Cell Respiration Worksheets and Answers
Cell respiration worksheets are a useful tool for students learning about this vital biological process. These worksheets serve as a comprehensive resource, providing practice questions and exercises to help reinforce understanding of the topic. With a focus on key concepts and principles, these worksheets are designed to engage students and enhance their knowledge of cell respiration. Whether you are a teacher looking for supplementary materials or a student seeking additional practice, these worksheets are an excellent resource to support your learning journey.
Table of Images 👆
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Cellular Respiration Review Worksheet Answers
- Holt Biology Worksheets and Answers
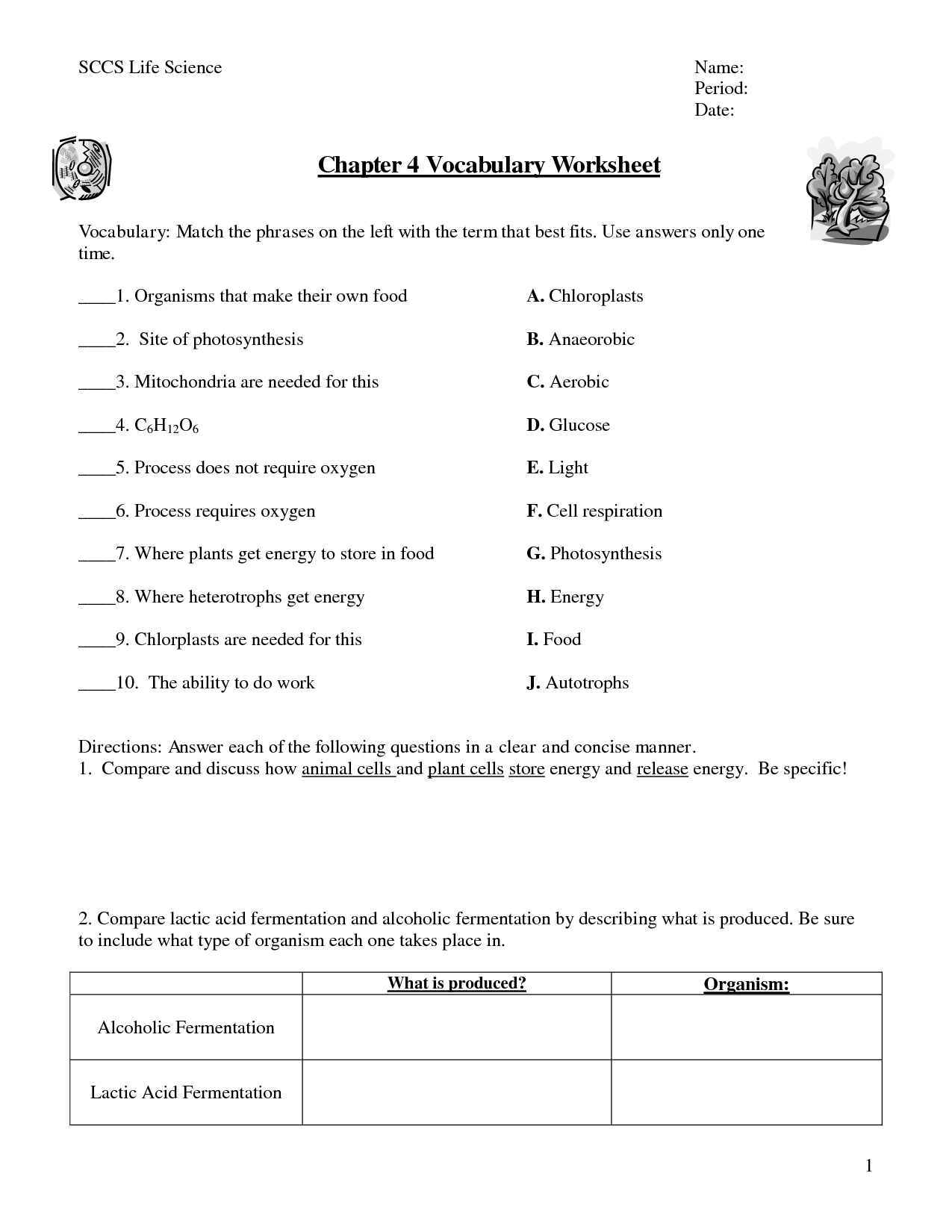
- Cellular Respiration Worksheets and Answers
- Photosynthesis and Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is cell respiration?
Cell respiration is the process by which cells break down nutrients and convert them into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This process involves the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide, and occurs in the mitochondria of cells. Cell respiration is essential for the survival and functioning of organisms, as ATP is the primary source of energy that powers cellular activities.
What are the three main stages of cell respiration?
The three main stages of cell respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport chain). Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, the citric acid cycle further oxidizes pyruvate to produce high-energy molecules, and oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules to generate ATP, the cell's main source of energy.
Describe glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. This anaerobic pathway occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and involves a series of 10 enzymatic reactions that ultimately produce ATP, the primary energy source of cells. Glycolysis plays a vital role in cellular respiration, generating energy through the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen.
What is the role of the electron transport chain in cell respiration?
The electron transport chain plays a crucial role in cell respiration by transferring electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, generating a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This gradient is used to drive ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation, providing cells with the energy they need to carry out essential processes.
Explain the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxidative phosphorylation is a complex biological process that occurs in mitochondria where energy from the oxidation of nutrients is used to generate ATP, the cell's main energy currency. It involves a series of electron transport chain reactions where electrons are passed down a chain of proteins, pumping protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane and creating an electrochemical gradient. This gradient drives ATP synthesis by the enzyme ATP synthase, which uses the energy from proton movement to combine ADP and inorganic phosphate to form ATP. Overall, oxidative phosphorylation is an essential mechanism for producing cellular energy in the form of ATP through the coupling of electron transport chain reactions and ATP synthesis.
How is ATP produced during cell respiration?
ATP is primarily produced during cell respiration through a process called oxidative phosphorylation, which occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. In this process, high-energy electrons generated during the breakdown of glucose and other nutrients are passed along the electron transport chain, leading to the pumping of protons across the membrane and creating a proton gradient. The flow of protons back through ATP synthase enzyme drives the conversion of ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP, providing cells with a high-energy molecule for various cellular activities.
Describe the function of NAD+ and FAD in cell respiration.
NAD+ and FAD are coenzymes that play crucial roles in cell respiration by acting as electron carriers. During the process of cellular respiration, NAD+ and FAD accept electrons and protons from various metabolic reactions, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. By accepting these electrons and protons, NAD+ and FAD become reduced to NADH and FADH2, respectively, which then carry these high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain for oxidative phosphorylation. This transfer of electrons ultimately leads to the production of ATP, the primary energy source for cellular activities.
What is the importance of oxygen in the electron transport chain?
Oxygen is crucial in the electron transport chain as it serves as the final electron acceptor. This is a vital step in the process of cellular respiration, where electrons are passed down the chain to generate energy in the form of ATP. Without oxygen, the electron transport chain cannot function properly, leading to a halt in ATP production and ultimately causing the cell to undergo anaerobic processes that are less efficient and can be harmful in the long run.
Explain how anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that does not require oxygen, and it occurs in the absence of oxygen. It produces less energy compared to aerobic respiration, and the end products can include lactic acid or ethanol. On the other hand, aerobic respiration is a more efficient process that requires oxygen and occurs in the presence of oxygen, producing a significantly larger amount of energy in the form of ATP molecules. Additionally, aerobic respiration produces carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
Describe the overall equation for cell respiration.
The overall equation for cell respiration is C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) -> 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + energy (as ATP). This process involves the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy that the cell can utilize for various functions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


































Comments