of a nucleus made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in orbitals. Atoms combine to form molecules, which are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
What are the three subatomic particles found in an atom and what are their respective charges?
The three subatomic particles found in an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge (they are neutral).
How are electrons arranged in an atom?
Electrons are arranged in specific energy levels, or shells, around the nucleus of an atom. These energy levels are designated by quantum numbers and can hold a specific maximum number of electrons. The electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving on to higher energy levels, following the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. Each energy level can contain a certain number of sublevels, such as s, p, d, and f orbitals, which further determine the spatial distribution of electrons within an atom.
What is the atomic number of an element and what does it represent?
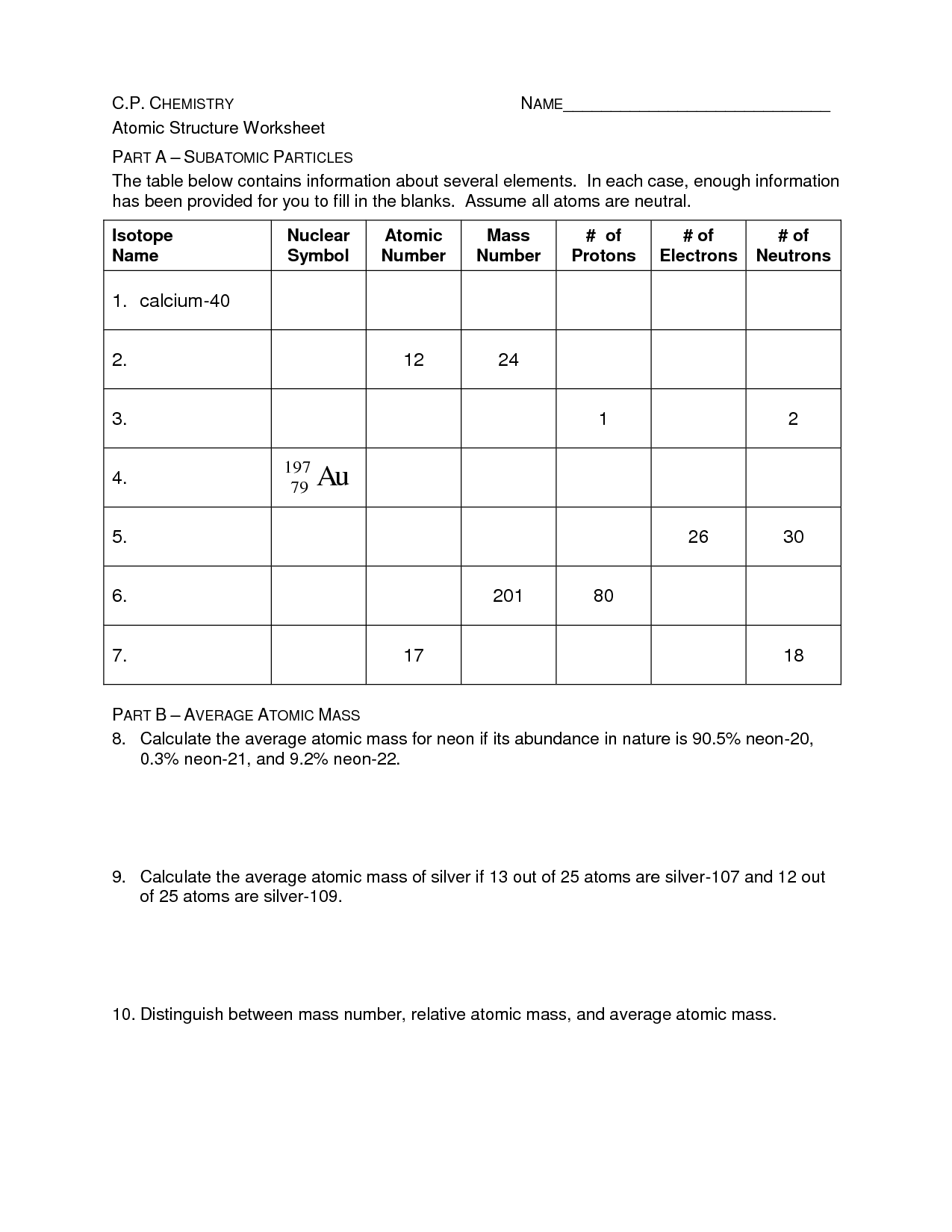
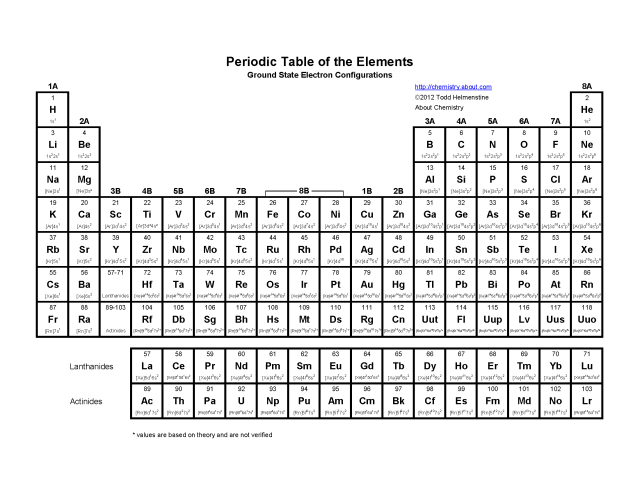
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It represents the identity of the element and determines its chemical properties. Each element has a unique atomic number, and elements are arranged on the periodic table in increasing order of atomic number.
What is the mass number of an atom and how is it calculated?
The mass number of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. It is calculated by adding the number of protons (which is the atomic number) and the number of neutrons together. The mass number is often written as a superscript before the symbol of the chemical element, such as in carbon-12 where 12 is the mass number.
What are isotopes and how do they differ from each other?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. This means that isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties but differ in their atomic mass. For example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon because they all have 6 protons but differ in their number of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses.
What is an electron configuration and how is it written?
An electron configuration is a way to represent the arrangement of electrons in an atom or ion. It specifies the distribution of electrons in different energy levels and sublevels within the atom. Electron configurations are typically written using a shorthand notation that indicates the number of electrons in each sublevel. The configuration is written starting from the lowest energy level and moving up, with the number of electrons in each sublevel placed as a superscript. For example, the electron configuration for carbon is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^2, indicating that there are 2 electrons in the 1s sublevel, 2 electrons in the 2s sublevel, and 2 electrons in the 2p sublevel.
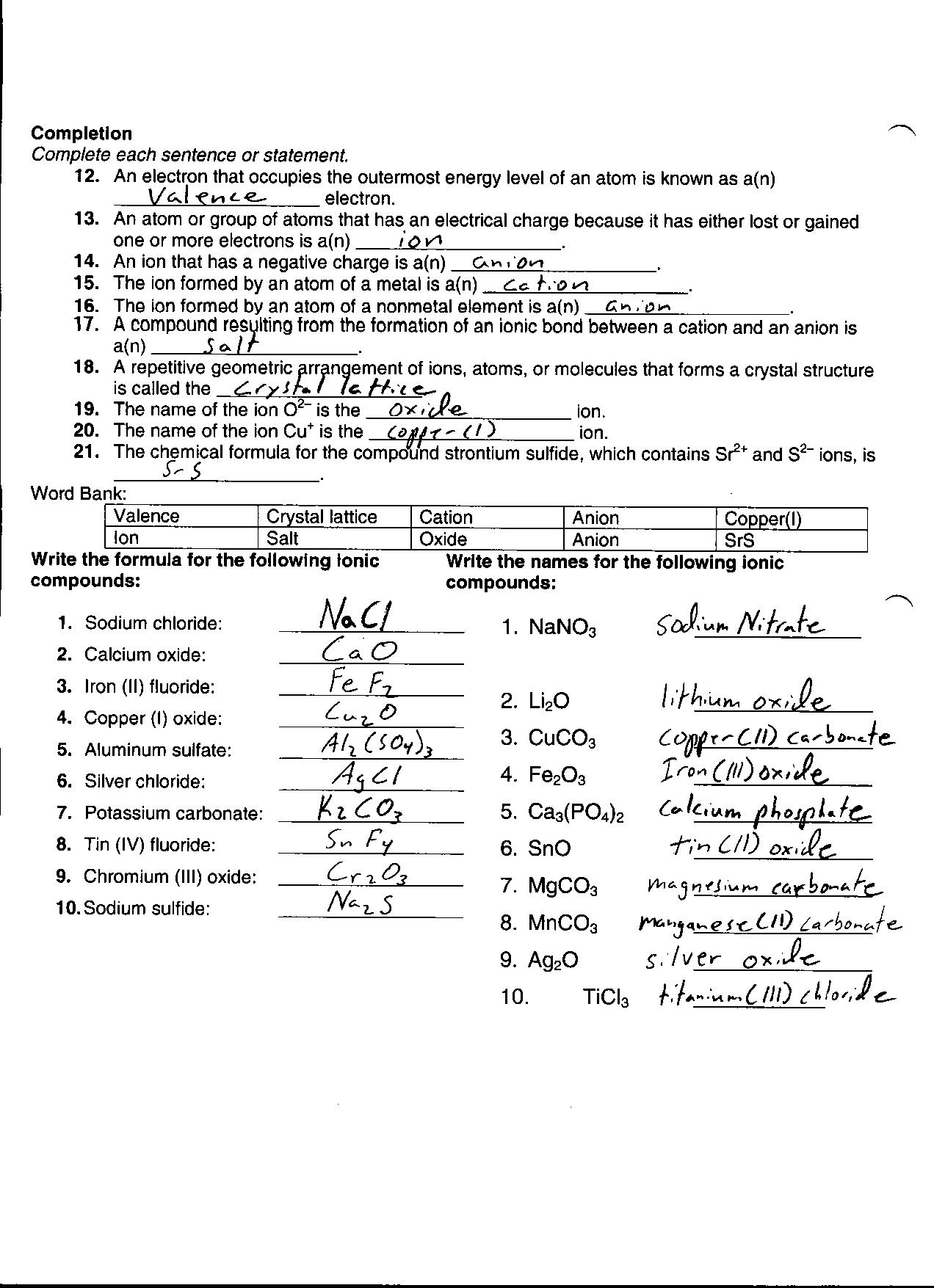
What is the significance of valence electrons in chemical bonding?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, and they play a crucial role in chemical bonding as they determine an atom's reactivity and ability to form bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons influences how easily an atom can gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This interaction of valence electrons among atoms leads to the formation of chemical bonds, which ultimately determines the properties and behavior of molecules and compounds.
What is an ion and how is it formed?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, giving it a positive or negative charge. Ions are formed when an atom either gains electrons to form a negatively charged ion (anion) or loses electrons to form a positively charged ion (cation). This process occurs through various chemical reactions or interactions with other atoms.
How does understanding atomic structure help explain the periodic table and the behavior of elements?
Understanding atomic structure helps explain the periodic table and the behavior of elements because the periodic table is organized based on the number of protons in an atom's nucleus and the electron configuration of an atom. This organization allows us to predict the chemical properties of elements, such as their reactivity and bonding behavior, based on their location in the periodic table. Additionally, knowledge of atomic structure helps us understand how elements interact with one another to form compounds, how they undergo chemical reactions, and why certain elements exhibit similar properties within the same group of the periodic table.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments