Cell Cycle Worksheet
Are you a biology student seeking a reliable and comprehensive resource to enhance your understanding of the cell cycle? Look no further! Our Cell Cycle Worksheet is specifically designed to provide you with a solid foundation of knowledge on this essential biological process. Whether you are studying for an exam or simply looking to reinforce your understanding, this worksheet is the perfect tool to guide you through the different phases of the cell cycle and help you grasp key concepts with ease.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- The Cell Cycle and Cancer Virtual Lab Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Worksheet
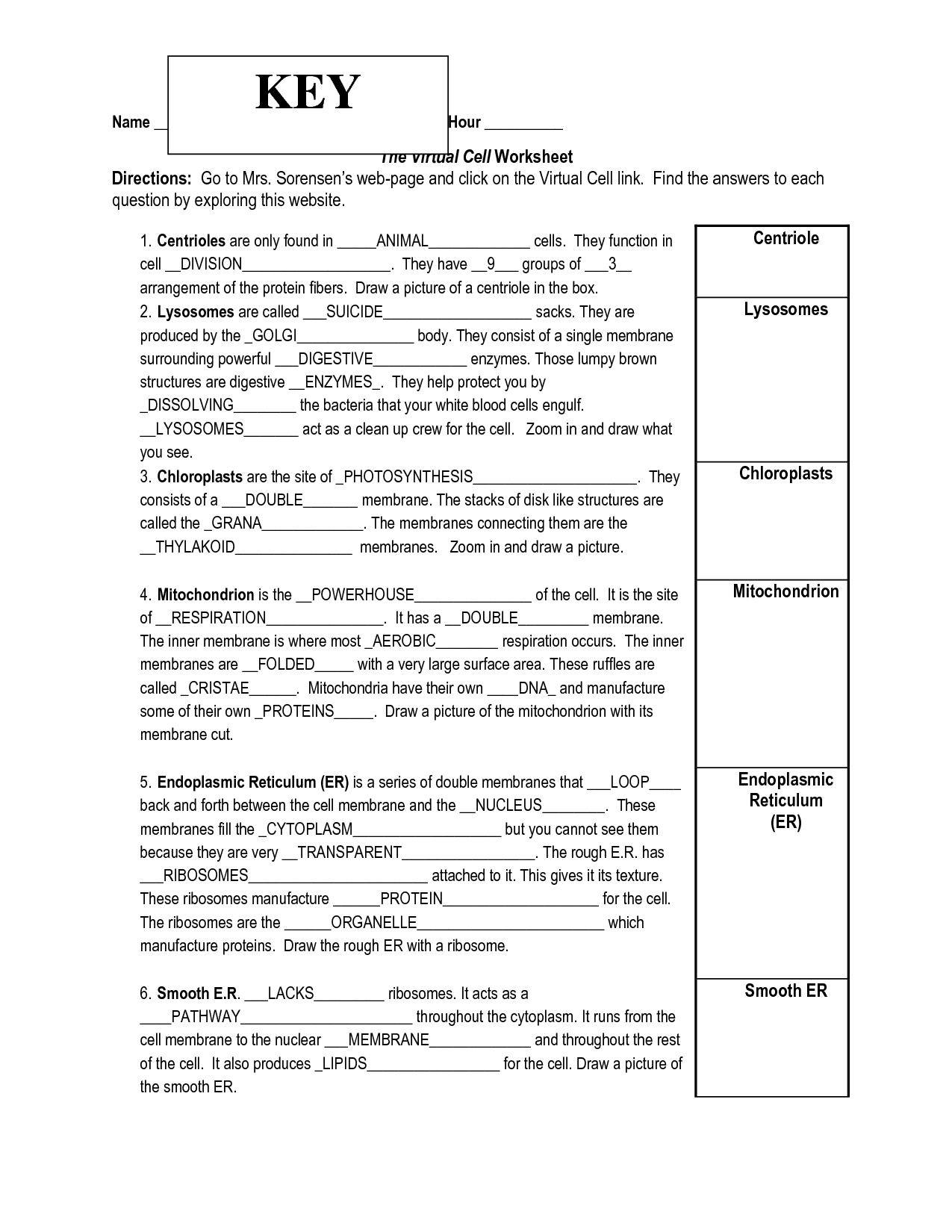
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure that cells can grow, replicate their DNA, and divide into two identical daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms, as well as for the reproduction of single-celled organisms. The cell cycle helps to maintain the integrity of genetic material and ensures that each cell receives the correct amount of DNA during division, allowing for the formation of new tissues and the replacement of old or damaged cells.
What are the two main phases of the cell cycle?
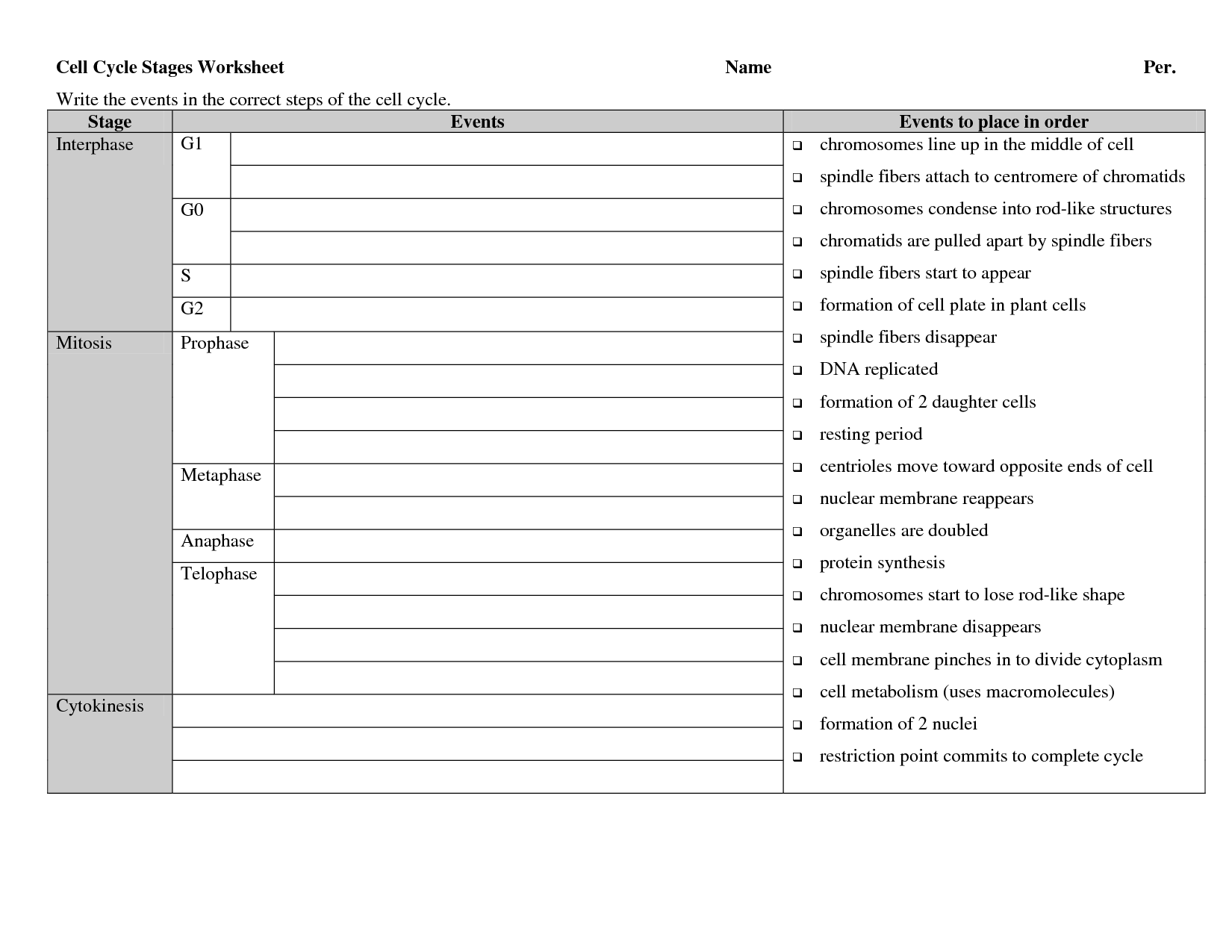
The two main phases of the cell cycle are interphase and mitotic phase. Interphase is the stage where the cell grows, carries out normal functions, and replicates its DNA. The mitotic phase includes mitosis, where the cell divides its nucleus, and cytokinesis, where the cell divides its cytoplasm, resulting in two daughter cells.
Describe the process of DNA replication during the cell cycle.
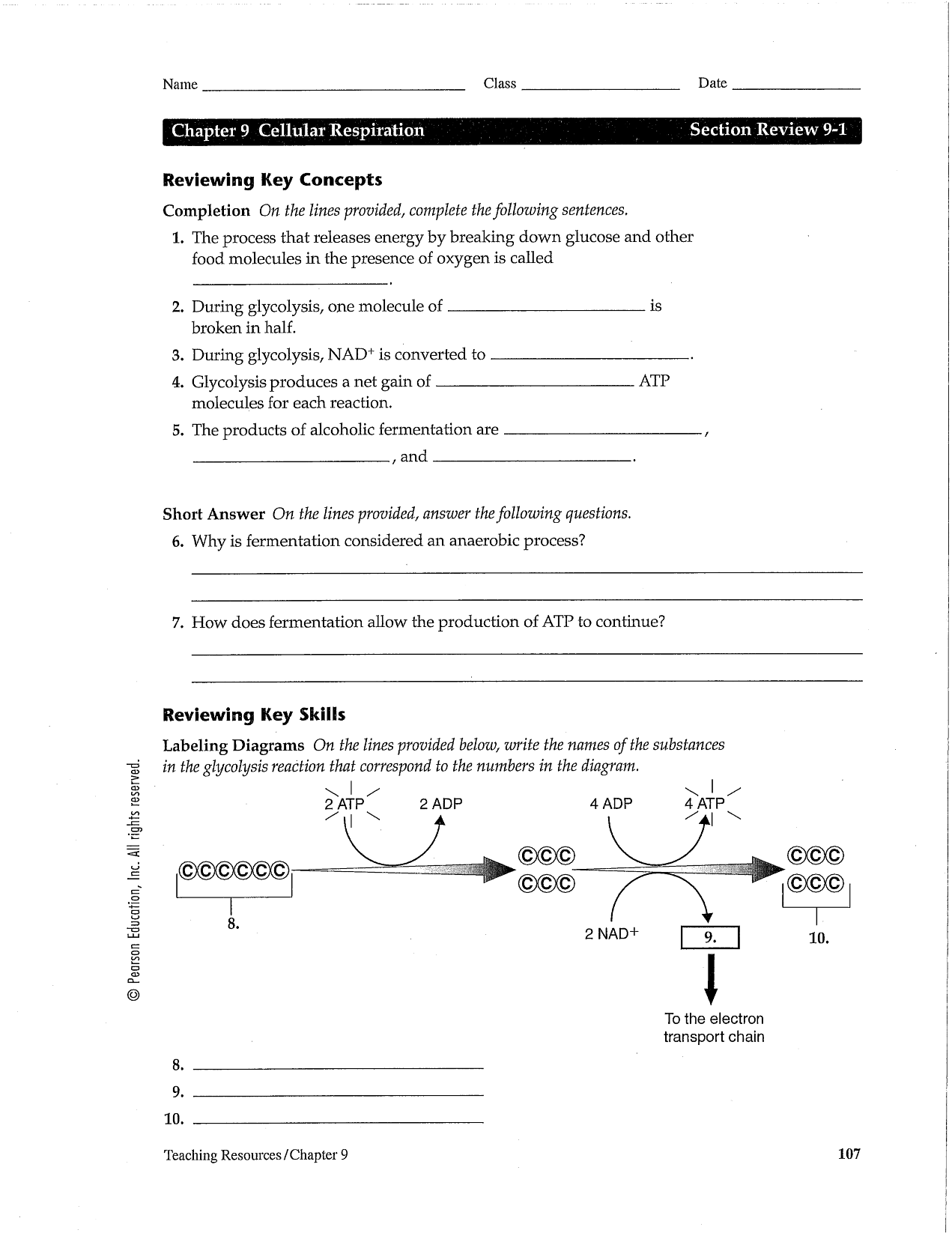
DNA replication occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle. The process begins with the unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicase enzymes, followed by the binding of primase to synthesise RNA primers. DNA polymerase then elongates the new strand by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand in a 5' to 3' direction. The leading strand is synthesised continuously while the lagging strand is synthesised in short Okazaki fragments, which are later joined by DNA ligase. Once the entire DNA molecule is replicated, the process concludes with the proofreading of newly synthesised strands for errors.
What is the significance of mitosis in the cell cycle?
Mitosis is a crucial phase in the cell cycle as it is responsible for the division of a cell's genetic material into two identical daughter cells. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes, essential for growth, development, and tissue repair in organisms. Additionally, mitosis plays a key role in maintaining the genetic stability and integrity of an organism by preventing errors in DNA replication and distribution.
Explain the role of checkpoints in regulating the cell cycle.
Checkpoints play a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle by monitoring the progress of key events and ensuring that each phase is completed accurately before the cell can proceed to the next phase. These checkpoints assess DNA integrity, ensure accurate DNA replication, and verify proper chromosome alignment before cell division. If any irregularities or errors are detected, checkpoints can halt the cell cycle to allow for repair mechanisms to be activated or, in severe cases, trigger programmed cell death to prevent the propagation of damaged cells. Overall, checkpoints serve as guardians of genome stability and contribute to the maintenance of normal cellular function and prevention of abnormal cell growth and cancer formation.
What is the difference between interphase and the mitotic phase?
Interphase is the phase in the cell cycle where the cell grows and carries out normal functions before entering cell division, while the mitotic phase is the phase in the cell cycle where the cell divides into two new daughter cells through the process of mitosis. In interphase, the DNA is replicated, and the cell prepares for cell division, while in the mitotic phase, the replicated DNA is segregated and the cell physically divides into two identical daughter cells.
Describe the events that occur during prophase.
During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form. The centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell and begin to extend microtubules that will form the spindle apparatus. The chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers at their centromeres and start to move towards the center of the cell. Overall, prophase marks the beginning of mitosis where the cell prepares for division by organizing its genetic material and structure for successful separation into two daughter cells.
What is cytokinesis and how does it differ in animal and plant cells?
Cytokinesis is the process by which a cell divides its cytoplasm, forming two separate daughter cells following nuclear division. In animal cells, cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell in two, while plant cells form a cell plate between the two daughter nuclei that eventually becomes a new cell wall. This difference is due to the presence of a rigid cell wall in plant cells that needs to be accounted for during cell division.
What happens during the G1 phase of interphase?
During the G1 phase of interphase, the cell grows in size, synthesizes proteins, and carries out its normal functions. It prepares for DNA replication in the S phase by ensuring that it has the necessary resources and energy to duplicate its DNA accurately. Additionally, the cell checks for any damage to its DNA and processes signals that determine whether it should continue to divide or enter a resting state.
What are the consequences of uncontrolled cell division in the cell cycle?
Uncontrolled cell division in the cell cycle can lead to the development of cancer. These cells divide rapidly and uncontrollably, forming tumors that can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body. This unchecked growth can disrupt normal tissue function and ultimately result in serious health complications or even death. Additionally, uncontrolled cell division can also cause genetic mutations and impair the body's ability to repair damaged DNA, further contributing to the progression of cancer.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments