Cell Cycle Labeling Worksheet Answers
Are you struggling with understanding the concept of the cell cycle? Look no further! We have created a cell cycle labeling worksheet with detailed and accurate answers to help you comprehend this complex biological process. This worksheet is perfect for high school students or anyone interested in learning about cell biology.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- The 12 Cell Review Worksheet Answers Biology
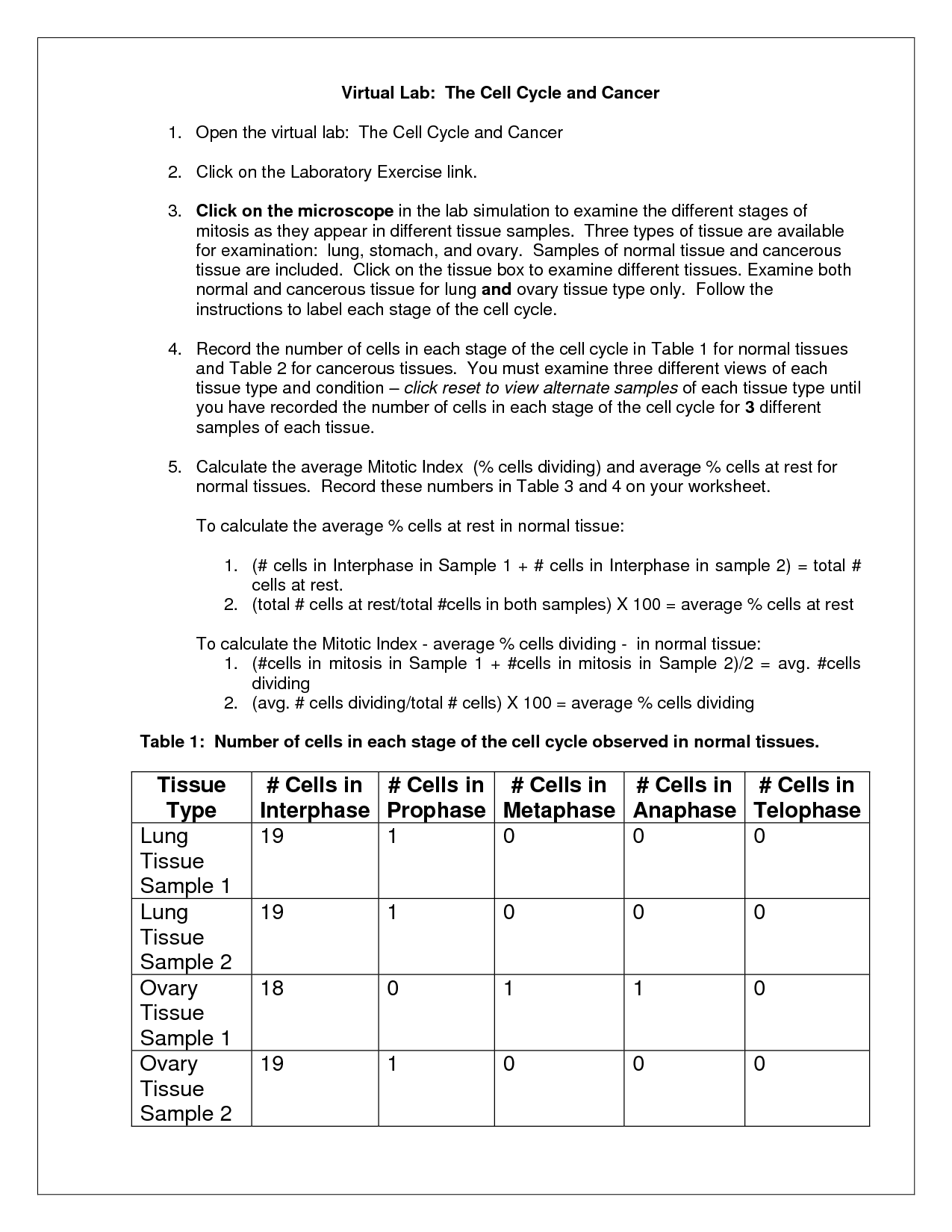
- Cell Cycle and Cancer Virtual Lab
- AP Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet
- Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell and Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
- Circulatory System Worksheet Answer Key
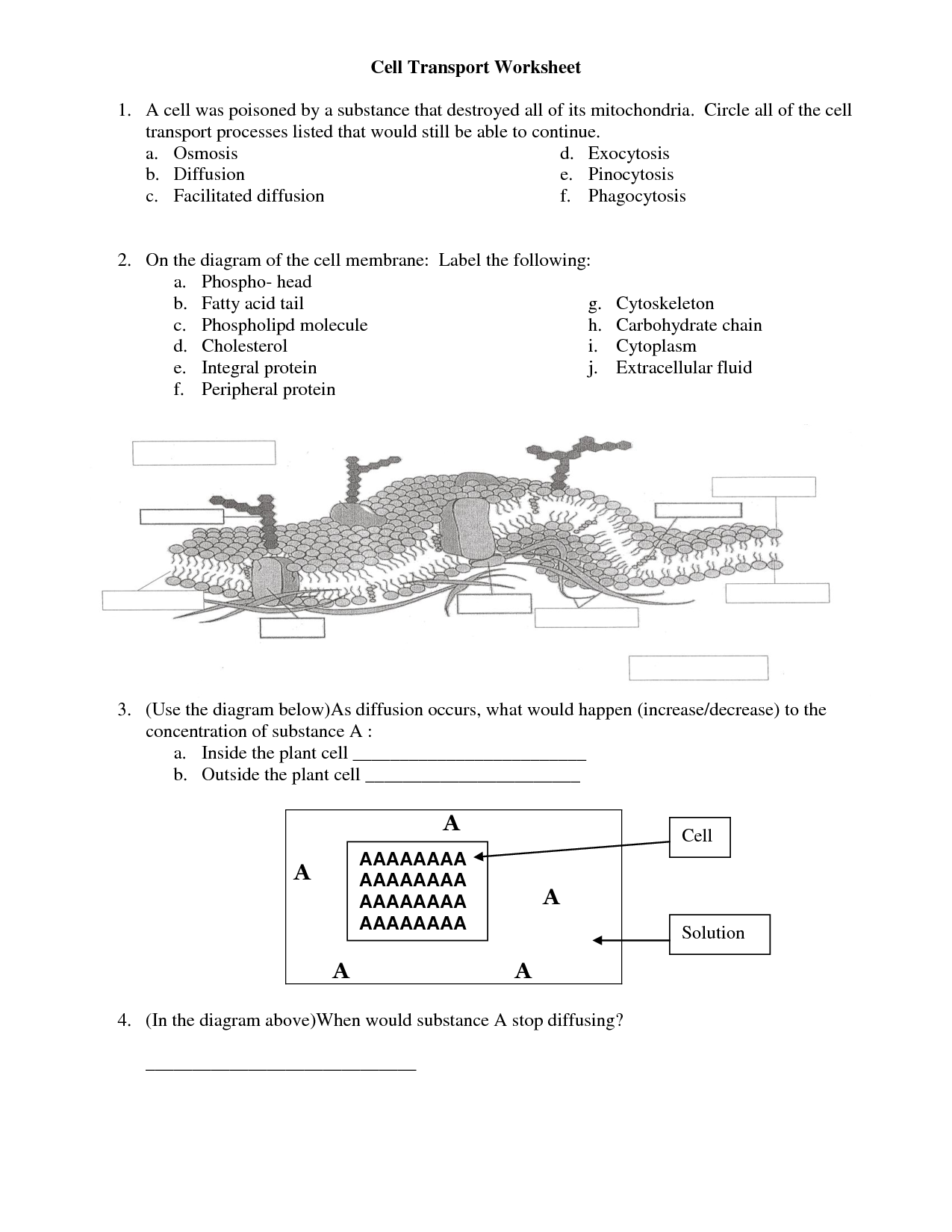
- Cell Transport Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
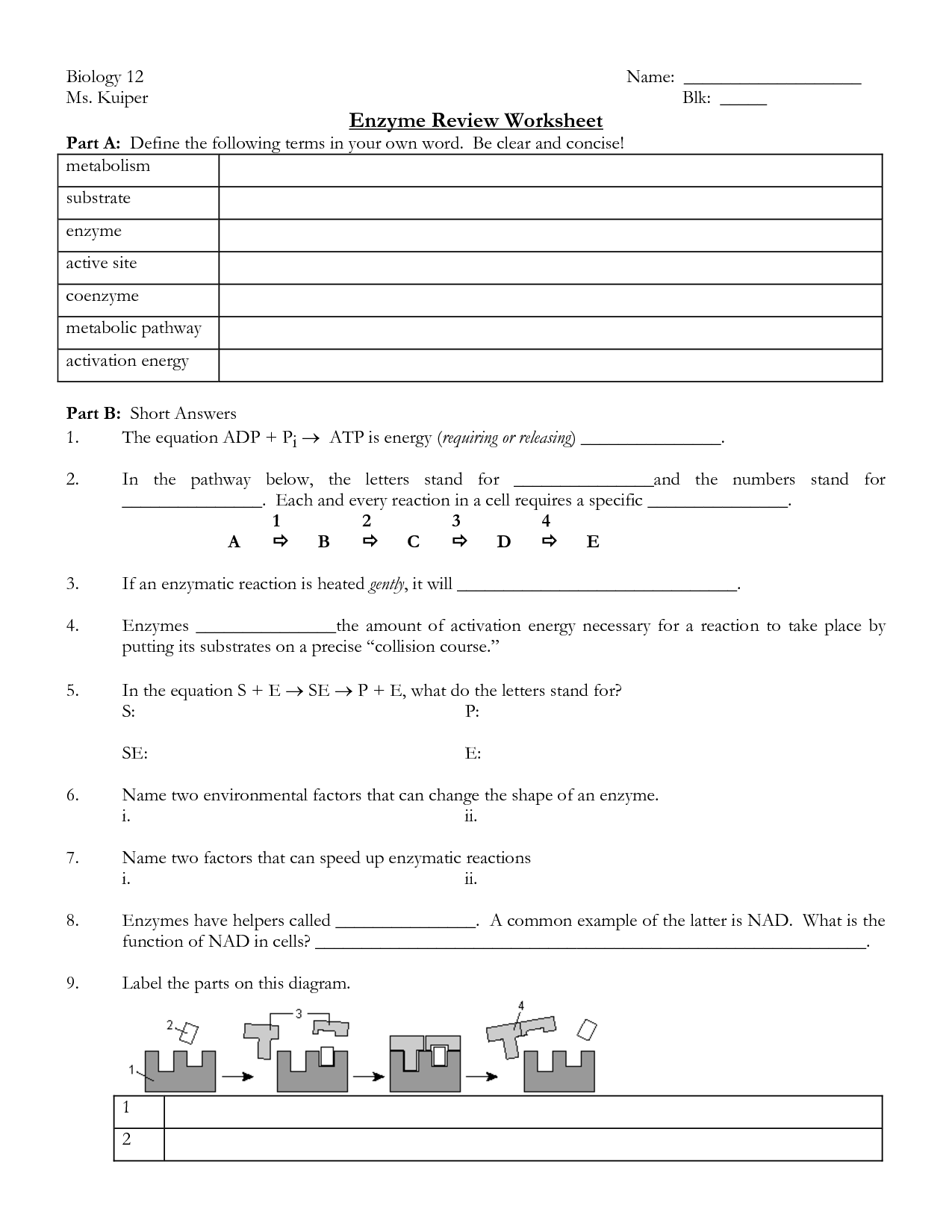
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure the accurate replication of cells by allowing them to grow and divide in a controlled manner. This process facilitates the growth, development, and maintenance of multicellular organisms, as well as enabling the repair and replacement of damaged or worn-out cells. The cell cycle consists of different phases, each with specific functions that help to regulate cell division and ensure genetic stability.
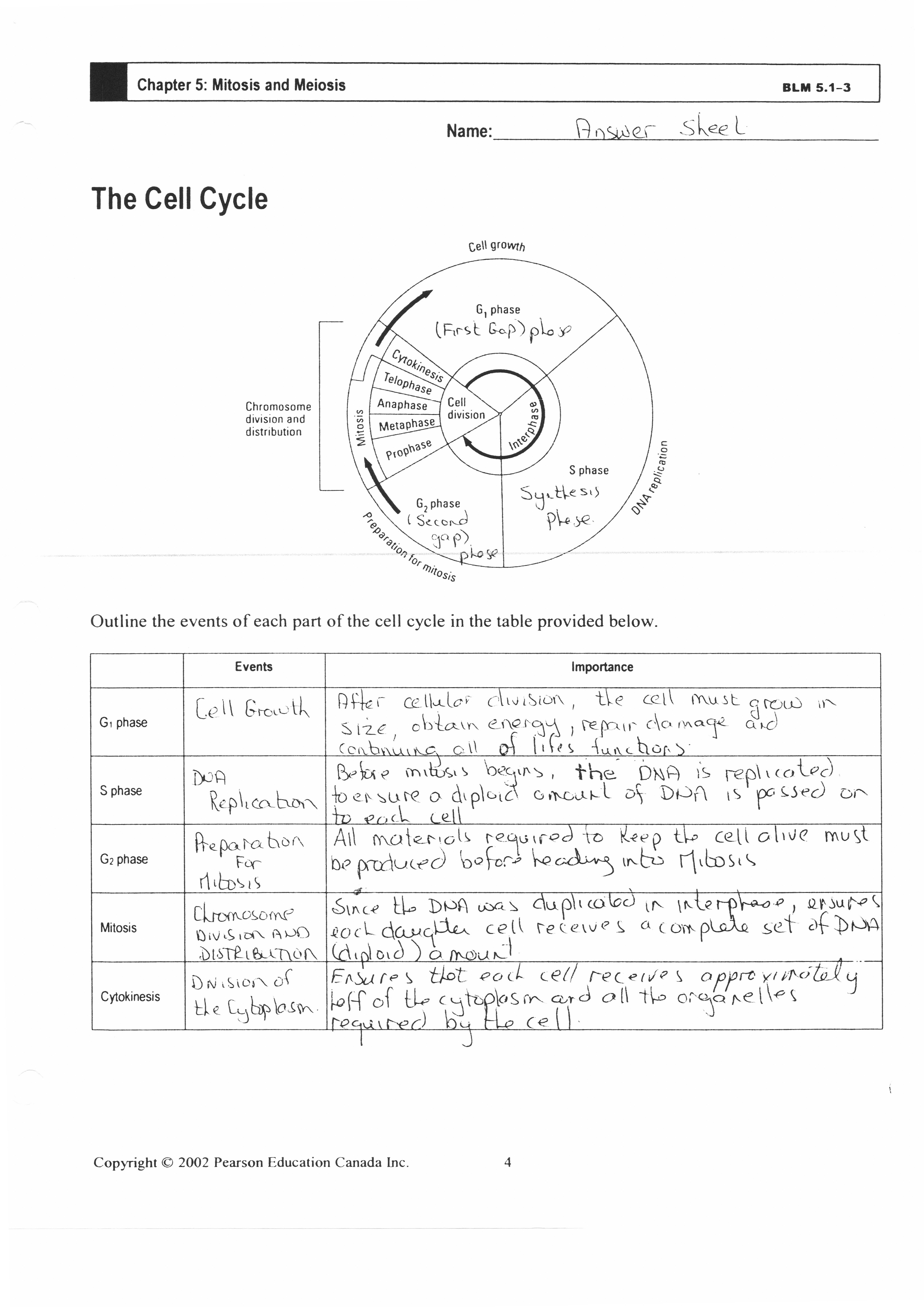
What are the four phases of the cell cycle?
The four phases of the cell cycle are G1 (Gap 1), S (Synthesis), G2 (Gap 2), and M (Mitosis). The G1 phase involves cell growth and preparation for DNA replication, while the S phase is when DNA synthesis occurs. In the G2 phase, the cell continues to grow and prepares for cell division. The M phase is where mitosis takes place, resulting in the division of the nucleus and the cell into two daughter cells.
Describe the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
The G1 phase, or Gap 1 phase, is the first phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows in size and carries out normal metabolic activities. During this phase, the cell also checks for any damage to its DNA and decides whether to proceed with the cell cycle. It is a critical phase where the cell assesses its environment and growth conditions to determine if it is favorable to continue on to the next phases of the cell cycle.
What happens during the S phase?
During the S phase of the cell cycle, DNA replication takes place. This means that the cell copies all of its genetic material so that each daughter cell formed during cell division will have an identical set of DNA. This is an essential process for the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next.
Explain the role of the G2 phase.
The G2 phase is the third phase of the cell cycle where the cell continues to grow and prepares for division. During this phase, the cell checks for any errors in the DNA replication that occurred during the S phase, so it can repair any damage before proceeding to mitosis. The G2 phase also ensures that the cell has enough energy and resources to successfully divide. Ultimately, the role of the G2 phase is to make sure the cell is ready for division and to prevent any potentially harmful mutations from being passed on to daughter cells.
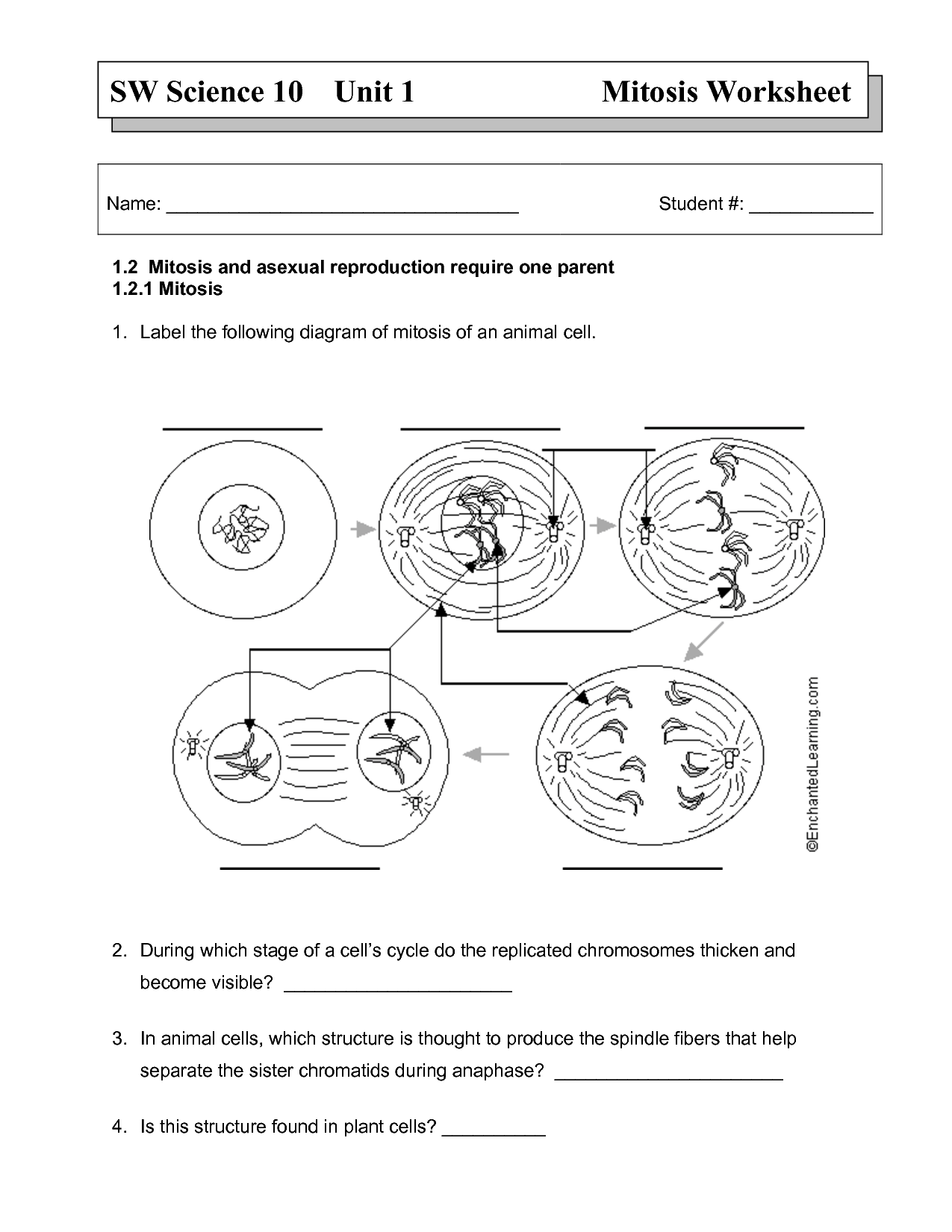
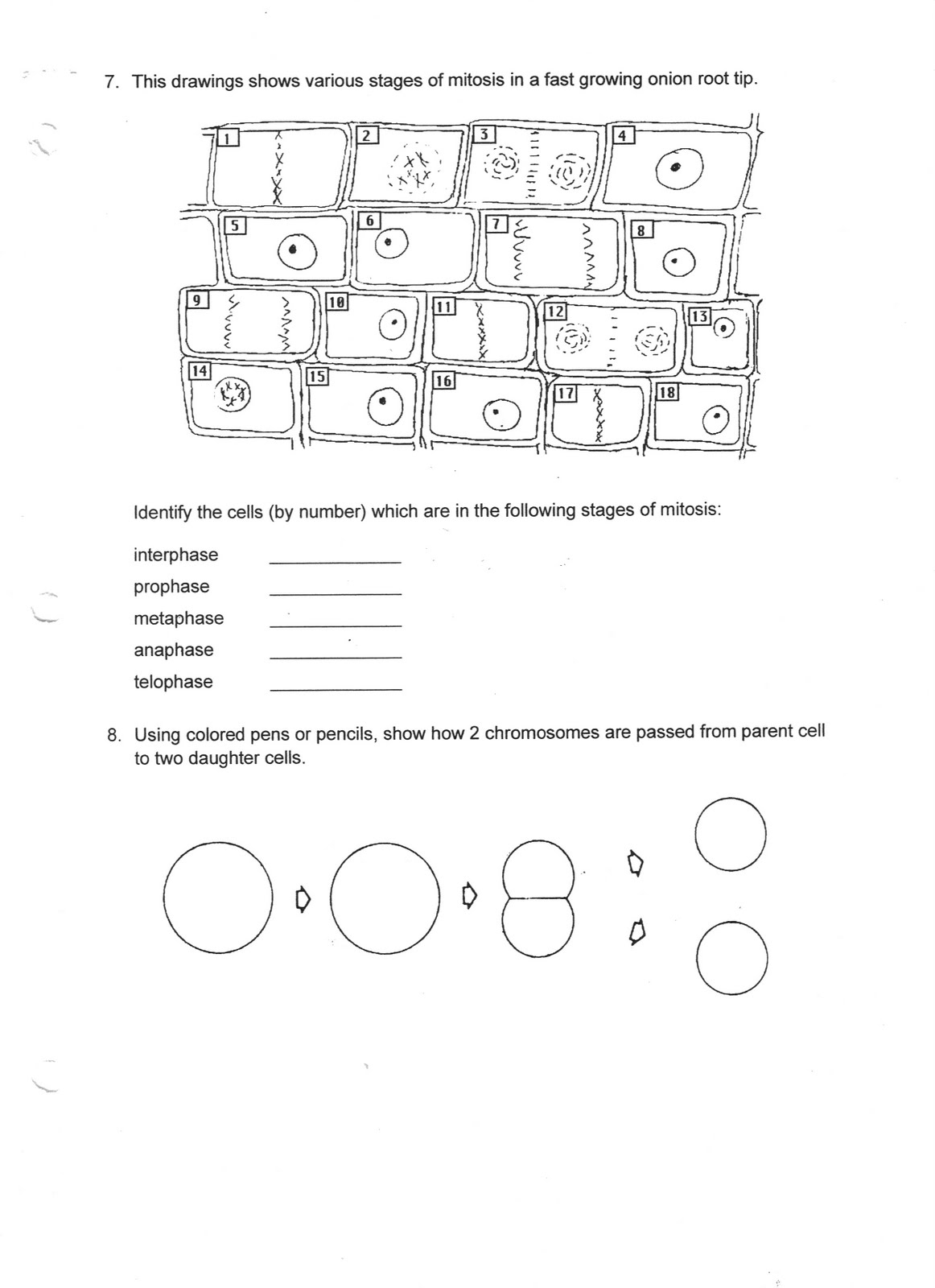
Describe the process of mitosis.
Mitosis is a type of cell division where a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. The process involves several key stages: prophase, during which chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down; metaphase, where chromosomes align at the cell's equator; anaphase, in which sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell; telophase, as two new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes; and finally cytokinesis, where the cell physically divides into two daughter cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes. Overall, mitosis plays a crucial role in growth, repair, and development in multicellular organisms.
What happens during cytokinesis?
During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of a cell divides into two daughter cells after the completion of nuclear division. This process involves the formation of a cleavage furrow in animal cells or a cell plate in plant cells, which physically separates the two daughter cells. Each daughter cell receives a copy of the genetic material and a portion of the organelles from the parent cell, allowing for the individualization and completion of the cell division process.
What is the purpose of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
The purpose of checkpoints in the cell cycle is to ensure that the cell has accurately completed crucial processes before progressing to the next stage. Checkpoints monitor the integrity of DNA, assess cell size, and check for any DNA damage or errors that could potentially lead to mutations. By halting the cell cycle progression if any abnormalities are detected, checkpoints help prevent the formation of genetically unstable or damaged cells, ultimately safeguarding against potential harm such as cancer development.
How do damaged or abnormal cells typically respond to checkpoints?
Damaged or abnormal cells typically respond to checkpoints by undergoing apoptosis, a programmed cell death process. Checkpoints are regulatory mechanisms within the cell cycle that monitor cell division and DNA integrity, ensuring that damaged or abnormal cells are either repaired or eliminated to prevent the proliferation of defective cells. When cells fail checkpoint controls, such as in the case of irreparable DNA damage or abnormal cell division, they activate signaling pathways that trigger apoptosis as a mechanism to remove and eliminate these potentially harmful cells from the body.
What are some factors that can influence the length of the cell cycle?
Several factors can influence the length of the cell cycle, including the type of cell (e.g., skin cells divide quickly, while liver cells divide slowly), external signals from the environment that can either promote or inhibit cell division, the availability of nutrients and growth factors that are needed for cellular processes, DNA damage checkpoints that can pause the cell cycle for repair, and the presence of specific proteins that regulate the timing of cell cycle phases. Additionally, age of the organism, hormonal signals, and genetic mutations can also impact the length of the cell cycle.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments