Cell Transport Worksheet
Are you an educator searching for a valuable resource to enhance your lesson on cell transport? Look no further! This blog post introduces an informative and engaging worksheet specifically designed to help your students grasp the concepts of cell transport. With a focus on the entity and subject, this worksheet serves as an excellent learning tool for biology students at the high school level.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Passive Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Transport Worksheet
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet Answers
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answers
- Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Worksheet
- Cell Membrane and Transport Worksheet
- Homeostasis and Cell Transport Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
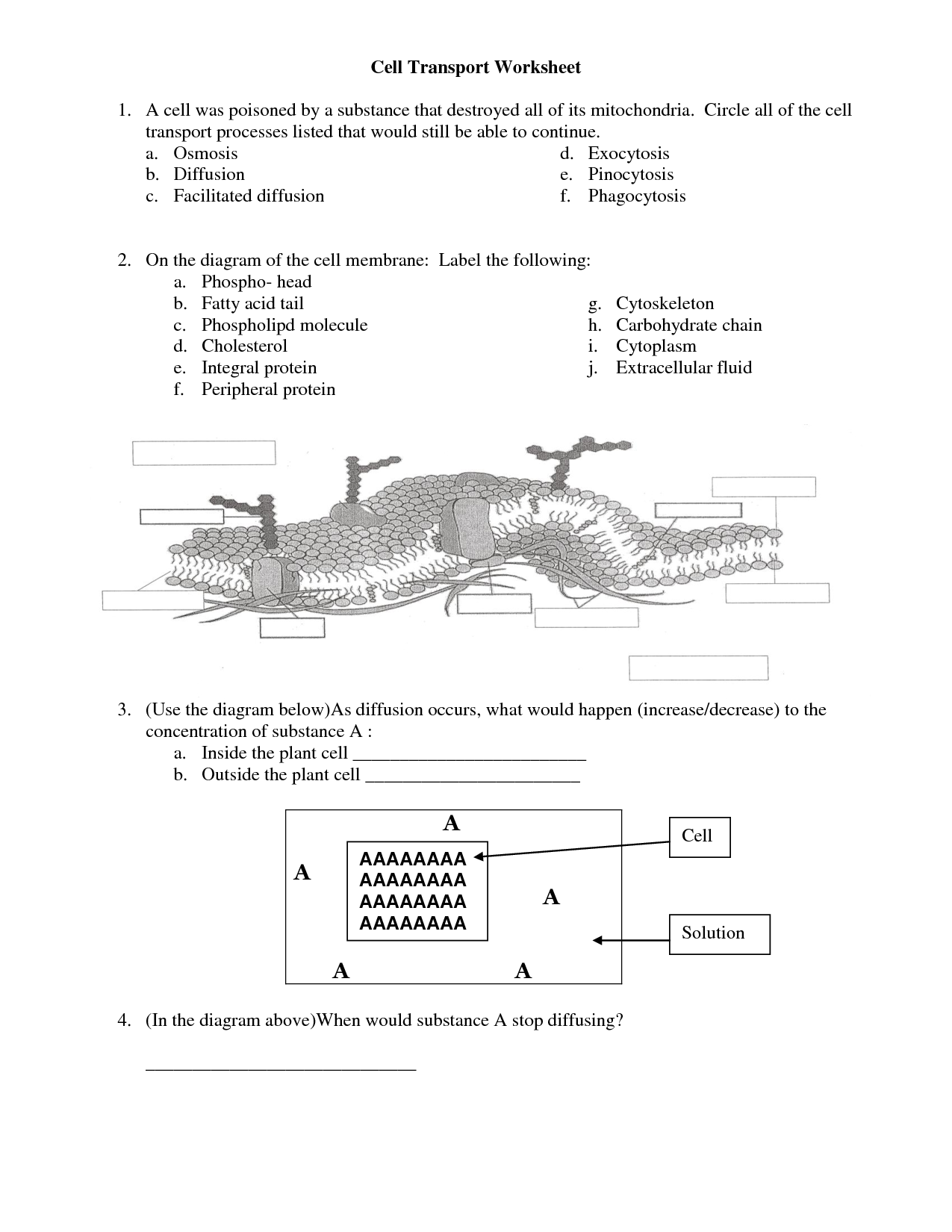
What is cell transport?
Cell transport refers to the movement of molecules in and out of cells, which is critical for maintaining cellular functions and balance. This process can occur through several mechanisms such as diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and endocytosis/exocytosis, all of which play a vital role in regulating the internal environment of cells by allowing essential nutrients to enter and waste products to be removed.
What are the two main types of cell transport?
The two main types of cell transport are passive transport, which includes diffusion and facilitated diffusion, and active transport, which includes primary active transport and secondary active transport. Passive transport does not require energy input, as molecules move down their concentration gradient, while active transport requires energy expenditure to pump molecules against their concentration gradient.
Describe the process of passive transport.
Passive transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane without requiring energy input from the cell. This process relies on the natural tendency of molecules to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, known as diffusion. Passive transport can occur through simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion (using transport proteins), or through osmosis (the movement of water across a membrane). Overall, passive transport allows molecules to move freely across the cell membrane to maintain proper balance and function within the cell.
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the process by which molecules or ions move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, eventually reaching an equilibrium. This passive transport mechanism occurs due to the random motion of particles and does not require energy input.
How does osmosis differ from diffusion?
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane, from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration. Diffusion, on the other hand, refers to the overall process of molecules moving from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, regardless of the type of molecule. While both osmosis and diffusion involve the movement of molecules, osmosis specifically deals with the movement of water molecules, making it a specialized form of diffusion.
What is active transport?
Active transport is a biological process in which a cell uses energy, typically in the form of ATP, to move molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient. This process is essential for the uptake of nutrients, ions, and other substances that are needed by the cell to function properly. It is often used to maintain internal homeostasis and enable the cell to concentrate specific molecules within its cytoplasm at higher levels than in the surrounding environment.
Provide an example of active transport.
One common example of active transport is the sodium-potassium pump found in animal cells. This pump actively transports sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, against their respective concentration gradients, using energy from ATP. This process helps maintain the cell's internal ion balance and is crucial for various cellular functions, such as nerve cell signaling.
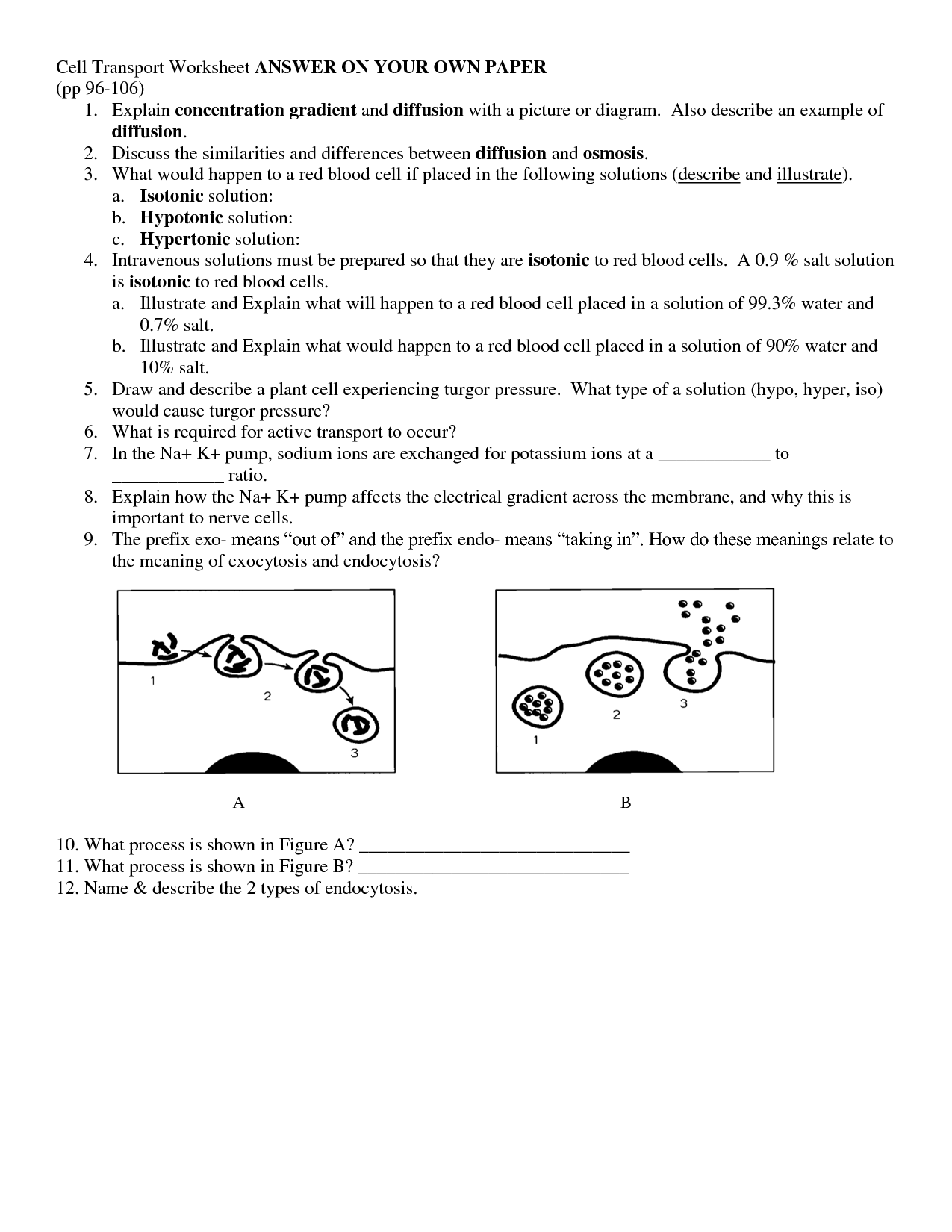
What is endocytosis?
Endocytosis is a cellular process where cells take in molecules or particles by engulfing them through the cell membrane. The engulfed material is then enclosed in a vesicle and brought into the cell. There are different types of endocytosis, such as phagocytosis (cell eating) and pinocytosis (cell drinking), which play vital roles in nutrient uptake, waste removal, and regulating cell signaling.
Explain the process of exocytosis.
Exocytosis is the process by which a cell releases substances from its cytoplasm into the external environment. It begins with the formation of a vesicle containing the substance to be released. The vesicle then moves towards the cell membrane and fuses with it, resulting in the opening of a pore through which the contents of the vesicle are expelled outside the cell. This process is crucial for various cellular functions, including the release of hormones, neurotransmitters, and waste products.
Compare and contrast endocytosis and exocytosis.
Endocytosis is a cellular process where cells engulf external particles or substances by forming vesicles from the cell membrane, bringing them into the cell. On the other hand, exocytosis is the process where cells release substances out of the cell by vesicles fusing with the cell membrane and releasing their contents externally. Both processes involve vesicles and membrane fusion, but endocytosis brings substances into the cell, while exocytosis expels substances out of the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments