Cell Review Worksheet Answers
Worksheets are a valuable tool for students of all ages to practice and reinforce their understanding of various subjects. Whether you're a teacher searching for ready-made resources or a student wanting extra practice, finding accurate and comprehensive answer sheets for specific worksheets can be a daunting task. In this blog post, we will provide the cell review worksheet answers, allowing biology students to easily check their work and solidify their knowledge of this essential topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key Review
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Answer Key
- Biology Worksheets with Answer Key
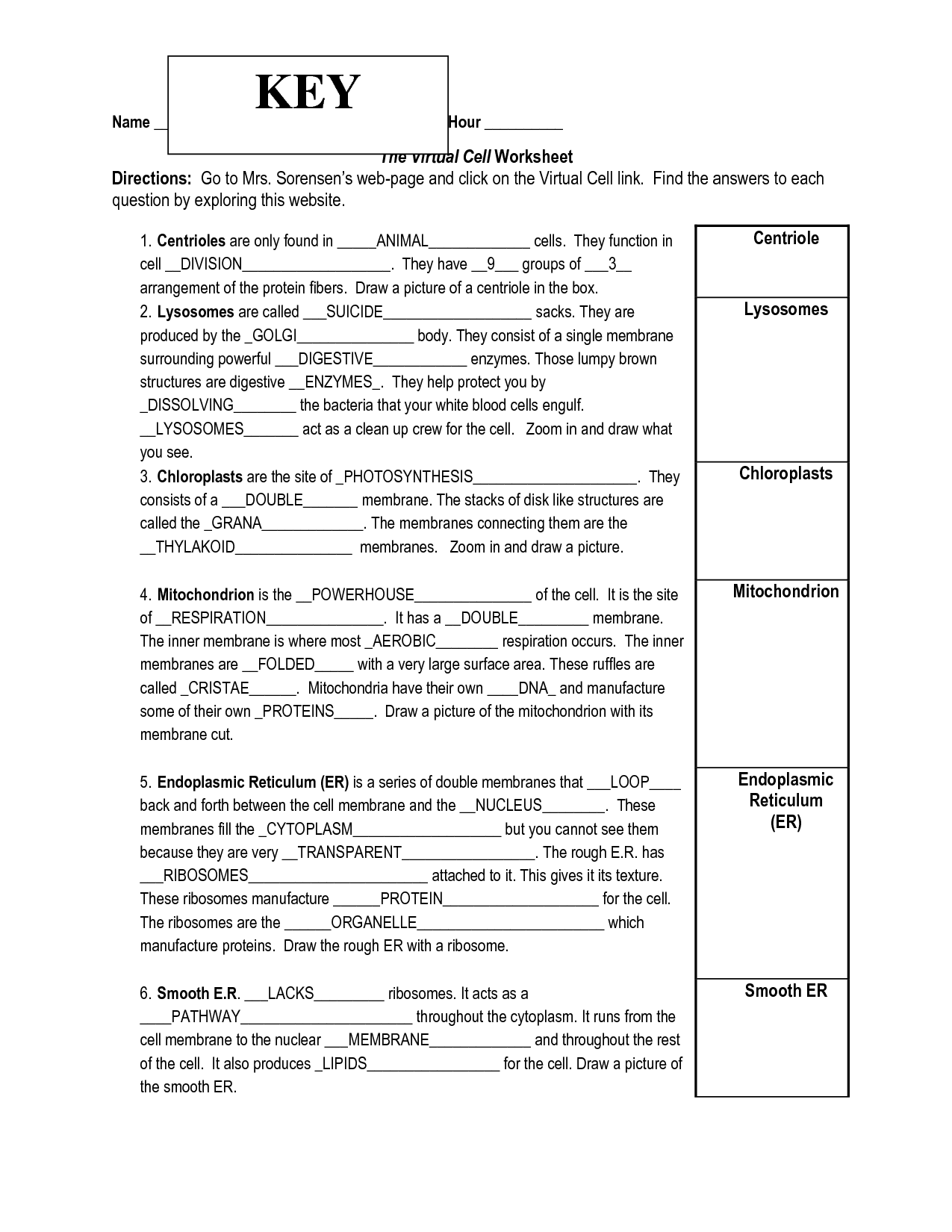
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Osmosis and Tonicity Worksheet Answer Key
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a cell?
A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of living organisms, containing specialized structures called organelles that perform specific functions to sustain life. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things and can vary in size, shape, and function depending on the organism they belong to.
What are the three main parts of a cell?
The three main parts of a cell are the cell membrane, which surrounds and protects the cell; the cytoplasm, which contains the organelles and provides a medium for chemical reactions to occur; and the nucleus, which houses the cell's genetic material and controls cellular activities.
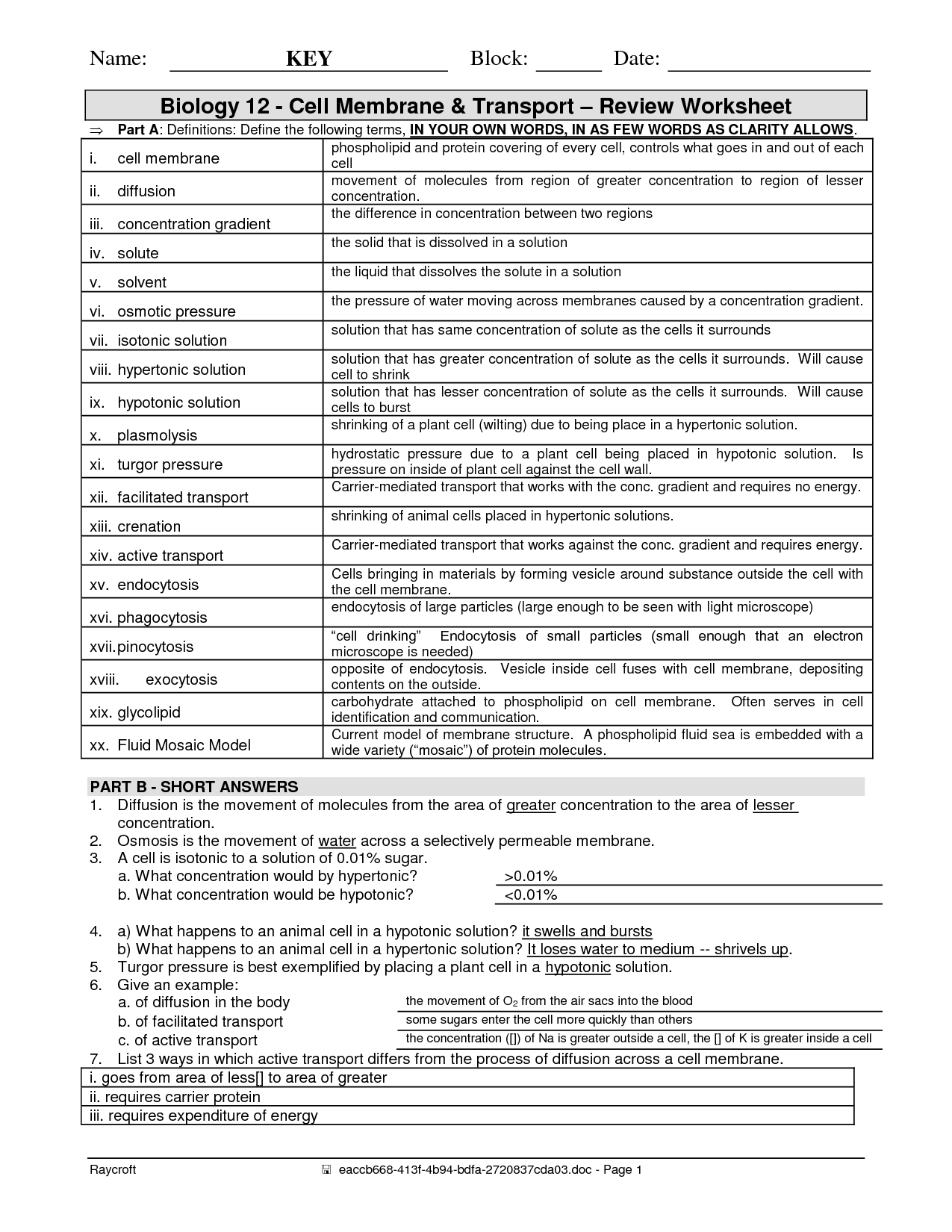
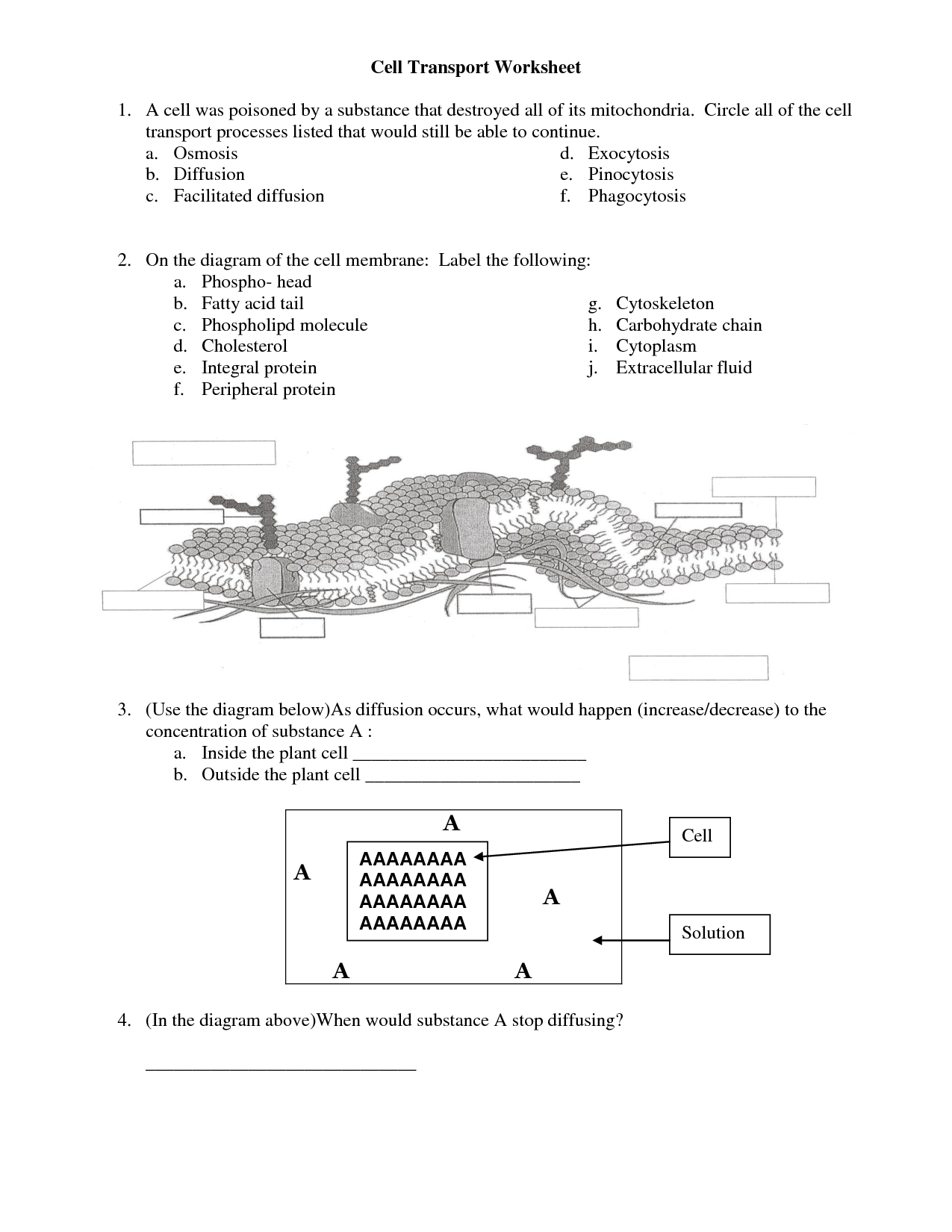
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane functions as a protective barrier that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It allows essential nutrients and molecules to enter the cell while removing waste products and preventing harmful substances from entering. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a key role in maintaining the cell's shape and structure, as well as in communication with other cells.
Where is DNA found within the cell?
DNA is found within the cell's nucleus, as well as in some organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. Within the nucleus, DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes.
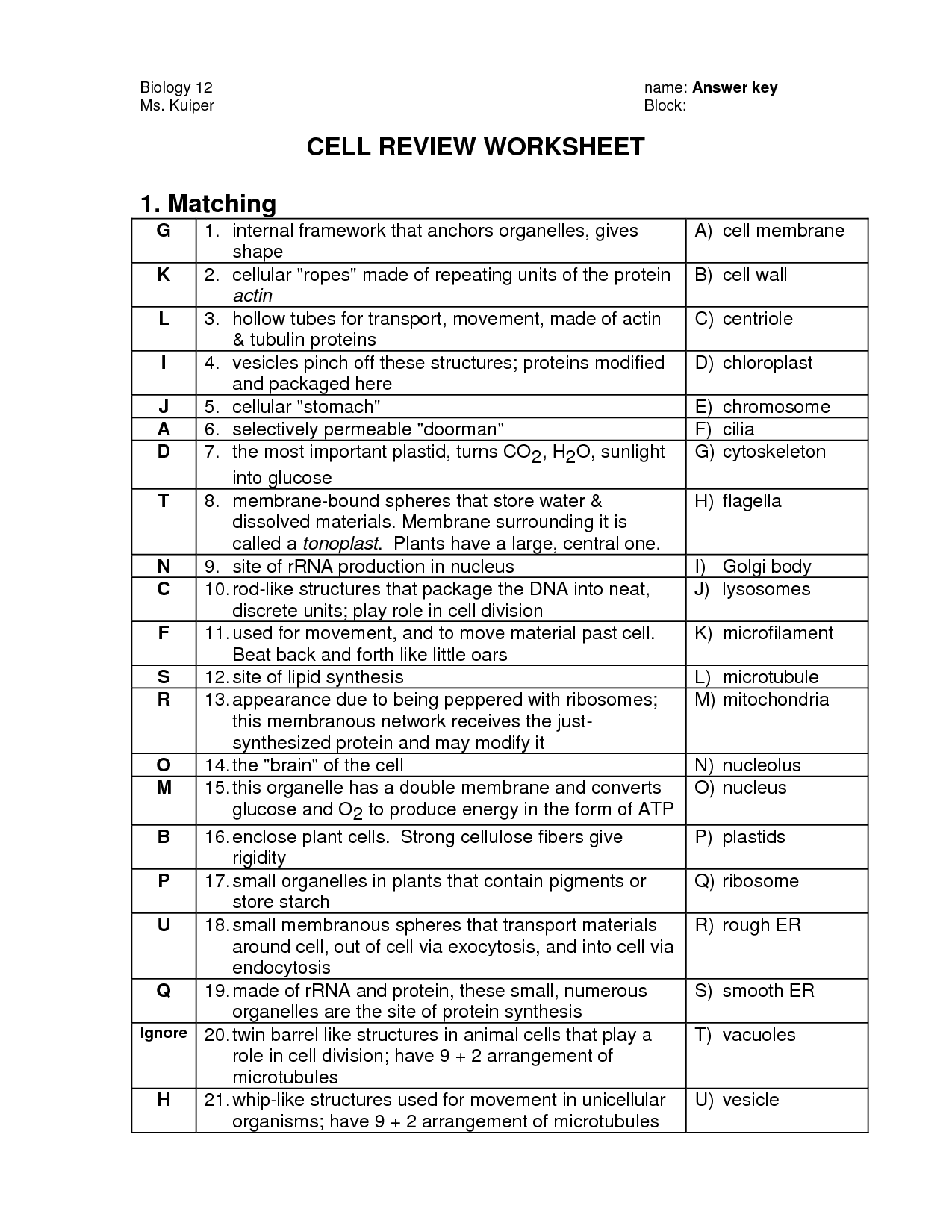
What is the role of mitochondria in a cell?
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for producing the energy currency of the cell, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), through the process of cellular respiration. They play a vital role in generating energy for various cellular processes, including metabolism, growth, and movement. Mitochondria also regulate cell signaling pathways, control cell growth and death, and are involved in processes like the regulation of calcium levels within the cell and the synthesis of important metabolites.
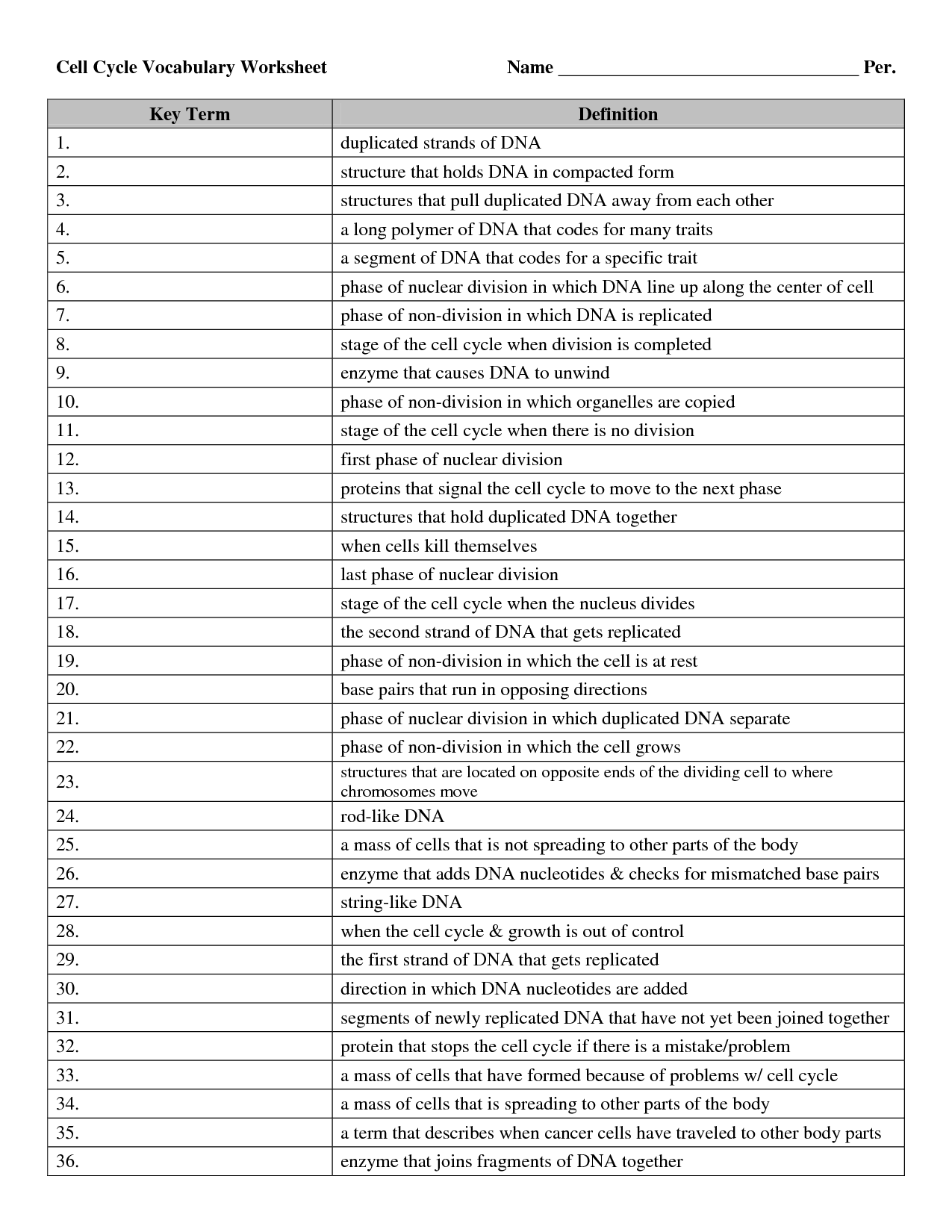
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and lack a defined nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a true nucleus enclosed by a membrane. Additionally, prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells contain various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Eukaryotic cells also tend to be larger and more organized than prokaryotic cells, which are typically smaller and have a simpler structure.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus functions as the distribution and shipping department of the cell, where it processes, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transportation to their specific destinations within the cell or for secretion outside the cell.
What is the purpose of ribosomes in a cell?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in a cell. They read the genetic information from messenger RNA (mRNA) and use this information to assemble amino acids into proteins through a process called translation. Ribosomes are essential for the production of proteins, which are crucial for the structure, function, and regulation of cells and organisms.
How do cells obtain energy?
Cells obtain energy through a process called cellular respiration, where they break down molecules such as glucose using oxygen to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the main energy carrier in cells. This process involves three main stages - glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain - which together generate ATP for various cellular activities.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum and its function in a cell?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and primarily involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification. Overall, the ER is essential for maintaining cell structure, regulating cell functions, and ensuring proper communication between different organelles within the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments