Cell Growth Worksheet
Are you seeking a tool to help students understand and master the concept of cell growth? Look no further. This blog post introduces a comprehensive cell growth worksheet designed to engage learners and enhance their knowledge in this critical subject.
Table of Images 👆
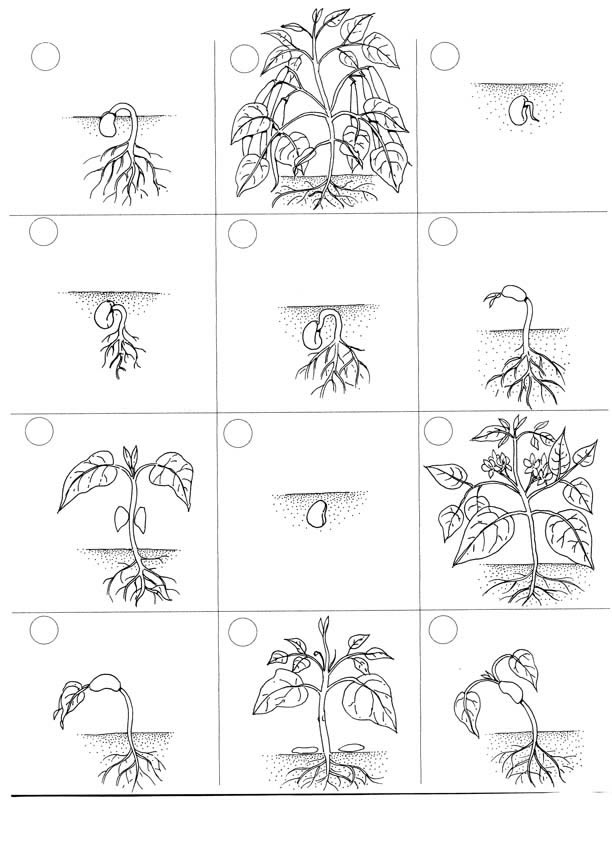
- Plant Life Cycle Book
- Interval Notation Worksheet
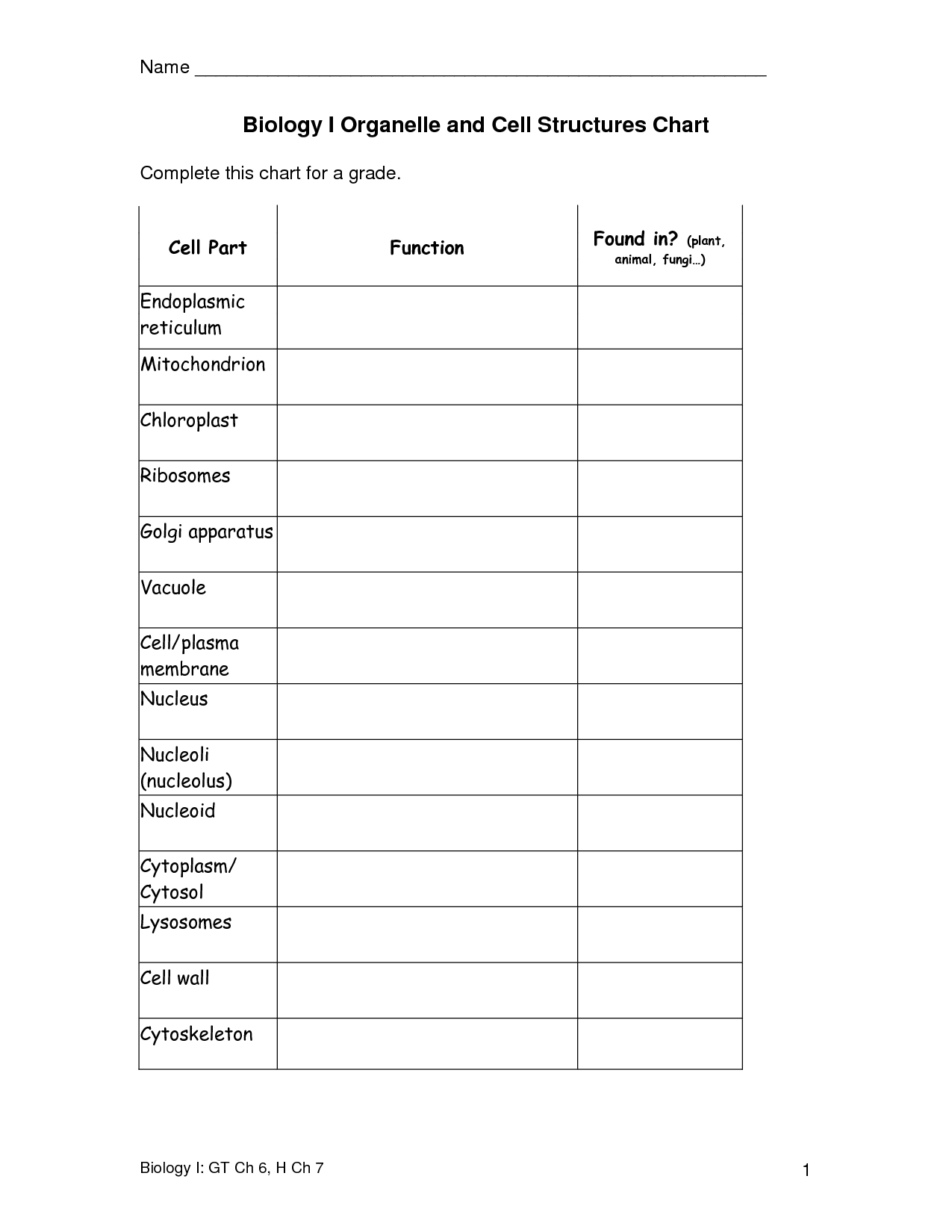
- Cell Structures and Organelles Chart
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
- Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Answers
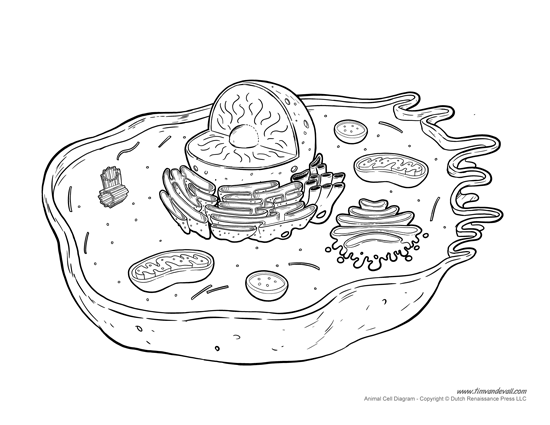
- Animal Cell Diagram Not Labeled
- Mitosis Matching Worksheet Answers
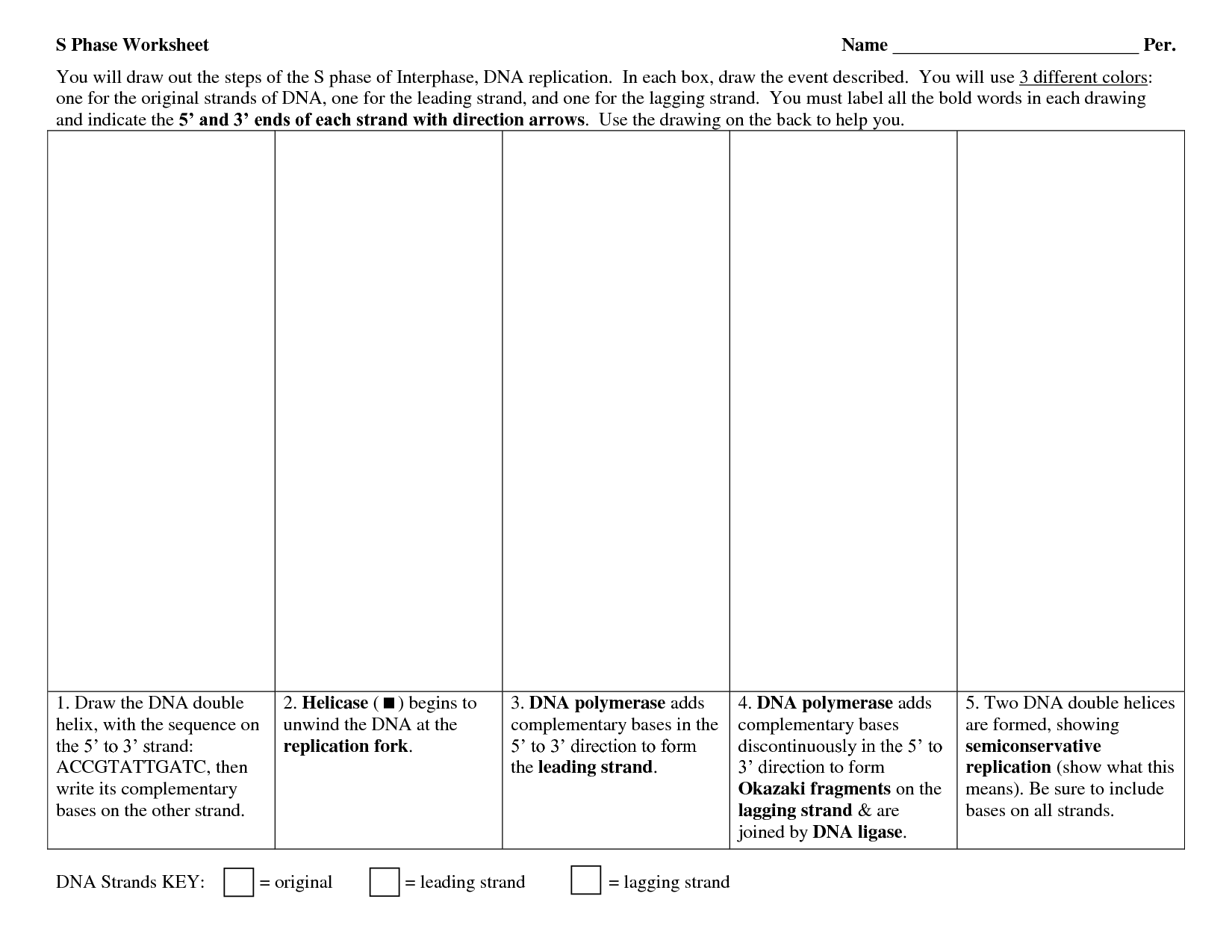
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- Classification of Living Things Worksheets 6th Grade
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is cell growth?
Cell growth refers to the process by which a cell increases in size and mass as it prepares to divide and reproduce. This growth is regulated by various internal and external factors that control the balance between cell proliferation and cell death, ultimately leading to the maintenance and development of tissues and organisms.
What factors influence cell growth?
Several factors influence cell growth, including genetics, hormones, nutrients, growth factors, and environmental conditions such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels. The availability of essential nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and vitamins is crucial for cell growth, as well as the presence of appropriate signaling molecules that regulate cell division and differentiation. External stimuli such as mechanical stress, radiation, and chemical signals can also impact cell growth and proliferation. Additionally, genetic factors play a significant role in determining how quickly and efficiently cells grow and divide.
How do cells proliferate?
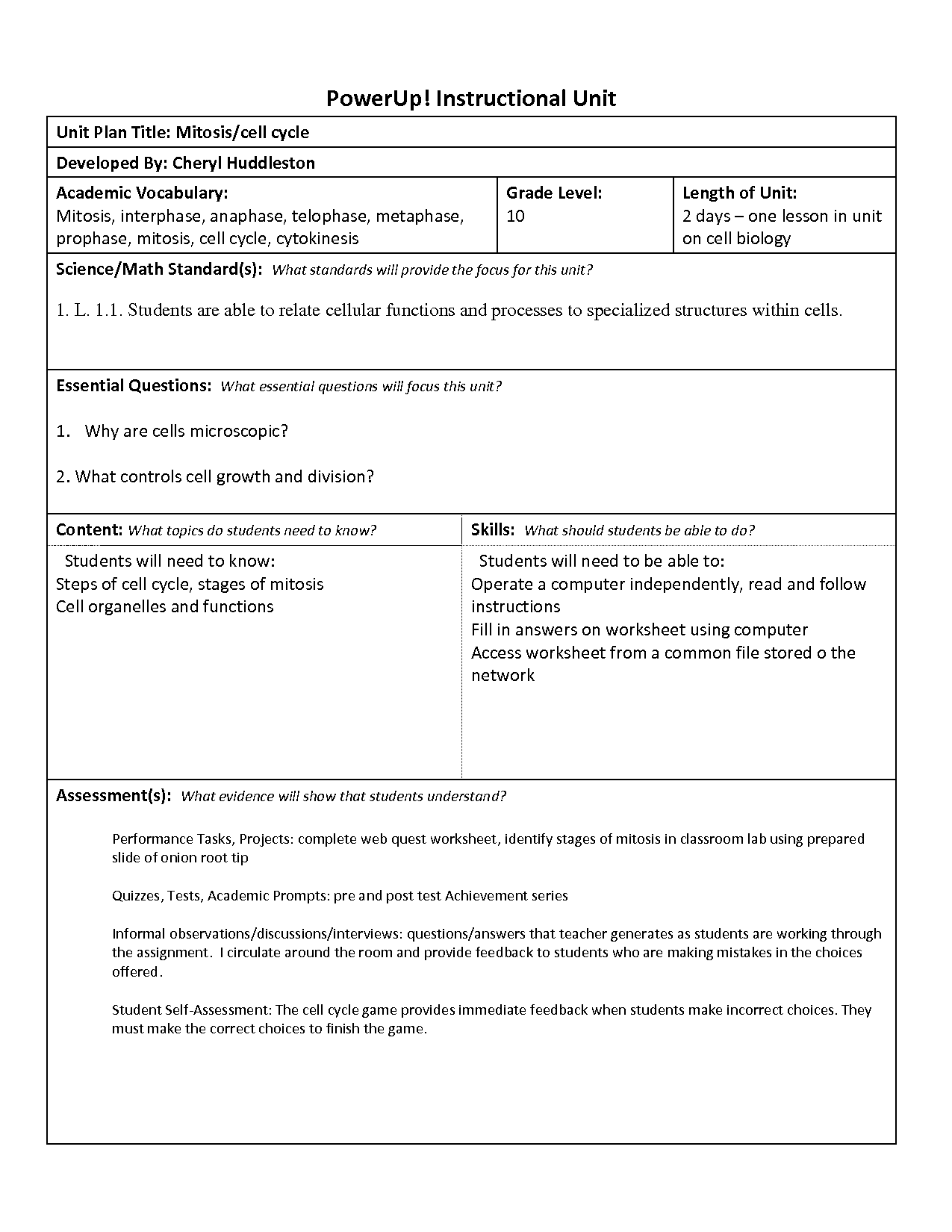
Cells proliferate through a process called cell division, where a cell replicates its DNA and divides into two daughter cells. This process typically involves several stages, including interphase (where the cell grows and duplicates its chromosomes), mitosis (where the duplicated chromosomes are segregated into the daughter cells), and cytokinesis (where the cytoplasm divides to create separate cells). Cell division allows for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in multicellular organisms.
How does cell growth differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Cell growth differs between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in several ways. Prokaryotic cells tend to grow and divide at a faster rate due to their simpler structure and lack of internal organelles. They typically have a shorter cell cycle and can replicate more quickly under favorable conditions. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a more complex structure with membrane-bound organelles and undergo a more regulated and controlled cell cycle. This results in a slower growth rate compared to prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells also have a longer interphase where cells grow and carry out their normal functions before progressing to mitosis, which is the phase of cell division.
What role does DNA replication play in cell growth?
DNA replication plays a crucial role in cell growth by ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of genetic instructions during cell division. As a cell grows and prepares for division, it must duplicate its entire genome through DNA replication to pass on the necessary genetic information to the new cells. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity of the genetic material and allowing for proper cell growth and division.
What is the cell cycle and how is it related to cell growth?
The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. It consists of four main phases: Gap 1 (G1), Synthesis (S), Gap 2 (G2), and Mitosis (M). Cell growth happens during the G1 phase of the cell cycle when the cell increases in size and synthesizes proteins and organelles in preparation for DNA replication during the S phase. The cell cycle is closely related to cell growth as it governs the orderly progression of events that lead to the growth and division of cells.
What are the main stages of the cell cycle?
The main stages of the cell cycle are interphase, which includes G1 phase (cell growth), S phase (DNA replication), and G2 phase (preparation for cell division), followed by mitosis (cell division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasm division), resulting in the formation of two daughter cells with identical genetic material.
How are cells regulated to ensure controlled growth?
Cells are regulated to ensure controlled growth through a combination of intrinsic mechanisms, such as the presence of checkpoint proteins that monitor cell cycle progression and initiate cell division or apoptosis based on DNA damage or other irregularities, as well as extrinsic signals from the cellular environment that influence cell growth. Key regulators like cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) play a central role in driving the cell cycle and ensuring that cells proceed through each phase in an orderly manner. Various signaling pathways, such as the PI3K-Akt pathway, also help to regulate cell growth by responding to growth factors and nutrient availability. Together, these mechanisms help cells maintain a balance between proliferation and inhibition, ensuring controlled growth and preventing uncontrolled cell division that could lead to diseases like cancer.
What is the significance of cell growth in development and tissue repair?
Cell growth plays a critical role in development and tissue repair as it is essential for the formation of new tissues and organs. During development, cell growth is necessary for the rapid increase in cell number, differentiation, and organization to form complex structures. In tissue repair, cell growth is crucial for replacing damaged or dead cells and restoring the normal function of the tissue. Proper regulation of cell growth ensures the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and functionality, highlighting its significance in both development and repair processes.
How can abnormal cell growth lead to diseases such as cancer?
Abnormal cell growth can lead to diseases such as cancer because when cells divide and grow uncontrollably, they can form a tumor. These tumors can invade nearby tissues and organs, disrupting their normal function. Additionally, abnormal cells can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, leading to the formation of secondary tumors in a process known as metastasis. This uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells can disrupt the body's normal physiological processes and lead to the development of cancer.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments