Cells and Microscope Worksheet
Are you a student or a teacher exploring the amazing world of cells and microscopes? If so, you may be searching for a helpful tool to enhance your understanding and learning experience. Look no further, as we introduce the Cells and Microscope Worksheet! Designed for students of biology and science enthusiasts alike, this worksheet provides an interactive and organized way to study the fascinating subject of cells and their microscopic counterparts. With its comprehensive content, engaging activities, and clear explanations, this worksheet is sure to be a valuable resource for anyone interested in deepening their knowledge of this captivating topic.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the function of a microscope?
A microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify extremely small objects or organisms that are not visible to the naked eye. It functions by using lenses to bend and focus light so that the object being observed appears larger and more detailed, allowing for detailed examination and study of specimens in fields such as biology, medicine, chemistry, and material science.
What is the difference between a compound microscope and a stereo microscope?
A compound microscope is designed for viewing thin, transparent specimens with high magnification and resolution, using a system of lenses to focus light onto the specimen. In contrast, a stereo microscope, also known as a dissecting microscope, provides lower magnification levels and is used for viewing larger, opaque specimens in 3D. Additionally, a stereo microscope typically has two eyepieces and offers a wider field of view, enabling the observer to work with the specimen under magnification.
How does a light microscope work?
A light microscope works by passing light through a specimen and using lenses to magnify the image. The specimen is placed on a slide and illuminated with a light source, which passes through the specimen and is captured by the objective lens. The objective lens then magnifies the image, and further magnification is achieved by the eyepiece lens. The magnified image is then viewed through the eyepiece, allowing for detailed observation of the specimen.
What is the purpose of staining cells before observing them under a microscope?
Staining cells before observing them under a microscope is done to enhance contrast and visibility of cellular structures and components. By adding dyes or stains that bind to specific cellular structures, such as DNA, proteins, or organelles, it is easier to distinguish different parts of the cell and observe their shapes, sizes, and interactions more clearly under the microscope. Staining also helps researchers or scientists to differentiate between different cell types, identify abnormalities, and study their functions and behavior in more detail.
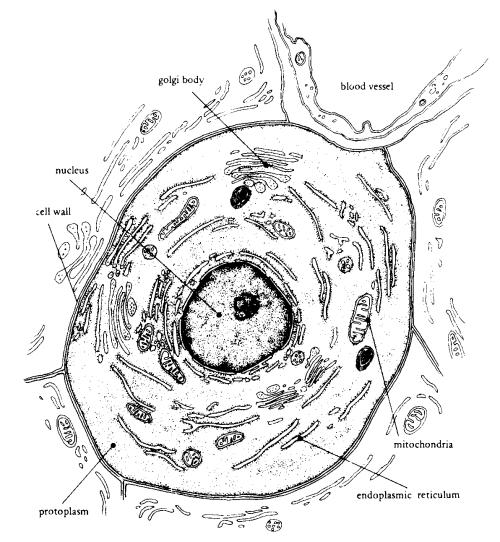
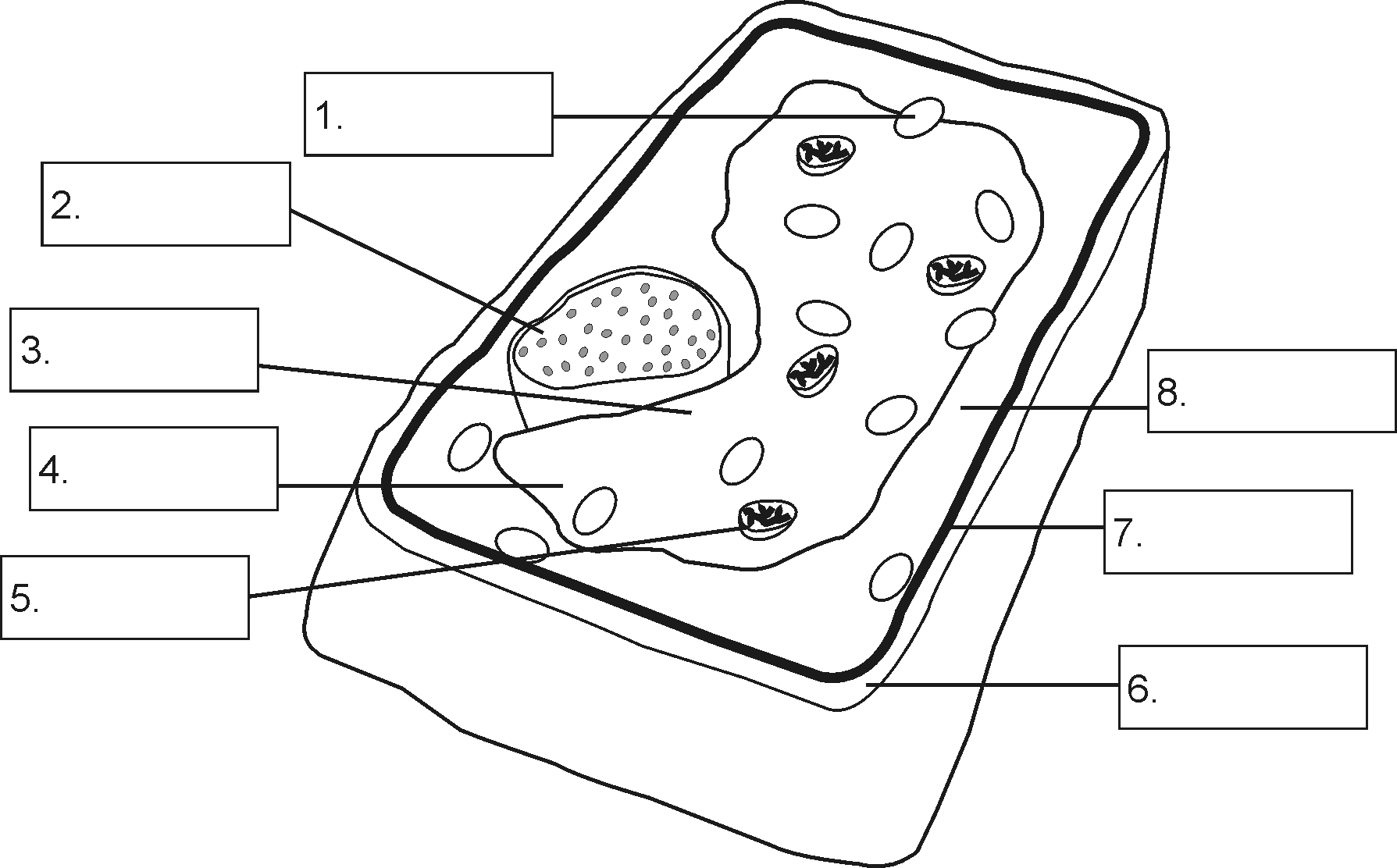
What are the three main parts of a cell?
The three main parts of a cell are the cell membrane, which separates the cell from its environment and controls what enters and leaves the cell; the cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance that contains the organelles and where many cellular processes occur; and the nucleus, which contains the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA and controls the cell's activities.
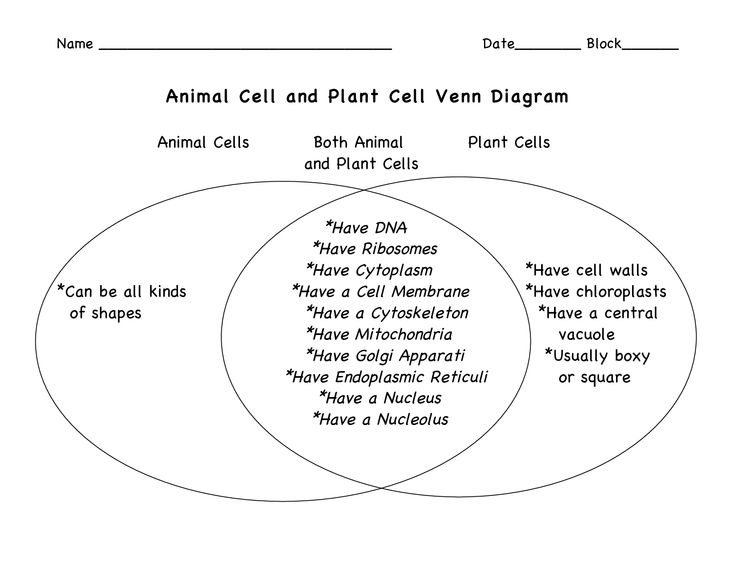
What are the differences between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are typically smaller and simpler in structure, lacking membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, containing a well-defined nucleus and various organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Prokaryotic cells have circular DNA in the nucleoid region, while eukaryotic cells have linear DNA contained within the nucleus. Additionally, prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually via binary fission, while eukaryotic cells reproduce sexually or asexually depending on the organism.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a protective barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, allowing nutrients to enter and waste products to exit. It also plays a crucial role in cell recognition, cell communication, and maintaining the overall structure and shape of the cell. Additionally, the cell membrane contains various proteins and receptors that are involved in signaling pathways and interactions with other cells in the body.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus in a cell plays a crucial role in controlling the cell's activities and storing genetic information. It houses the cell's DNA, which contains instructions for the cell's growth, development, and reproduction. The nucleus also regulates gene expression by coordinating the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA. Additionally, the nucleus helps maintain the cell's overall structure and organization by directing the synthesis of proteins and coordinating cellular processes.
What are mitochondria and what is their function in cells?
Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are known as the powerhouses of the cell. Their primary function is to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which serves as the primary energy source for cellular processes. Mitochondria are involved in various metabolic pathways, such as the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, to produce ATP through the process of cellular respiration. Additionally, they play essential roles in regulating cell growth, signaling, and cell death.
What is the significance of studying cells and using microscopes in scientific research?
Studying cells and using microscopes are crucial in scientific research because cells are the fundamental units of life and hold information vital for understanding biological processes. Microscopes enable scientists to observe and analyze cells at a microscopic level, providing insights into their structure, function, and behavior. This knowledge is essential for expanding our understanding of diseases, genetics, and development, ultimately contributing to advancements in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments